AI Text-to-Speech (TTS) technology represents one of the most remarkable achievements in human-computer interaction, transforming written words into natural-sounding speech that increasingly rivals human voice quality. From its humble beginnings with mechanical-sounding vocoder systems in the 1960s to today's sophisticated neural networks capable of emotional expression and multilingual fluency, TTS technology has revolutionized accessibility, content creation, and digital communication. Modern TTS systems now serve as the voice of virtual assistants, screen readers, audiobooks, and countless applications that bridge the gap between written and spoken communication, making digital content more accessible and engaging across global audiences.
How Did Text to Speech Begin? The Early Forms and Limitations
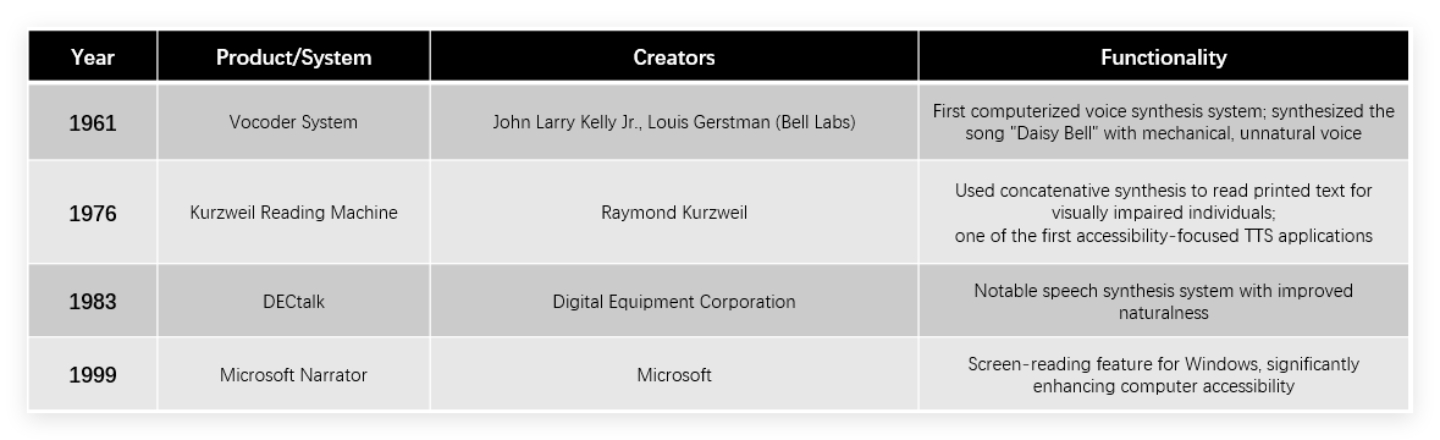
The journey of text to speech technology begins in the early 1960s, when researchers at Bell Labs created the first computerized voice synthesis system. In 1961, John Larry Kelly Jr. and Louis Gerstman developed the "vocoder" system that synthesized the song "Daisy Bell" - though the resulting voice was extremely mechanical and unnatural. This marked the first step in a technological evolution that would span decades.
The 1970s saw the first practical applications of text to speech technology with the introduction of the Kurzweil Reading Machine in 1976. Using concatenative synthesis techniques, this groundbreaking device was designed to read printed text for visually impaired individuals, representing one of the first real-world applications of text to speech technology focused on accessibility.
By the 1980s, multilingual text to speech systems emerged from Bell Labs, with engineers like Ann Syrdal at AT&T Bell Laboratories pushing speech synthesis toward greater naturalness. The DECtalk system (1983) became particularly notable during this period. Later, in 1999, Microsoft introduced the Narrator feature for Windows, significantly enhancing computer accessibility by providing screen-reading capabilities.
Key Characteristics of Early Text to Speech Systems:
- Relied on Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) as seen in products like IBM's ViaVoice
- Required large amounts of annotated data
- Generated mechanical, monotonous speech lacking emotional variation
- Handled only limited vocabulary and contextual understanding
- Primarily served accessibility needs and basic command recognition
Despite these limitations, these early text to speech systems laid the foundation for the sophisticated voice synthesis technologies we enjoy today. The technical constraints of the era meant that applications remained largely confined to specialized use cases where functionality mattered more than naturalness or expressiveness.
What Were the Turning Points in AI Text to Speech Development?
The evolution of text to speech technology experienced several crucial turning points that addressed the limitations of earlier systems and established the groundwork for today's advanced capabilities.
A significant milestone came in 2011 when Google released its Text-to-Speech API, which fostered a developer ecosystem and brought text to speech technology into cloud services and mobile platforms. This democratization of access marked an important shift in how the technology could be implemented and utilized across different applications.
Perhaps the most revolutionary advancement occurred in the 2010s with the introduction of deep learning and neural networks. Technologies like Tacotron and WaveNet dramatically improved the naturalness of synthesized speech, enabling the simulation of human emotions and intonations that had been sorely lacking in previous generations of text to speech systems.
Revolutionary Developments That Transformed Text to Speech:
- Google's 2011 Text-to-Speech API that expanded developer access
- Neural network architectures like Tacotron and WaveNet in the 2010s
- Platforms like Narration Box supporting 140+ languages and 700+ AI voices
- ElevenLabs' 2022 self-supervised learning approach enabling voice cloning with minimal samples
These turning points collectively transformed text to speech from a rigid, mechanical technology with limited applications into a versatile tool capable of producing natural-sounding, emotionally expressive speech across multiple languages and contexts. The progression from concatenative synthesis to neural models represents not just technical improvement but a fundamental shift in how machines generate human-like speech patterns.
What is the Current State of AI Text to Speech Technology?
Today's text to speech landscape is dominated by sophisticated neural models that have revolutionized how machines convert written text into spoken language. The current generation of text to speech systems leverages powerful AI architectures to produce increasingly natural-sounding voices that can express emotion, adjust pacing, and even mimic human speech patterns.
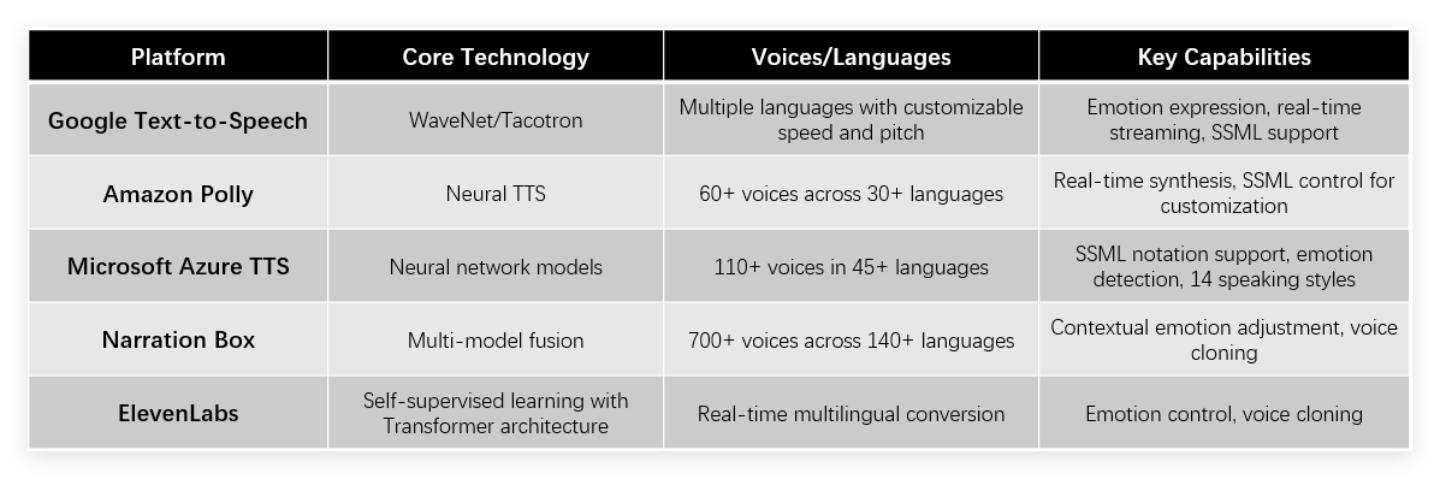
Several major platforms currently lead the text to speech market, each with unique capabilities. Google Text-to-Speech employs WaveNet/Tacotron technologies to support multiple languages and emotions with customizable speed and pitch. Amazon Polly offers neural TTS with over 60 voices across 30+ languages and real-time synthesis capabilities. Microsoft Azure TTS provides more than 110 voices in 45+ languages with SSML notation support. Platforms like Narration Box use multi-model fusion to deliver 700+ voices across 140+ languages with contextual emotion adjustment, while ElevenLabs combines self-supervised learning with Transformer architectures for real-time multilingual conversion with emotion control.
The technical capabilities of modern text to speech systems have expanded dramatically, allowing them to handle complex challenges that were once impossible. These systems can automatically switch between multiple languages and dialects, control emotional expression parameters, clone and personalize voices, and apply context-aware intonation and emphasis.
Key Applications Driving Text to Speech Adoption:
- Accessibility assistance for visually impaired users
- Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant
- Content creation for audiobooks, podcasts, and news broadcasting
- Educational tools and language learning platforms
- E-commerce product description narration
The technology has evolved from handling basic word-to-sound conversion to understanding semantic context, emotional nuance, and linguistic complexity. This progression represents a fundamental shift from viewing text to speech as merely a utilitarian accessibility tool to recognizing it as a sophisticated communication technology with applications across numerous industries and use cases.
How Does AI Text to Speech Surpass Human Capabilities?
Text to speech technology offers distinct advantages over human speech production, particularly in scenarios requiring consistency, scale, and customization. While human voice actors bring unmatched nuance to individual performances, AI-powered systems excel in different but equally valuable ways.
Modern text to speech systems demonstrate remarkable efficiency, generating vast amounts of speech content rapidly without fatigue or quality degradation. This allows for 24/7 operation and the ability to process large volumes of text that would be impractical for human voice actors. A complete audiobook that might take weeks for a human narrator can be produced in hours or even minutes with high-quality text to speech systems.
The linguistic versatility of today's platforms is equally impressive. Systems like Meta VoiceBox support over 100 languages, including many minority languages with small speaker populations. This level of coverage would require an impractical number of human voice actors, making text to speech the only viable option for truly global voice content delivery across linguistic boundaries.
Unlike human speakers whose performances may vary based on health, emotions, or fatigue, text to speech systems deliver consistent output regardless of when or how frequently they're used. This reliability ensures uniformity in voice applications, making them ideal for maintaining brand consistency in commercial contexts.
The customization flexibility of text to speech technology allows for unprecedented control over speech parameters. Users can adjust rate, emotional tone, pause length, and other characteristics on demand to suit specific needs or preferences. This adaptability makes text to speech particularly valuable for personalized voice experiences like accessibility tools that must adapt to individual user requirements.
Optimal Application Scenarios:
- Automated content production at scale
- Multilingual customer service applications
- Real-time accessibility services
- Applications requiring absolute consistency
Industry experts recommend leveraging these strengths while recognizing that human voice talent still excels in highly emotional contexts. For applications requiring heightened emotional expression or brand personality, a hybrid approach combining AI generation with human post-production refinement often yields optimal results while maintaining the efficiency advantages of text to speech technology.

What Are the Limitations of AI Text to Speech Technology?
Despite remarkable advances, text to speech technology still faces significant limitations that require human intervention in certain contexts. Understanding these constraints helps set appropriate expectations and identify areas for future improvement.
Current text to speech systems continue to struggle with prosody management—achieving natural rhythm, stress patterns, and intonation, particularly for longer passages or emotionally complex content. Handling rare terms and specialized vocabulary often results in incorrect pronunciations without manual intervention. Homograph disambiguation (words spelled identically but pronounced differently based on context) frequently confuses these systems. Additionally, high-quality models require substantial computing resources, limiting deployment in mobile or low-latency environments.
Several use cases still demand human oversight or complete human performance. Content requiring nuanced emotional delivery, such as poetry or dramatic readings, benefits significantly from human touch. Complex contextual nuances like sarcasm, irony, and wordplay often get lost in synthetic speech. Technical terminology and rare proper nouns typically require human verification for accuracy. High-stakes content like legal terms and medical diagnoses warrant human review to ensure precision, while film dubbing and character voice acting still require human performers' emotional range.
These limitations stem from several underlying factors. AI models typically rely on averaged data, making them less adaptable to the complex contextual demands of natural speech rhythm and emotion. Current systems struggle to generalize effectively to rare words, code-switching, and contextual ambiguities not well-represented in training data. Resource constraints limit widespread adoption in computationally restricted environments, while some models may suffer from biases in their training datasets.
Promising Research Directions:
- Enhanced contextual understanding for dynamic intonation adjustment
- Model optimization for improved mobile and edge device compatibility
- Expanded multilingual and cross-cultural capabilities
- Memory networks for handling long-text dependencies
- Privacy-preserving personalization for specialized domains
- Multimodal integration combining visual and audio information
While text to speech technology continues advancing rapidly, these limitations highlight the complementary relationship between artificial and human voice production. The future likely involves strategic combinations that leverage the unique strengths of each approach rather than complete replacement of human voice talent.

What Are the FAQs About Text to Speech?
Q: What is AI text to speech technology?
A: Text to speech technology converts written text into natural-sounding spoken language using deep learning models like WaveNet and Tacotron. Modern systems can simulate intonation, emotion, and speech rate variations, creating increasingly natural vocal output that approximates human speech patterns. The technology has evolved dramatically from early mechanical-sounding systems to today's sophisticated neural models capable of nuanced expression.
Q: What are the main applications of text to speech technology?
A: Text to speech technology serves diverse purposes across multiple domains. It powers accessibility tools providing voice feedback for visually impaired users or those with reading difficulties. In education, it supports language learning, e-book narration, and online courses to enhance learning experiences. Customer service applications use text to speech for automated voice response systems to improve efficiency. Content creators leverage the technology for generating narration for podcasts, video explanations, and audiobooks to reduce production costs and time investments.
Q: How can the naturalness of text to speech output be improved?
A: Enhancing text to speech naturalness involves implementing advanced neural network architectures like Tacotron 2 or FastSpeech that generate more natural-sounding speech. Incorporating emotional analysis models helps infuse speech with appropriate emotional coloring based on content. Training on diverse voice data enhances variety and naturalness in speech output. Additionally, fine-tuning prosody parameters and leveraging contextual information significantly improves the perceived naturalness of synthesized speech.
Q: What are the leading text to speech services available today?
A: The market features several prominent text to speech services with distinctive capabilities. Google Cloud Text-to-Speech offers multiple language and voice options with SSML support for precise voice control. Amazon Polly provides numerous languages and voices with neural network speech synthesis optimized for enterprise applications. Microsoft Azure Speech delivers high-quality synthesis with support for custom voice models. IBM Watson Text to Speech features multiple voice and language options suitable for business integration.
Q: What privacy and ethical considerations surround text to speech technology?
A: Text to speech technology raises important privacy and ethical concerns that require careful consideration. Data privacy protocols must ensure proper protection of user voice data in compliance with relevant regulations. Voice cloning applications should obtain explicit user consent before creating voice replicas to avoid privacy violations. Implementation of safeguards against using text to speech technology for creating false information or fraudulent activities is increasingly essential as voice synthesis quality improves.
What Does the Future Hold for Text to Speech Technology?
The evolution of text to speech technology represents a remarkable journey from the mechanical utterances of early systems to today's increasingly natural and versatile voice synthesis. This progression highlights both the tremendous advances made and the challenges that remain in bridging the gap between synthetic and human voice production.
As we look toward the future, several critical developments seem likely to shape the continued evolution of text to speech technology. Improvements in contextual understanding will likely enhance prosody and emotional expression, making synthetic speech even more indistinguishable from human speech. Computational optimizations will bring high-quality voice synthesis to more devices and environments, including mobile platforms and edge computing scenarios. Meanwhile, cross-cultural and multilingual capabilities will continue expanding, making text to speech technology more accessible and useful across global contexts.
However, alongside these technical advances, important questions about the ethical implications of increasingly perfect voice synthesis demand attention. The potential for voice cloning to be misused for deception raises concerns about authentication and trust in audio content. Privacy considerations surrounding the collection and use of voice data for training models require thoughtful regulatory frameworks and industry practices. Additionally, as text to speech systems continue improving, we must consider the impact on human voice professionals whose skills may be partially automated.
Key Considerations for the Future:
- Balancing technological advancement with ethical safeguards
- Developing complementary human-AI approaches leveraging unique strengths of both
- Creating regulatory frameworks that promote innovation while preventing misuse
- Focusing on accessibility and inclusion across languages and cultures
The ideal future for text to speech technology likely lies in complementary human-AI approaches that leverage the unique strengths of both. While text to speech excels at efficiency, consistency, and scalability, human voices bring unmatched emotional nuance and artistic interpretation to specialized contexts. By recognizing these complementary strengths, we can develop text to speech applications that enhance human capabilities rather than merely replacing them.
Ultimately, text to speech technology represents a fascinating intersection of linguistics, computer science, and cognitive modeling that continues to transform how we interact with machines and access information. As this technology matures, maintaining a critical perspective on both its capabilities and limitations will be essential for harnessing its benefits while mitigating potential risks. The goal should be developing text to speech systems that serve genuine human needs while respecting ethical boundaries and enhancing human connection and expression.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!







No comments yet. Be the first to comment!