The emergence of AI email assistant technology represents one of the most significant productivity innovations of recent years. These intelligent tools have transformed from simple spell-checkers to sophisticated systems capable of drafting complete emails, prioritizing messages, and automating routine tasks. Finding the best AI email assistant for your specific needs can dramatically improve workplace efficiency and communication quality. Let's explore the development trajectory of AI email assistants, their current capabilities, advantages, limitations, and future prospects.
How Did AI Email Assistant Technology Begin?
The earliest incarnation of the AI email assistant can be traced back to basic spelling and grammar checkers. These rudimentary tools primarily focused on correcting surface-level errors in email composition. Many users initially experienced email AI assistant technology through these basic functions before more advanced capabilities emerged. As the technology progressed, second-generation tools began identifying sentence structure issues, while third-generation solutions introduced style suggestions to enhance clarity and tone in communications.
Notable early AI email assistant applications included:
- Grammarly: Initially focused on grammar and spelling checking before gradually incorporating style and tone recommendations
- Boomerang: Offered scheduled sending, automatic reminders, and basic reply suggestions
- Sanebox: Utilized simple rules and machine learning to categorize emails and establish priority rankings
These pioneering tools addressed fundamental challenges in email communication such as basic errors, time management, and email classification. However, they suffered from significant limitations:
- Limited comprehension: They could only identify surface errors without understanding context or user intent
- Low automation: Most functions required manual activation, lacking intelligent automation
- Restricted application scenarios: Only suitable for highly structured emails like meeting invitations or confirmation messages
- Insufficient personalization: Unable to provide customized suggestions based on user habits and historical data

What Were the Key Turning Points in AI Email Assistant Development?
The evolution of AI email assistants has been marked by several technological breakthroughs that dramatically expanded their capabilities:
Technological Advancements
The integration of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and deep learning represented a pivotal development, enabling AI to understand context, recognize tone and intent, and facilitate more natural human-machine interaction. Another major milestone was the application of generative AI technologies like GPT-3/4, which made it possible to automatically generate complete emails, context-relevant replies, and personalized recommendations based on minimal prompts.
Additionally, the emergence of integrated automation and multi-platform collaboration tools supported advanced functionalities like cross-platform data retrieval, calendar integration, and automated follow-ups. The AI email assistant Outlook represented a significant advancement in this area, bringing sophisticated AI capabilities to one of the world's most widely used email platforms.
Landmark Products
Key products that signified turning points in this technological evolution include:
- Microsoft Copilot (2021): Integrated with Outlook, leveraging GPT-3 to generate email drafts and automatically summarize lengthy emails while combining enterprise data with users' historical emails to enhance personalization. The AI email assistant Outlook functionality within Copilot has become a benchmark for enterprise-level email management.
- Google Smart Compose (2018): Employed Transformer models to predict email content in real-time, reducing input time
These advancements addressed previous limitations by significantly enhancing the naturalness and personalization of email generation, enabling complex tasks like automated replies, email summarization, and priority ranking, and supporting integration with calendars, CRM systems, and other productivity tools.
These limitations made early email assistants inadequate for the complex and dynamic communication needs of modern users. With technological advancements, particularly breakthrough developments in artificial intelligence, email assistants underwent a significant evolution, transforming from simple spell-checking tools into intelligent systems capable of understanding context, generating content, and providing personalized recommendations. This transformation not only changed how users interact with email but also opened new possibilities for improving productivity and communication quality. The following section will explore key turning points in AI email assistant development, focusing on technological advances and landmark products.
AI Email Assistants Current State
Today's AI email assistants represent sophisticated ecosystems of tools powered by advanced technologies. They can handle increasingly complex tasks that were once exclusively in the domain of human capabilities.
Leading Contemporary Tools
Several prominent tools define the current AI email assistant landscape:
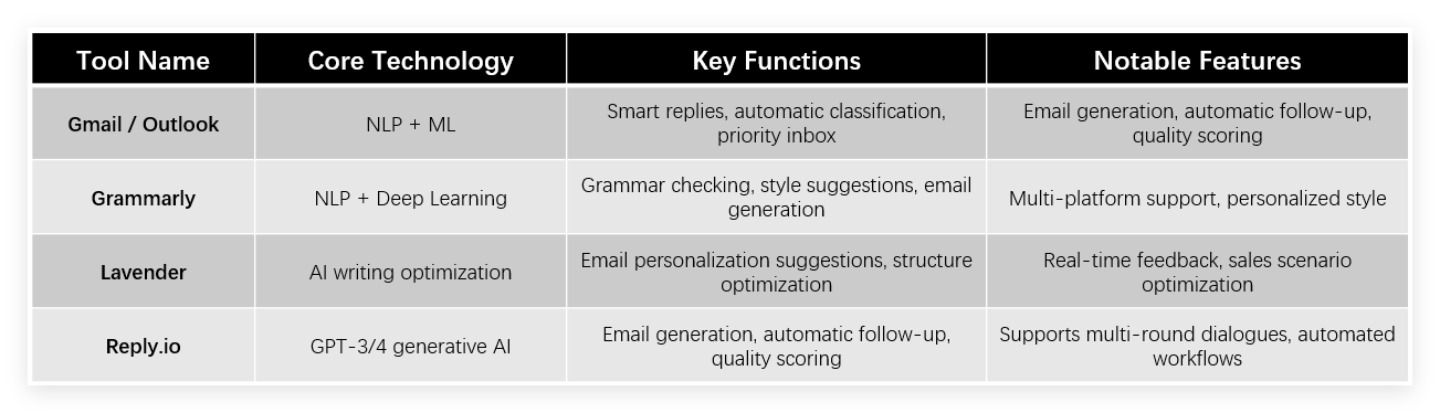
Complex Capabilities
Modern AI email assistants have evolved to handle a sophisticated range of tasks that significantly reduce manual workload. These systems now seamlessly generate personalized emails tailored to specific recipients while crafting contextually appropriate replies based on previous conversations. Their analytical capabilities extend to summarizing lengthy email threads, distilling key information that might otherwise require careful reading of dozens of messages.
Furthermore, they intelligently categorize incoming communications and assign appropriate priority levels, even routing messages to relevant departments without human intervention. The technology proactively monitors communication patterns, automatically following up on unanswered emails to ensure important conversations don't fall through the cracks. Their integration capabilities with calendars, customer relationship management platforms, and other productivity tools create unified workflows that eliminate repetitive task-switching.
The email AI assistant market has expanded significantly, with organizations increasingly adopting these tools to streamline communication workflows and improve productivity. For users seeking the best AI email assistant, evaluating specific features against their unique requirements is essential for optimal results.
Practical Applications
For everyday users, AI email assistants offer numerous practical benefits:
- Quickly drafting and polishing business emails without repeated revisions
- Automatically filtering spam and low-priority messages to improve productivity
- Generating meeting minutes or email summaries for efficient information archiving
- Providing batch personalized responses to customer inquiries in sales and customer service scenarios
- Optimizing email tone to avoid inadvertently offensive language
- Generating customer follow-up emails to enhance sales efficiency
While these AI email assistants offer impressive capabilities and practical applications, they represent a significant technological breakthrough in how we manage communication. These systems have successfully democratized advanced productivity tools, making sophisticated email management accessible to average users rather than just corporate executives with administrative support. The integration with existing workflow systems has created seamless experiences that reduce context-switching and cognitive load.
Despite these remarkable advances, the challenge of achieving truly context-aware, culturally sensitive email assistance across diverse global communication needs remains an ongoing area for development. The increasing reliance on AI for communication raises questions about the preservation of authentic human voice and relationship-building through correspondence. Privacy concerns also persist as these systems process sensitive communications. Additionally, there remains a notable gap between advertised capabilities and actual performance in complex linguistic and cultural contexts, particularly with non-English languages and nuanced communications. Organizations must carefully evaluate the trade-offs between efficiency gains and potential dependencies on proprietary systems that may create vendor lock-in.

Why Are AI Email Assistants Superior to Manual ones?
AI email assistants offer several distinctive advantages over manual email handling in specific contexts. Understanding these advantages can help users maximize the benefits of these technologies.
Key Advantages Over Manual Processing
AI email assistants offer significant operational benefits. They generate high-quality emails in seconds, processing information up to 10 times faster than humans, while requiring no rest and enabling 24/7 monitoring of communications. These tools automatically adhere to corporate style guidelines, reducing inconsistencies while maintaining personalization even in large-scale email campaigns.
From a practical perspective, AI assistants automatically identify important messages using historical data and context, preventing omissions. Tools like DeepL Mail provide multilingual support for cross-border communications, while assistants like Yesware track unanswered emails and prompt follow-ups. This technology reduces time spent on word choices and sentence structures, allowing greater focus on communication objectives.
Most Effective Implementation Scenarios
These advantages become particularly valuable in specific contexts. Sales and customer service departments benefit from batch personalized responses and automated follow-ups, while positions handling large email volumes (executives, support teams) see significant efficiency gains. AI excels in sentiment analysis by identifying potential complaints in customer emails, automating repetitive tasks like weekly reports, and managing cross-time zone communications through automatic conversion and scheduling.
Professional Recommendations
Industry experts recommend leveraging AI's automation while maintaining human review for critical emails, continuously training AI for specific business scenarios, and prioritizing data privacy with robust security measures. Regular proofreading prevents culturally sensitive errors, while clear instruction labeling (e.g., "#urgent") improves overall processing efficiency.
What Limitations Do AI Email Assistants Face?
Despite their impressive capabilities, AI email assistants still encounter significant limitations that necessitate human intervention in certain contexts.
Scenarios Requiring Human Oversight
Human involvement remains essential in several circumstances:
- Communications involving complex judgments, sensitive topics, or requiring high empathy (such as crisis public relations or important negotiations)
- Handling unstructured, highly personalized communication needs (like executive-level strategic communications or creative collaborations)
- Scenarios requiring deep understanding of external environments and context (such as legal or compliance-related emails)
- Highly sensitive decisions, such as layoff notifications or legal dispute communications
These scenarios highlight the irreplaceable nature of human discernment in high-stakes communications, where emotional intelligence and ethical considerations often transcend what can be encoded into algorithmic decision-making systems.
Root Causes of Current Limitations
These limitations stem from several fundamental challenges:
- Lack of Human Judgment and Empathy: AI struggles to understand complex emotions and implied intentions
- Limited Contextual Understanding: There remains room for improvement in comprehending lengthy email chains and integrating cross-platform information
- Data Privacy and Security Risks: Automated processing requires stringent user data protection to prevent breaches
These fundamental challenges reflect the current technological boundaries of AI systems that, despite their sophistication, still operate within constrained understanding of human communication dynamics and organizational complexity.
Technical Improvement Directions
Several technical advancements could address these limitations:
- Introducing long-term memory mechanisms (such as Meta's RAG architecture) to strengthen multimodal and cross-platform information integration capabilities and enhance contextual awareness
- Incorporating stronger emotion recognition and contextual understanding modules, such as combining voice/video to improve emotional recognition, enhancing human-machine interaction naturalness
- Enhancing privacy protection mechanisms through local deployment and end-to-end encryption
These emerging technological approaches represent promising pathways toward more sophisticated AI email assistants that can better navigate the complexities of human communication while maintaining robust security standards and respecting privacy boundaries.
FAQs About AI Email Assistant
Q: What is an AI email assistant and what can it do?
A: An AI email assistant uses artificial intelligence to help manage emails by automatically composing messages, generating replies, organizing inboxes, scheduling meetings, and extracting tasks while adjusting tone based on user preferences. Mailbutler's Smart Assistant exemplifies these capabilities by streamlining email composition and task management in one integrated tool.
Q: What advantages does using an AI email assistant offer?
A: AI email assistants save time through automation, improve writing quality with contextual adjustments, enhance response efficiency, offer greater personalization based on user history, and optimize email marketing through data analysis. These benefits collectively reduce manual effort while increasing communication effectiveness.
Q: What common features do AI email assistants offer?
A: Key features include intelligent classification and priority ranking, automated replies, seamless calendar integration for scheduling, and robust security protection. These core functionalities form the foundation of most AI email assistant platforms available today.
Q: What should users be aware of when using AI email assistants?
A: Users should recognize limitations in contextual understanding, risks of over-automation creating impersonal communication, data privacy concerns when handling sensitive information, and initial setup investments. Balancing automation with personal oversight remains essential for optimal results.
Q: Which mainstream AI email assistant tools are available?
A: Leading tools include Mailbutler (cross-platform with task extraction), Google Duet AI (Gmail integration with drafting capabilities), HubSpot Content Assistant (marketing optimization), Boomerang Respondable (response rate improvement), and Missive (team collaboration). The Outlook AI email assistant has gained popularity in enterprise settings due to its Microsoft ecosystem integration.
Q: How do AI email assistants perform with complex or sensitive emails?
A: Testing by The Washington Post showed mixed results for sensitive communications like layoff notices, with Claude scoring highest at 50/100 while outperforming human writers. Other tools scored lower due to mechanical language, highlighting that while AI can structure content effectively, human refinement remains necessary for emotional nuance and authenticity.
Future Hold for AI Email Assistant Technology
The trajectory of AI email assistant technology reveals a remarkable evolution from basic spell-checkers to sophisticated communication tools powered by advanced AI. These assistants have transformed from correcting simple errors to understanding context, generating personalized content, and automating complex workflows.
As we look to the future, several critical considerations emerge. The balance between automation and personalization will remain a central challenge. While AI email assistants excel at efficiency and consistency, they continue to struggle with the nuanced emotional intelligence that characterizes effective human communication. Developers must address this gap while maintaining robust privacy protections and transparent operational models.
From a broader perspective, the ethical implications of increasingly autonomous communication tools warrant careful consideration. How might these technologies reshape workplace communication norms? What responsibilities do developers have to ensure these tools enhance rather than diminish authentic human connection?
Despite these challenges, the future of AI email assistants appears promising. Ongoing advancements in multimodal understanding, emotional intelligence, and privacy-preserving architectures will likely expand their capabilities while addressing current limitations. As these technologies evolve, they may fundamentally transform not just how we manage email, but how we communicate in digital environments more broadly.
The most successful implementations will likely be those that thoughtfully integrate AI capabilities with human oversight, leveraging technological efficiency while preserving the irreplaceable qualities of human judgment, creativity, and empathy. In this balanced approach lies the true potential of AI email assistant technology: not as a replacement for human communication, but as a powerful enhancement that frees us to focus on our most meaningful exchanges.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!






No comments yet. Be the first to comment!