The software development world is being upended — not by a new language or framework, but by the meteoric rise of the AI App Builder. No longer confined to speeding up workflows or writing snippets of code, AI is now taking center stage, redefining what it even means to develop an application.
The AI App Builder isn’t just another shiny tool in the developer’s toolkit — it’s a fundamental rewire of the entire creation process. These platforms aren’t here to assist developers; they’re beginning to replace core parts of the process — from UI design and backend logic to full-stack deployment. With AI capable of generating entire applications from prompts, the question isn’t whether we’ll use app builder AI — it’s how much human input will even be needed. But with this disruption comes a wave of challenges: job displacement, loss of code transparency, and ethical dilemmas around intellectual property. Are we empowering innovation, or trading craftsmanship for convenience?

How Has the AI App Builder Evolved Over Time?
The Humble Beginnings: Template-Based Solutions
The journey of AI App Builder technology didn't begin with the sophisticated machine learning models we see today. In fact, the earliest incarnations were relatively simple template-based systems that emerged in the early 2010s. Platforms like Bubble and Webflow pioneered the visual development approach, allowing users to create applications through drag-and-drop interfaces without writing traditional code.
These early solutions could handle basic problems like creating simple CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) applications, basic e-commerce sites, and straightforward business websites. While revolutionary for their time, they were essentially sophisticated form builders with limited customization capabilities. The "intelligence" was primarily rule-based, offering pre-defined templates and workflows rather than truly adaptive AI functionality.
The Machine Learning Revolution: Key Turning Points
The real transformation began around 2018-2019 when companies started integrating genuine machine learning capabilities into their development platforms. GitHub Copilot, launched by GitHub in collaboration with OpenAI, marked a pivotal moment in 2021. This wasn't just another code completion tool—it was the first mainstream app builder ai solution that could understand context, generate meaningful code snippets, and learn from vast repositories of existing code.
Following GitHub's breakthrough, we witnessed an explosion of innovation. Replit's Ghostwriter emerged as another game-changer, offering real-time code generation and debugging assistance. Meanwhile, Microsoft's Power Platform began incorporating AI capabilities that allowed business users to build app with ai assistance, bridging the gap between technical and non-technical creators.
The introduction of GPT-3 and later GPT-4 created another seismic shift. Suddenly, AI App Builder platforms could understand natural language descriptions and translate them into functional code. Platforms like Builder.ai and Appy Pie began leveraging these large language models to create more sophisticated applications from simple text descriptions.
Current State: Sophisticated AI-Powered Development
Today's AI App Builder ecosystem is powered by several core technologies that would have seemed like science fiction just a few years ago:
Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows these platforms to understand human requirements expressed in plain English. When you tell an AI App Builder to "create a user authentication system with social media login options," it can parse this request and generate the appropriate code structures, database schemas, and user interface components.
Computer Vision capabilities enable these systems to analyze wireframes, mockups, or even hand-drawn sketches and convert them into functional interfaces. This technology has made it possible for designers to see their visions come to life without extensive coding knowledge.
Code Generation Models trained on millions of code repositories can now produce production-ready code that follows best practices, includes proper error handling, and maintains security standards. These models don't just generate code—they understand architectural patterns, design principles, and can even optimize for performance.
Automated Testing and Deployment features ensure that applications built with AI assistance meet quality standards. Modern AI App Builder platforms can generate comprehensive test suites, identify potential vulnerabilities, and even handle continuous integration and deployment processes.
What Are the Key Advantages and Limitations of AI App Builder Technology?
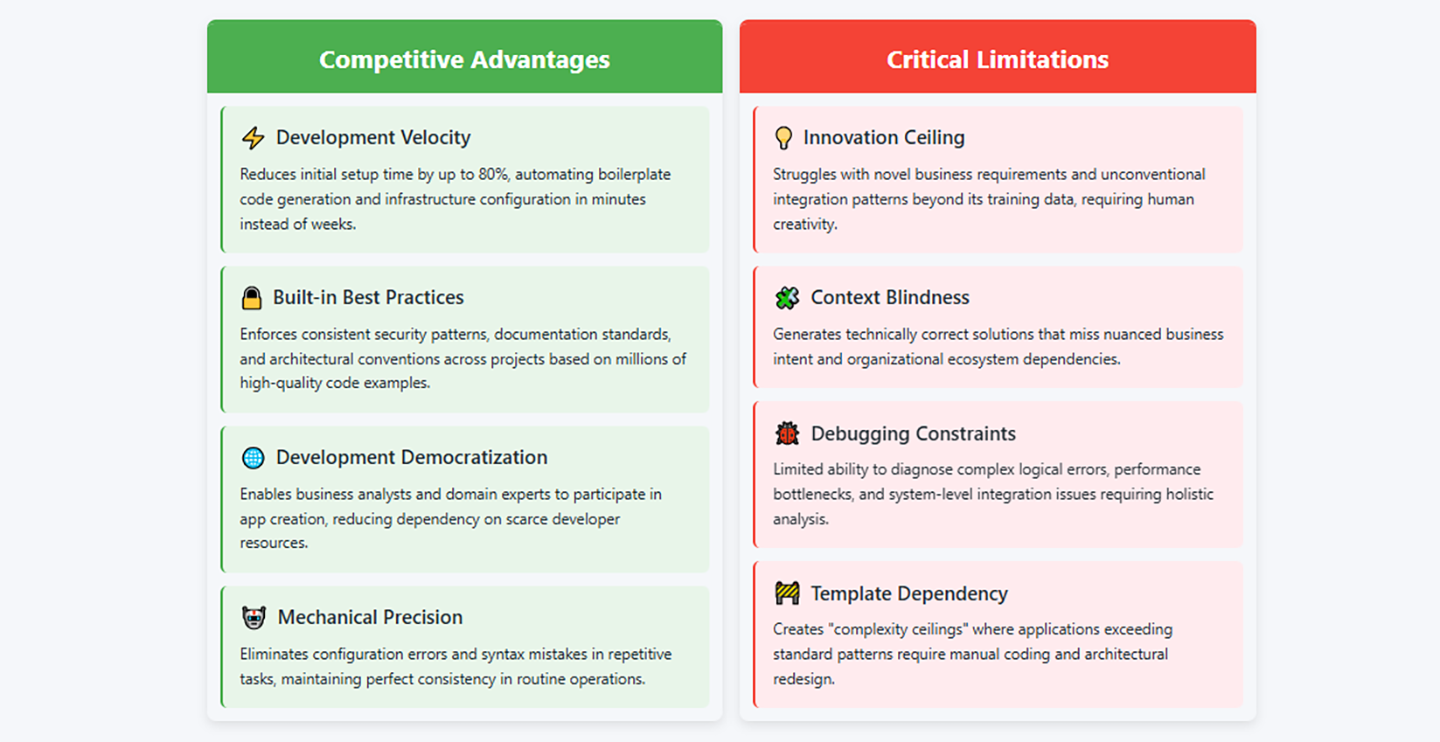
Where AI App Builder Excels: The Competitive Edge
The superiority of AI App Builder technology becomes apparent when we examine its performance in specific domains. Speed and efficiency represent perhaps the most obvious advantage. While a traditional development team might spend weeks setting up project architecture, database schemas, and basic CRUD operations, an AI App Builder can accomplish these tasks in minutes.
I've observed development teams reduce their initial setup time by up to 80% when using app builder ai solutions. This isn't just about writing code faster—it's about eliminating the repetitive, boilerplate work that consumes valuable developer time. The AI handles the mundane tasks while humans focus on solving complex business problems and creating unique user experiences.
Consistency and best practices represent another area where AI excels. Human developers, regardless of their skill level, can have inconsistent coding styles, forget to implement security measures, or skip documentation. An AI App Builder trained on millions of high-quality code examples consistently applies industry best practices, security patterns, and documentation standards.
The democratization of development might be the most transformative advantage. When business analysts, designers, and domain experts can build app with ai assistance, we're no longer bottlenecked by the availability of skilled developers. This doesn't mean replacing developers—it means enabling more people to participate in the creation process.
Error reduction in routine tasks represents another significant advantage. AI doesn't get tired, doesn't overlook details, and doesn't make typos in configuration files. While it can certainly make logical errors, it excels at handling the mechanical aspects of development that often trip up human developers.
The Limitations: Where Human Intervention Remains Essential
Despite these advantages, AI App Builder technology faces significant limitations that prevent it from completely replacing human developers. Creative problem-solving remains a uniquely human strength. When faced with novel business requirements or complex integration challenges, AI systems often struggle to devise innovative solutions.
The limitation stems from AI's training on existing patterns and solutions. While this makes it excellent at reproducing known approaches, it can't truly innovate or think outside established paradigms. When you need to build app with ai for a completely new use case or integrate disparate systems in unprecedented ways, human creativity and domain expertise become irreplaceable.
Context understanding presents another significant challenge. AI App Builder systems often struggle with nuanced business requirements, implicit assumptions, and the broader context of how an application fits into an organization's ecosystem. They might generate technically correct code that completely misses the business intent.
Quality assurance and debugging of complex issues remain heavily dependent on human expertise. While AI can catch syntax errors and common bugs, it struggles with logical errors, performance optimization under specific conditions, and the kind of holistic system thinking required for large-scale applications.
Customization beyond templates represents perhaps the most significant limitation. Most app builder ai solutions work exceptionally well within their defined parameters but struggle when requirements deviate significantly from their training patterns. This creates a "ceiling effect" where simple to moderately complex applications work brilliantly, but highly specialized or innovative applications require traditional development approaches.
How Is AI App Builder Transforming Different Industries?
Positive Disruption: Enabling Innovation Across Sectors
The impact of AI App Builder technology extends far beyond the software development industry itself. In healthcare, we're witnessing a remarkable transformation where medical professionals can now create specialized applications without extensive technical knowledge.
The education sector has embraced these tools to create personalized learning platforms. Teachers and educational administrators are using app builder ai solutions to build custom learning management systems, student assessment tools, and parent communication platforms.
Small and medium businesses represent perhaps the most transformed sector. Previously, custom software solutions were largely the domain of large corporations with substantial IT budgets. Now, a local restaurant can build app with ai assistance to create a comprehensive ordering system, inventory management platform, and customer loyalty program—all without hiring a development team.
The non-profit sector has particularly benefited from this democratization. Organizations with limited budgets can now create sophisticated donor management systems, volunteer coordination platforms, and impact tracking applications.
Negative Impacts: The Disruption Challenges
However, this transformation hasn't been uniformly positive. The traditional software development industry faces significant pressure as clients increasingly question the value of custom development when AI alternatives exist. Junior developers, in particular, find themselves competing with AI systems that can handle many entry-level tasks more efficiently.
We're seeing a commoditization effect where basic application development becomes a low-margin, high-volume business. This forces development agencies to either specialize in highly complex, AI-resistant projects or compete primarily on price—neither of which is sustainable for many traditional firms.
The quality control industry faces unique challenges as AI App Builder platforms can generate applications faster than traditional testing methodologies can validate them. This creates a gap between development speed and quality assurance capabilities, potentially leading to more applications reaching production with undiscovered issues.
System integration specialists and database administrators are finding their roles evolving rapidly. While AI can handle standard configurations, the complexity of enterprise environments still requires human expertise. However, the volume of work requiring this expertise is changing, forcing these professionals to adapt their skill sets.
What Ethical Concerns Should We Address with AI App Builder Technology?
Intellectual Property and Code Ownership Dilemma
The ethical environment surrounding AI App Builder technology presents complex challenges that our industry has yet to fully address. Intellectual Property is perhaps the most contentious issue. When AI systems generate code based on training data that includes millions of open source and proprietary code bases, who owns the final application?
Recent legal challenges have highlighted this complexity. Litigation cases have raised fundamental questions about whether AI-generated code derived from copyrighted training material constitutes fair use or copyright infringement. While the legal system grapples with these issues, developers using AI App Builder solutions are in a gray area of potential liability.
The situation is further complicated by the fact that AI App Builder systems may inadvertently copy copyrighted code patterns, proprietary algorithms, or even specific implementations from their training data. Unlike human developers who can consciously avoid copying protected code, AI systems lack this ethical awareness and legal understanding.
Data Security and Privacy Vulnerabilities
Information security issues represent another critical ethical dimension. When enterprises build applications with the help of AI, they often input sensitive business requirements, proprietary algorithms, and confidential data into AI platforms. This creates potential vectors for data leakage, competitive intelligence theft, and privacy breaches.
Most AI application builder platforms process user input through cloud services, which raises concerns about data residency, access control, and long-term storage. Even those platforms that claim not to store user data may retain information in logs, cache systems, or model training processes. A recent security incident at a large AI platform provider, where developer input was temporarily accessible to other users due to a cache misconfiguration, highlighted these risks.
Privacy impact is more than just an immediate security issue. AI systems that learn from user interactions may inadvertently encode sensitive information into their models and may expose this information in future interactions with other users. This poses ongoing privacy risks that traditional development tools cannot avoid.
Plagiarism and attribution challenges
Academic and professional integrity issues arise when AI-generated code is highly similar to existing implementations and the source is not cited. Unlike traditional software development, where developers deliberately tweak existing solutions and give them credit, AI application building systems may copy patterns without disclosing the source.
This challenge extends beyond simple code duplication to architectural decisions, API design, and even user interface patterns. When solutions generated by AI application building systems are highly similar to proprietary systems, it becomes nearly impossible to tell whether they are independent inventions or unintentional plagiarism.
The credit problem also affects programmers’ careers. When junior developers over-rely on AI-generated code and lack an understanding of the underlying principles, they may miss out on important learning opportunities and develop gaps in foundational knowledge.
How Can We Effectively Leverage AI App Builder While Mitigating Risks?
Strategic Implementation for Affected Industries
Addressing the industry disruption challenges I outlined earlier requires a strategic approach that embraces AI App Builder technology while preserving human value creation. For traditional development firms, the solution lies in repositioning rather than resisting. Instead of competing with AI on routine tasks, successful firms are focusing on high-value services like AI strategy consulting, custom AI model training, and complex system architecture.
I recommend that development organizations adopt a hybrid approach where app builder ai solutions handle standardized components while human developers focus on unique business logic, integration challenges, and user experience optimization. This model has proven successful at companies like Thoughtworks and Accenture, where AI handles up to 40% of routine development tasks, allowing human developers to concentrate on innovation and client consultation.
For educational institutions, the key is preparing students for an AI-augmented future rather than pretending AI doesn't exist. Forward-thinking computer science programs now teach students how to effectively collaborate with AI tools, evaluate AI-generated code, and focus on skills that complement rather than compete with artificial intelligence.
Small businesses should approach AI App Builder technology with realistic expectations and proper planning. While these tools can dramatically reduce development costs, successful implementation requires clear requirements definition, adequate testing procedures, and plans for ongoing maintenance. I've seen too many small businesses rush into AI-generated applications without considering long-term support and scalability requirements.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Ethical Concerns
Addressing the ethical challenges requires proactive measures at both organizational and industry levels. For intellectual property protection, organizations should implement clear policies about AI-generated code ownership, conduct regular audits for potential IP conflicts, and maintain detailed documentation about AI tool usage in their development processes.
Legal compliance strategies should include regular consultation with IP attorneys familiar with AI-generated content, implementation of code scanning tools that can identify potentially problematic similarities, and establishment of insurance policies that cover AI-related IP disputes. Some organizations are also beginning to use "clean room" development processes where AI-generated code is reviewed and rewritten by human developers who haven't seen the original training data.
To address data security concerns, organizations using AI App Builder platforms should implement data classification systems, use on-premises or private cloud AI solutions for sensitive projects, and establish clear data governance policies for AI tool usage. Regular security audits should specifically examine AI platform integrations and data flows.
Transparency and attribution can be improved through better tooling and processes. Some organizations are developing internal standards that require documentation of AI assistance in code comments, implementation of automated tools that track AI-generated code sections, and establishment of review processes that ensure human understanding of all AI-generated components.
Building Sustainable AI-Human Collaboration
The future success of AI App Builder technology depends on creating sustainable collaboration models between artificial intelligence and human developers. This requires rethinking traditional development roles and creating new career paths that leverage both human creativity and AI efficiency.
Professional development should focus on skills that complement AI capabilities: system design, user experience research, business analysis, and AI tool evaluation. Developers who master these areas while becoming proficient with AI App Builder platforms will find themselves in high demand.
Organizations should also invest in continuous learning programs that help their teams stay current with evolving AI capabilities while developing uniquely human skills. This includes training in prompt engineering, AI output evaluation, and the ability to build app with ai assistance while maintaining code quality and security standards.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between traditional app builders and AI App Builders?
A: Traditional app builders rely on pre-defined templates and drag-and-drop interfaces, while AI App Builder platforms use machine learning to understand natural language requirements and generate custom code. AI-powered solutions can handle more complex logic, adapt to unique requirements, and learn from vast code repositories to suggest optimal implementations.
Q: Can AI App Builder completely replace human developers?
A: No, AI App Builder technology cannot completely replace human developers. While AI excels at routine tasks, code generation, and following established patterns, human developers remain essential for creative problem-solving, complex system architecture, business requirement analysis, and quality assurance of sophisticated applications.
Q: How secure are applications built with AI App Builder platforms?
A: Security depends largely on the specific platform and implementation approach. Reputable AI App Builder platforms incorporate security best practices into their generated code, but organizations should still conduct security reviews, implement proper testing procedures, and ensure compliance with their specific security requirements.
Q: How do I choose the right AI App Builder for my project?
A: Consider factors like your technical requirements, team expertise, security needs, and budget. Evaluate platforms based on their supported technologies, integration capabilities, scalability options, and the quality of their generated code. It's also important to assess the platform's ability to handle your specific use case and industry requirements.
Conclusion
The rise of the AI App Builder marks one of the most disruptive turning points in software development since the creation of high-level programming languages. This isn’t just another incremental upgrade — it’s a redefinition of who gets to build, how fast they can do it, and what’s even considered “development” in the age of intelligent automation. As we’ve explored, these tools promise to democratize coding, slash time-to-market, and unlock bold new forms of human-AI collaboration.
But let’s be clear: adopting AI tools isn’t enough. Real success in this new frontier demands a radical shift in mindset. It requires more than just technical curiosity — it calls for strategic foresight, ethical vigilance, and a deep understanding of what AI can and can’t do. Because while these platforms are astonishing in their capabilities, they’re also riddled with risks — from overreliance and skill erosion to intellectual property grey zones and algorithmic bias.
The real winners in this AI-powered evolution won’t be those who blindly automate — they’ll be the ones who know when not to. Those who see the AI App Builder not as a substitute for human intelligence, but as a force multiplier. In a world where anyone can generate code, it’s the human edge — creativity, empathy, strategic thinking — that will separate impactful innovation from shallow automation.
The future of application development isn't about man versus machine. It's about building symbiotic systems where AI handles the heavy lifting — and humans bring the vision, values, and purpose. If we get that balance right, we’re not just building better apps — we’re rewriting the very rules of digital creation.
The AI App Builder era has only just begun. Those bold enough to embrace its potential — and wise enough to confront its consequences — will shape the next generation of software, and with it, the future of how we live, work, and connect in a digital world.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!






No comments yet. Be the first to comment!