The landscape of software development has undergone a revolutionary transformation in recent years, with AI Developer Tools emerging as the cornerstone of modern programming practices. From simple code completion utilities to sophisticated generative AI systems, these tools have evolved from niche experimental projects to essential components of the developer's toolkit. As we stand at the threshold of 2025, the question is no longer whether AI will reshape software development, but rather how we can harness its power responsibly while navigating the complex challenges it presents.
The significance of AI Developer Tools extends far beyond mere productivity enhancements. These systems represent a fundamental shift in how we approach software creation, testing, and maintenance. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and the adoption of AI tools brings forth critical considerations around ethics, security, and the future of human expertise in programming.

How Have AI Developer Tools Evolved?
The Foundation Years: From Rule-Based Systems to Machine Learning
The journey of AI Developer Tools began in the 1950s with the birth of artificial intelligence itself. When John McCarthy coined the term "artificial intelligence" at the Dartmouth Conference in 1956, few could have imagined that this would eventually lead to systems capable of generating complex software code. The early decades were dominated by rule-based systems that relied on predefined logic and structured approaches to problem-solving.
The 1960s brought us ELIZA, created by Joseph Weizenbaum at MIT, which demonstrated the first glimpse of natural language processing capabilities. While primitive by today's standards, ELIZA laid the groundwork for understanding how machines could interact with human language—a crucial foundation for modern AI coding assistants.
The transition from rule-based systems to machine learning marked a pivotal moment in AI development. This shift enabled systems to learn from data rather than being explicitly programmed for every scenario. The introduction of neural networks in the 1980s and their subsequent development provided the computational framework that would eventually power today's sophisticated AI Developer Tools.
The Deep Learning Revolution
The 2010s witnessed a paradigm shift with the rise of deep learning and neural networks. Geoffrey Hinton's breakthrough work in 2012 with ImageNet demonstrated the power of deep neural networks, setting the stage for the generative AI revolution that would follow. This period saw the development of increasingly sophisticated language models that could understand and generate human-like text.
The launch of IBM's Watson in 2011, which defeated human champions on Jeopardy!, showcased AI's ability to process natural language and provide contextually relevant responses. This demonstration of AI's potential to understand and work with human language was a crucial stepping stone toward the development of coding assistants.
The Modern Era: Generative AI and Code Generation
The real transformation began in 2020 with OpenAI's release of GPT-3, featuring 175 billion parameters. This massive language model demonstrated unprecedented capabilities in generating human-like text, including code. The subsequent release of GitHub Copilot in 2021 marked the first mainstream implementation of AI-powered code generation, fundamentally changing how developers approach their craft.
The release of ChatGPT in 2022 brought AI to the masses, reaching 100 million users within just two months. This accessibility breakthrough demonstrated that AI could be both powerful and user-friendly, paving the way for widespread adoption of AI tools in software development.
By 2024, the landscape had transformed dramatically. Current statistics show that 81% of developers now use AI-powered coding assistants, with 97% of enterprise developers using generative AI coding tools daily. This represents a fundamental shift in how software is created, with AI becoming an integral part of the development process rather than an optional enhancement.
What Are the Key Advantages and Limitations of AI Developer Tools?
Advantages: Transforming Developer Productivity
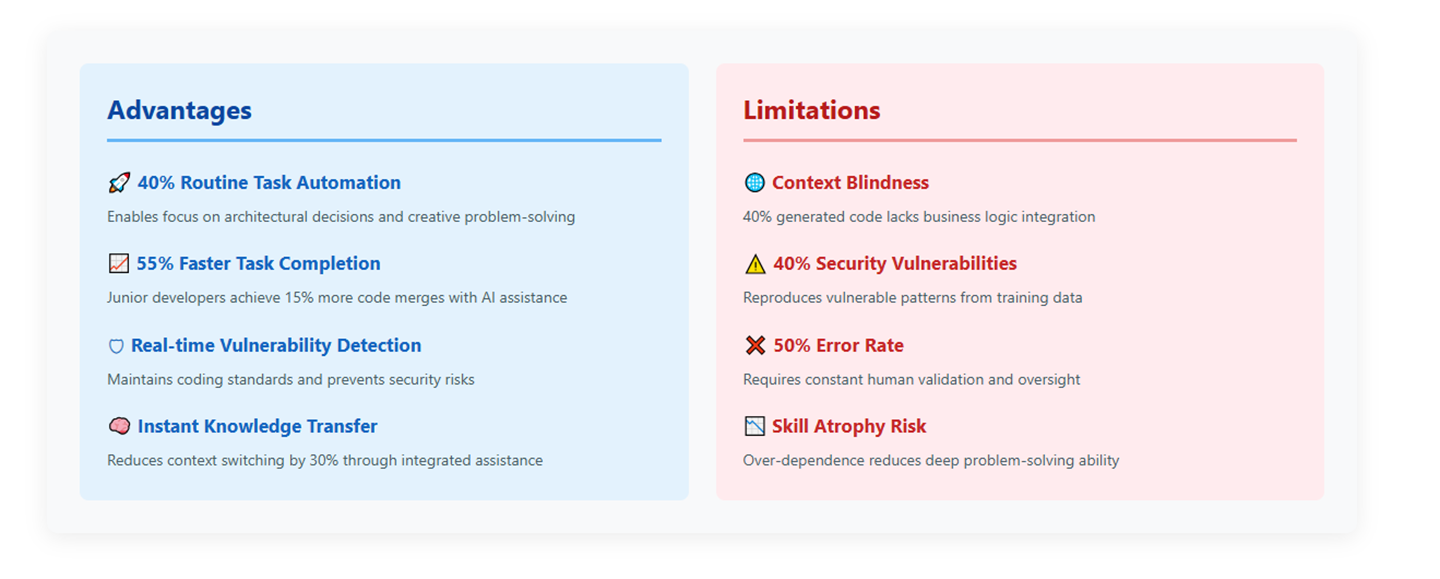
AI Developer Tools have delivered substantial benefits that extend far beyond simple code completion. Research indicates that AI coding assistants can automate up to 40% of routine coding tasks, freeing developers to focus on higher-level architectural decisions and creative problem-solving.
Productivity Enhancements: The most significant advantage lies in productivity improvements. Studies show that developers using GitHub Copilot experience 15% more code merges and 8.7% more pull requests. For junior developers, the impact is even more pronounced, with some experiencing up to 55% faster task completion rates. This acceleration enables teams to deliver features more rapidly while maintaining quality standards.
Code Quality Improvements: AI tools excel at maintaining consistent coding standards and detecting errors in real-time. These systems can identify syntax errors, suggest best practices, and even predict potential security vulnerabilities before they become problematic. The ability to provide instant feedback and suggestions helps developers write cleaner, more maintainable code.
Learning and Knowledge Transfer: AI Developer Tools serve as powerful learning platforms, providing instant explanations of complex code patterns and suggesting alternative approaches. This capability is particularly valuable for junior developers who can learn from the accumulated knowledge embedded in these systems.
Efficiency Gains: Beyond code generation, AI tools reduce context switching by providing relevant information within the development environment. This integration minimizes the need to search external resources, allowing developers to maintain focus on their current tasks.
Limitations: Understanding the Boundaries
Despite their impressive capabilities, AI Developer Tools face significant limitations that developers must understand and navigate carefully.
Context and Understanding Gaps: One of the most significant limitations is AI's inability to fully grasp project context and business logic. While these tools can generate syntactically correct code, they often miss the broader implications of their suggestions within the specific project ecosystem. This limitation can lead to solutions that work in isolation but fail to integrate properly with existing systems.
Security and Vulnerability Concerns: Research has revealed troubling security implications. Studies indicate that approximately 40% of AI-generated programs contain security vulnerabilities. The tools' training on vast public codebases means they can inadvertently reproduce vulnerable code patterns, potentially introducing security risks into production systems.
Accuracy and Reliability Issues: Academic research has shown that AI coding assistants provide incorrect answers up to 50% of the time when compared to human solutions. This unreliability requires constant human oversight and validation, potentially negating some of the productivity gains these tools provide.
Skill Atrophy and Over-Dependence: Perhaps most concerning is the risk of developers becoming overly dependent on AI tools, potentially leading to skill degradation over time. The convenience of AI assistance may discourage developers from developing deep problem-solving skills and understanding fundamental programming concepts.
How Do AI Developer Tools Impact Different Industries?
Positive Industry Transformations
Software Development Sector: Contrary to fears of job displacement, the software development industry is experiencing growth. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 17.9% increase in software developer employment between 2023 and 2033, indicating that AI is augmenting rather than replacing human developers. This growth is driven by increased demand for AI-integrated systems and the need for skilled professionals to develop and maintain these technologies.
Financial Services: The finance industry has embraced AI Developer Tools for algorithmic trading, risk assessment, and fraud detection systems. AI-powered development tools enable financial institutions to create more sophisticated analytical systems and respond rapidly to market changes. The ability to generate and test complex financial models quickly has become a competitive advantage in this sector.
Healthcare: AI Developer Tools are accelerating medical software development, particularly in areas such as electronic health records, diagnostic systems, and drug discovery platforms. These tools help healthcare technology companies develop compliant, secure systems more efficiently while maintaining the strict regulatory requirements of the medical field.
Education Technology: The education sector benefits from AI-powered development tools that enable the creation of personalized learning platforms and adaptive curricula. These systems can process vast amounts of educational data to create customized learning experiences for students.
Industry Challenges and Disruptions
Quality Assurance and Testing: While AI tools increase development speed, they also create new challenges for quality assurance teams. The volume of code produced requires proportionally more testing and review. Security teams report needing to scale their operations to match the increased output from AI-assisted development teams.
Traditional IT Roles: Some traditional IT roles face transformation as AI tools automate routine tasks. System administrators, junior developers, and certain types of technical writers may need to adapt their skill sets to remain relevant in an AI-augmented environment.
Cybersecurity: The cybersecurity industry faces new challenges as AI tools can potentially generate malicious code or introduce vulnerabilities. Security professionals must develop new strategies to detect and prevent AI-generated threats while also leveraging AI tools for defensive purposes.
What Ethical Concerns Surround AI Developer Tools?
Copyright and Intellectual Property Issues
The most pressing ethical concern involves copyright infringement and intellectual property rights. AI Developer Tools are trained on vast datasets that include copyrighted code from public repositories. This training methodology raises questions about whether AI-generated code might infringe on existing copyrights.
Recent legal challenges illustrate the complexity of this issue. Major music labels have sued AI companies for using copyrighted songs in training, while authors and media companies have initiated similar lawsuits against AI developers. The fundamental question remains: does training AI systems on copyrighted material constitute fair use, or does it represent a form of copyright violation?
Research from Carnegie Mellon University provides some perspective on the scope of this concern. Their study found that the frequency of AI-generated code snippets with striking similarity to license-protected code ranges between 0.88% and 2.01%. While this percentage is relatively low, it still represents a significant risk for organizations concerned about intellectual property liability.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
AI Developer Tools raise significant privacy concerns related to the handling of sensitive code and proprietary information. When developers use cloud-based AI assistants, portions of their code may be transmitted to external servers for processing. This transmission raises questions about data retention, security, and the potential for intellectual property theft.
The European Union's GDPR and similar privacy regulations worldwide impose strict requirements on how personal data is handled. Organizations must carefully evaluate whether their use of AI tools complies with these regulations, particularly when dealing with code that processes personal information.
Bias and Fairness Issues
AI systems can perpetuate and amplify biases present in their training data. In the context of coding, this might manifest as biased algorithm suggestions or coding patterns that disadvantage certain groups. For example, an AI system trained on historically male-dominated programming communities might generate code that reflects gender biases in variable naming or comment styles.
ransparency and Accountability
The "black box" nature of many AI systems creates challenges for transparency and accountability. When AI generates code, it can be difficult to understand the reasoning behind specific suggestions or to trace the source of potential problems. This lack of transparency complicates debugging and makes it challenging to assign responsibility for issues that arise from AI-generated code.

How Can We Responsibly Leverage AI Developer Tools?
Addressing Industry Transformation Challenges
Reskilling and Upskilling Initiatives: Organizations must invest in comprehensive training programs that help developers adapt to AI-augmented workflows. This includes training on AI tool capabilities, limitations, and best practices for integration. Companies should focus on developing hybrid human-AI collaboration skills rather than simply replacing human capabilities.
Hybrid Workflow Development: The most effective approach involves creating workflows that combine human expertise with AI capabilities. Developers should maintain responsibility for architecture decisions, code review, and quality assurance while leveraging AI for routine tasks and initial code generation.
AI Literacy Programs: Organizations should implement AI literacy programs that educate all team members about AI capabilities, limitations, and ethical considerations. This education should extend beyond technical teams to include project managers, quality assurance professionals, and business stakeholders.
Ethical Risk Mitigation Strategies
Intellectual Property Protection: Organizations should implement several strategies to mitigate copyright risks:
Use AI tools with built-in copyright protection features, such as Tabnine's Provenance and Attribution system
Establish clear policies for AI-generated code review and approval
Implement automated scanning systems that check AI-generated code against known copyrighted works
Maintain detailed documentation of AI tool usage for legal compliance
Data Privacy Safeguards: To address privacy concerns, organizations should:
Choose enterprise-grade AI tools with clear data handling policies
Implement proper access controls and data governance frameworks
Consider on-premises or hybrid deployment options for sensitive projects
Ensure compliance with relevant privacy regulations such as GDPR
Bias Detection and Mitigation: Organizations should establish processes to identify and address potential bias in AI-generated code:
Regular audits of AI-generated code for bias indicators
Diverse training data and model validation procedures
Clear escalation procedures for identifying and addressing bias issues
Ongoing monitoring of AI system outputs for fairness and equity
Technical Best Practices for Responsible AI Use
Human-Centered Design: AI Developer Tools should be implemented with human oversight as a central principle. Developers should treat AI as a collaborative partner rather than a replacement for human judgment. This approach ensures that critical decisions remain under human control while leveraging AI's efficiency for routine tasks.
Code Review and Quality Assurance: Organizations should implement enhanced code review processes that specifically account for AI-generated code. This includes:
Mandatory human review of all AI-generated code before integration
Automated testing procedures tailored to AI-generated code patterns
Security scanning specifically designed to catch AI-related vulnerabilities
Documentation requirements for AI tool usage in development processes
Security-First Approaches: Given the security risks associated with AI-generated code, organizations should adopt security-first approaches:
Implement automated vulnerability scanning for all AI-generated code
Use AI tools with built-in security features and regular security updates
Establish incident response procedures for AI-related security issues
Regular security training for developers using AI tools
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Organizations should establish systems for continuous monitoring and improvement of AI tool usage:
Regular assessment of AI tool effectiveness and accuracy
Feedback mechanisms for developers to report issues or concerns
Ongoing evaluation of AI tool impact on code quality and security
Adaptation of processes based on emerging best practices and lessons learned
Organizational Governance Frameworks
AI Ethics Committees: Organizations should establish AI ethics committees that include technical experts, legal professionals, and business stakeholders. These committees should develop and maintain organizational policies for AI use, address ethical concerns, and provide guidance on difficult decisions.
Clear Usage Policies: Organizations need comprehensive policies that define appropriate and inappropriate uses of AI tools. These policies should address:
Approved AI tools and their intended uses
Data handling and privacy requirements
Intellectual property considerations
Security and compliance requirements
Escalation procedures for ethical concerns
Training and Support Programs: Ongoing training programs should ensure that all team members understand both the capabilities and limitations of AI tools. This training should cover technical aspects, ethical considerations, and best practices for responsible use.
FAQs
Q: Are AI Developer Tools replacing human developers?
A: No, AI Developer Tools are augmenting rather than replacing human developers. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 17.9% growth in software developer employment between 2023 and 2033, indicating that AI is creating new opportunities rather than eliminating jobs.
Q: How significant are the security risks of AI-generated code?
A: Security risks are substantial, with studies showing that approximately 40% of AI-generated programs contain security vulnerabilities. However, these risks can be mitigated through proper code review processes, automated security scanning, and choosing enterprise-grade AI tools with built-in security features.
Q: What is the risk of copyright infringement when using AI coding assistants?
A: Research indicates that 0.88% to 2.01% of AI-generated code snippets show striking similarity to license-protected code. While relatively low, this risk can be managed through tools with copyright protection features and proper legal compliance procedures.
Q: How can organizations ensure responsible use of AI Developer Tools?
A: Organizations should implement comprehensive governance frameworks including AI ethics committees, clear usage policies, enhanced code review processes, and ongoing training programs. Treating AI as a collaborative partner rather than a replacement for human judgment is essential.
Q: What are the most important best practices for using AI coding assistants?
A: Key best practices include maintaining human oversight of all AI-generated code, implementing robust security scanning, providing clear context when prompting AI tools, regular code review processes, and continuous monitoring of AI tool effectiveness and accuracy.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI Developer Tools represents one of the most significant transformations in software development history. From the early rule-based systems of the 1950s to today's sophisticated generative AI platforms, these tools have fundamentally altered how we approach software creation. With market projections indicating growth from $4.5 billion in 2024 to $10 billion by 2030, and adoption rates reaching 81% among developers, AI Developer Tools have moved from experimental curiosities to essential components of modern development workflows.
The advantages of these tools are undeniable: they can automate up to 40% of routine coding tasks, improve code quality through real-time error detection, and accelerate learning for junior developers by up to 55%. However, these benefits come with significant challenges, including security vulnerabilities in 40% of AI-generated code, potential copyright infringement issues, and the risk of developer skill atrophy through over-dependence.
The impact on industries extends far beyond software development itself. While the technology sector is experiencing 17.9% projected job growth, other industries are grappling with the need for reskilling and adaptation. The ethical considerations surrounding copyright, data privacy, and bias require careful attention and proactive management.
The Strategic Importance of Responsible Innovation
As we navigate this transformation, the key to success lies not in avoiding AI tools but in implementing them responsibly. Organizations must develop comprehensive frameworks that address intellectual property concerns, implement robust security measures, and maintain human oversight of critical decisions. The most successful implementations will be those that treat AI as a collaborative partner rather than a replacement for human expertise.
The future of software development will be defined by our ability to harness AI's power while maintaining the human creativity, judgment, and ethical considerations that are essential to creating meaningful, secure, and beneficial software systems. By following best practices, implementing appropriate safeguards, and maintaining a commitment to continuous learning and adaptation, we can realize the tremendous potential of AI Developer Tools while mitigating their risks.
The journey of AI Developer Tools is far from over. As these systems become more sophisticated and integrated into our development workflows, our approach to using them must evolve with equal sophistication. The organizations and developers who embrace this challenge thoughtfully and responsibly will be best positioned to thrive in the AI-augmented future of software development.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!






No comments yet. Be the first to comment!