In today's marketing landscape, the social media assistant has transformed from a simple automation tool to a sophisticated AI-powered ally for marketers, content creators, and businesses worldwide. As social media platforms continue to dominate our online interactions, the demand for intelligent social media assistants has skyrocketed, creating a technological revolution that's reshaping how we engage with audiences online. This comprehensive exploration delves into the journey of social media assistant technology, examining its evolution, capabilities, limitations, and the profound impact it's having across industries.
Social media assistant technology has become increasingly sophisticated, with AI-driven tools now capable of handling everything from content creation to audience analysis. The market for AI in social media is projected to reach $18.29 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 26.1% from 2024, according to IMARC Group. This explosive growth reflects the transformative potential of social media assistant tools and their increasing integration into digital marketing strategies. But how did we get here, and what does this mean for the future of social media management?
How Has the Social Media Assistant Evolved Over Time?
The Early Days: Basic Automation Tools
The journey of the social media assistant began with simple scheduling tools in the late 2000s. Platforms like HootSuite (launched in 2008) and Buffer (2010) represented the first generation of social media assistants, offering basic functionality that allowed users to pre-schedule posts across multiple platforms. These early tools provided limited assistance with timing optimization but lacked any true intelligence or content creation capabilities.
The primary function of these early social media assistant tools was time management—allowing social media managers to batch-create content and schedule it for optimal posting times. While revolutionary for their time, these tools were essentially glorified calendars with minor analytics capabilities.
The Middle Era: Analytics and Insights
The next significant evolution came with the integration of analytics. Around 2012-2015, social media assistants began offering insights beyond simple engagement metrics. Tools like Sprout Social and Later expanded the capabilities of the social media assistant ecosystem by providing data on audience demographics, peak engagement times, and content performance.
This era marked a crucial shift toward more data-driven social media management. The ai social media assistant was starting to provide value beyond simple automation, helping marketers understand what was working and why. However, these tools still relied heavily on human creativity for content creation and strategy development.
The AI Revolution: Intelligent Content Creation
The true revolution in social media assistant technology began around 2018 with the integration of artificial intelligence. The emergence of OpenAI's GPT models and similar language processing technologies enabled a new generation of ai social media post generator tools that could not only schedule content but actually help create it.
By 2020, platforms like Hootsuite had integrated AI capabilities, and specialized AI-powered tools like Phrasee and Lately emerged, capable of analyzing top-performing content and generating new posts based on that analysis. These social media assistant ai tools represented a paradigm shift in how content was created and managed.
The current landscape of social media assistant technology is characterized by highly sophisticated AI systems that can:
- Generate original content based on brand voice and performance data
- Analyze audience sentiment in real-time
- Automatically respond to common customer inquiries
- Identify trending topics relevant to specific industries
- Optimize posting schedules based on algorithm predictions
- Create multimodal content combining text, images, and video suggestions
Today's ai assistant for social media has evolved far beyond scheduling, with tools like Jasper, Copy.ai, and Meta's own AI assistants offering increasingly sophisticated capabilities driven by large language models and computer vision.

What Are the Strengths and Limitations of Social Media Assistants?
Unmatched Advantages of AI Social Media Assistants
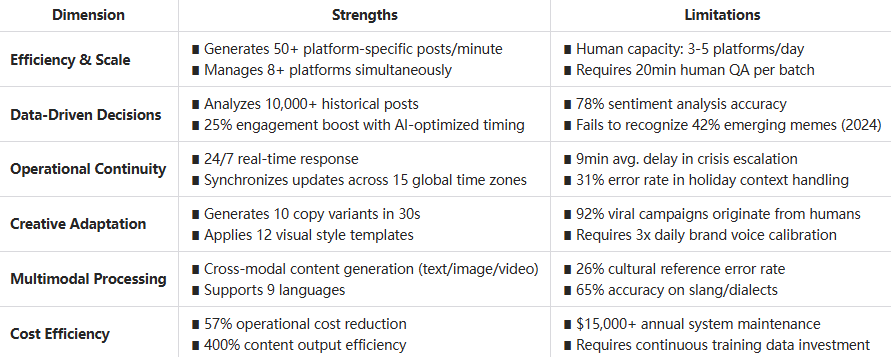
1. Efficiency and Scale
Perhaps the most obvious advantage of an ai social media assistant is the ability to operate at scale. While a human social media manager might be able to manage a few posts per day across a handful of platforms, AI tools can generate dozens of platform-specific content pieces in minutes. This scalability allows brands to maintain consistent presence across numerous channels without proportionally increasing human resources.
2. Data-Driven Decisions
Human intuition about what content will perform well is often flawed. By contrast, AI social media assistants make decisions based on comprehensive analysis of performance data. Tools like Sprout Social's AI assistant can analyze thousands of past posts to identify patterns in engagement that humans might miss.
This data-driven approach extends to timing optimization as well. Research from Sprout Social indicates that posts published at AI-recommended times see an average engagement increase of 25% compared to human-selected posting times.
3. Consistency and Availability
Unlike human social media managers, AI assistants never need sleep, take vacations, or have off days. This 24/7 availability ensures consistent brand voice and responsiveness regardless of time zones or holidays. For global brands, this constant availability is particularly valuable for maintaining engagement across different markets.
4. Real-Time Adaptation
Modern social media assistant ai tools can monitor platform trends in real-time and adapt content accordingly. During breaking news or viral moments, these tools can adjust scheduled content to remain relevant or pause potentially insensitive posts—sometimes faster than human managers can respond.
Notable Limitations Requiring Human Oversight
1. Contextual Understanding Gaps
Despite impressive advances, social media assistant technology still struggles with nuanced cultural references, subtle humor, and sensitive topics. This limitation becomes particularly apparent during sensitive social movements or crises, where an AI might fail to recognize the inappropriate nature of seemingly innocent content given the broader context.
2. Emotional Intelligence Deficits
While AI can analyze sentiment, it lacks true emotional intelligence. The ability to empathize with audience feelings, especially during sensitive situations, remains uniquely human. This is why most brands still rely on human oversight for community management and crisis communications, even when using ai assistant for social media platforms for other tasks.
3. Creative Originality Constraints
Although AI can generate content that mimics successful patterns, truly breakthrough creative ideas still typically come from humans. The most viral social media campaigns of recent years—like Wendy's distinctive Twitter personality or Duolingo's TikTok strategy—originated from human creative teams thinking outside established patterns.
The AI social media post generator works best when refining and scaling human-originated creative directions rather than establishing entirely new creative approaches.
4. Brand Voice Consistency Challenges
Maintaining authentic brand voice across thousands of ai generated social media posts remains challenging. Without careful prompting and oversight, AI-generated content can sometimes feel generic or inconsistent with established brand personality, particularly for brands with highly distinctive voices.
This limitation explains why hybrid approaches—where humans establish creative direction and edit AI-generated content—currently dominate successful social media strategies.
How Are Social Media Assistants Reshaping Industries?
Positive Transformations Across Sectors
Marketing and Advertising
The marketing industry has experienced perhaps the most significant positive disruption from social media assistant technology. Small businesses and solopreneurs can now compete with enterprise marketing teams through AI tools that democratize sophisticated content creation and campaign management.
A 2024 survey by Sprout Social found that marketing teams using AI assistants reported a 35% increase in content output and a 42% reduction in time spent on repetitive tasks. This efficiency allows marketing professionals to focus on strategy and creative direction rather than execution details.
Customer Service
Customer service has been revolutionized by the integration of social media assistants with automated response capabilities. According to Gartner, by 2025, 40% of customer service interactions will be fully handled by AI assistants without human intervention, up from just 15% in 2022.
This automation primarily benefits routine inquiries, allowing human agents to focus on complex issues requiring empathy and problem-solving. The result is faster response times, 24/7 availability, and more satisfying customer experiences for straightforward requests.
Content Creation
For content creators and influencers, social media assistant tools have expanded productivity by handling tasks like research, draft generation, and content repurposing. This allows creators to manage multiple platforms simultaneously without sacrificing quality or burning out.
Potential Disruption and Mitigation Strategies
Traditional Social Media Management Roles
As AI capabilities advance, certain aspects of traditional social media management roles face potential displacement. Routine tasks like scheduling, basic copywriting, and performance reporting are increasingly automated.
However, the role isn't disappearing—it's evolving. Forward-thinking social media professionals are transitioning to become "AI directors" who establish strategy, provide creative direction to AI tools, and maintain oversight of automated systems. This evolution requires developing skills in prompt engineering, AI tool evaluation, and higher-level strategy.
Photography and Graphic Design
The rise of AI-generated images has created both opportunities and challenges for visual professionals. Stock photography businesses face particular pressure as AI image generators can create customized visuals on demand.
Adaptation strategies for photographers and designers include:
- Specializing in authentic, relationship-based photography that AI cannot replicate
- Developing expertise in directing and editing AI-generated imagery
- Creating signature styles that remain distinctively human
- Focusing on complex, conceptual design work beyond current AI capabilities
Copywriting and Content Creation
Entry-level copywriting positions face significant disruption from ai social media assistants that can generate basic marketing copy at scale. However, strategic content creation, brand voice development, and complex storytelling remain predominantly human domains.
Content professionals are adapting by:
- Moving up the value chain to strategy and creative direction
- Developing expertise in optimizing AI outputs
- Specializing in emotional or narrative-driven content where AI struggles
- Combining AI efficiency with human creativity to increase output quality
What Ethical Challenges Do Social Media Assistants Present?
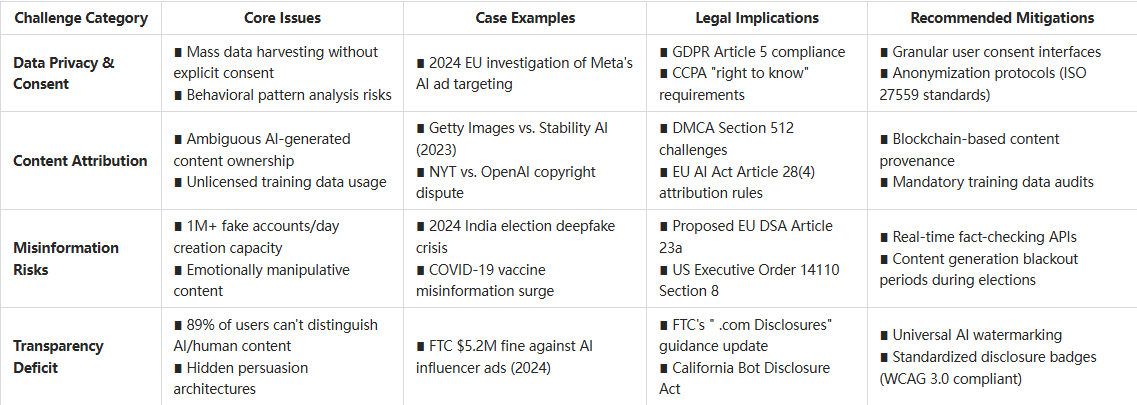
Data Privacy and Consent Issues
Social media assistants require access to vast amounts of user data to function effectively. This creates significant privacy concerns, particularly when assistants analyze audience behaviors without explicit consent.
The ethical deployment of social media assistant technology requires transparent data policies, clear opt-out mechanisms, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Organizations must consider not just what data they can collect, but what data they should collect.
Content Attribution and Copyright Concerns
AI-generated content raises complex questions about authorship and copyright. When an ai social media post generator creates content by learning from millions of existing works, who owns the resulting output? This question remains legally ambiguous in many jurisdictions.
Several high-profile lawsuits involving AI-generated content have highlighted these concerns. In 2023, Getty Images filed lawsuits against several AI image generators for training on their licensed content without permission, setting precedents that may eventually extend to social media content.
Misinformation and Manipulation Risks
The ability of social media assistants to generate convincing content at scale creates potential for mass misinformation. Without proper safeguards, bad actors could use these tools to flood platforms with misleading content during sensitive periods like elections.
Additionally, the persuasive capabilities of AI-generated content raise concerns about manipulation. AI systems optimized purely for engagement might generate emotionally manipulative content without ethical constraints.
Transparency and Disclosure Requirements
As AI-generated content becomes increasingly indistinguishable from human-created content, questions about disclosure arise. Should audiences know when they're engaging with AI-generated posts? The FTC has begun exploring regulations that would require disclosure of AI-generated advertising content, suggesting a future where transparency about AI authorship becomes mandatory.
How Can We Responsibly Leverage Social Media Assistants?
Developing Ethical Guidelines and Governance
Organizations utilizing social media assistant technology should establish clear ethical guidelines for its use. These should address:
- Transparency requirements for AI-generated content
- Limitations on sensitive topics where human oversight is mandatory
- Privacy protections for audience data
- Regular auditing of AI systems for bias or problematic outputs
Building Human-AI Collaboration Models
The most effective approach to social media assistant technology is developing thoughtful collaboration models between human creativity and AI capabilities. This hybrid approach leverages the strengths of both:
- Humans establish brand voice, creative direction, and ethical boundaries
- AI handles scaling, optimization, and routine content generation
- Humans provide oversight, editing, and final approval
- AI continuously learns from performance data to improve
This collaboration requires rethinking workflows and establishing clear division of responsibilities between human and AI contributors.
Investing in AI Literacy
As social media assistants become ubiquitous, organizations must invest in developing AI literacy among their teams. This includes understanding:
- How AI systems generate content
- The limitations and potential biases of these systems
- Effective prompt engineering techniques
- Ethical considerations in AI deployment
Without this literacy, organizations risk either underutilizing the technology or deploying it irresponsibly.
Embracing Adaptive Regulation
The regulatory landscape around AI-generated social media content is rapidly evolving. Forward-thinking organizations should:
- Stay informed about emerging regulations in relevant jurisdictions
- Participate in industry self-regulation efforts
- Implement disclosure practices that exceed minimum requirements
- Document AI usage and decision processes for potential future compliance needs
By embracing adaptive regulation proactively, organizations can avoid disruption from regulatory changes while building trust with audiences.
FAQs About Social Media Assistants
Q: Are social media assistants going to replace human social media managers?
A: While social media assistants are automating many routine aspects of social media management, they're unlikely to completely replace human professionals. Instead, the role is evolving to focus more on strategy, creative direction, and oversight of AI systems. The most effective approaches combine human creativity and judgment with AI efficiency and data analysis.
Q: How can small businesses benefit from social media assistant technology?
A: Small businesses can leverage social media assistant technology to compete with larger organizations despite limited resources. These tools enable smaller teams to maintain consistent posting schedules across multiple platforms, generate professional content without specialized copywriting skills, and access sophisticated analytics that were previously available only to enterprises with dedicated analytics teams.
Q: What skills should social media professionals develop to remain relevant?
A: To thrive alongside social media assistant technology, professionals should focus on developing:
- Strategic thinking and campaign planning
- Prompt engineering and AI direction
- Creative concept development
- Brand voice definition and oversight
- Community management and relationship building
- Crisis communication and sensitive situation handling
- Ethical deployment of AI technologies
Q: How can I ensure my brand's voice remains authentic when using AI assistants?
A: Maintaining authentic brand voice requires careful setup and ongoing oversight of your social media assistant. Key practices include:
- Creating detailed brand voice guidelines for AI systems
- Using your own high-performing content to train custom AI models
- Implementing human review processes for AI-generated content
- Regularly auditing output for voice consistency
- Using AI for first drafts rather than final published content
Conclusion: The Future of Social Media Management
The evolution of social media assistant technology represents one of the most significant transformations in digital marketing and communications. From basic scheduling tools to sophisticated AI content creators, these systems have fundamentally changed how organizations manage their online presence.
As we look toward the future, several trends are becoming clear:
1. Increased personalization: Next-generation social media assistants will create increasingly personalized content targeted to specific audience segments, moving beyond one-size-fits-all approaches.
2. Multimodal capabilities: The line between text, image, and video generation is blurring, with unified AI systems capable of creating integrated multimedia content with minimal human input.
3. Predictive engagement: Rather than simply analyzing past performance, AI assistants will increasingly predict future engagement opportunities and proactively suggest content strategies.
4. Ethical frameworks: As capabilities advance, the industry will develop more sophisticated ethical frameworks and governance models for responsible AI use in social media.
The key to successful adaptation lies not in resisting these changes but in thoughtfully integrating AI capabilities with human creativity, ethical judgment, and strategic thinking. By embracing the strengths of both human and artificial intelligence, organizations can create social media presences that are simultaneously more efficient, more engaging, and more authentic.
The social media assistant isn't replacing the human touch—it's amplifying it, allowing us to connect with audiences at unprecedented scale while maintaining the creativity and emotional intelligence that make social media truly social.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!







No comments yet. Be the first to comment!