AI notes assistants represent a remarkable fusion of natural language processing, machine learning, and user interface design. These intelligent tools transcend traditional note-taking applications by offering capabilities that were once firmly in the realm of science fiction: automatically organizing information, generating summaries, identifying key concepts, and even suggesting connections between seemingly unrelated ideas. From simple voice memos to sophisticated knowledge management systems, these AI-powered assistants have evolved to become indispensable companions for students, professionals, and researchers alike.
The rapid advancement of this technology marks a significant shift in how humans externalize and interact with their thoughts. Yet beneath the seamless interfaces lies a complex interplay of algorithms, data collection practices, and design choices that merit careful examination. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of AI notes assistant technology—tracing its development, assessing current capabilities, and exploring the profound implications its widespread adoption holds for various industries and society as a whole.
Whether you're already integrating these tools into your daily workflow or simply curious about their potential, understanding both the remarkable capabilities and inherent limitations of AI notes assistants will help you navigate this technological landscape more effectively and responsibly.

How Did AI Notes Assistant Technology Evolve Over Time?
The evolution of AI notes assistant technology didn't happen overnight. In fact, if we trace its development, we can identify several distinct phases and pivotal innovations that have shaped what these tools can accomplish today.
The Early Days: Digital Transcription
The earliest iteration of what we might consider an AI notes assistant appeared in the late 1990s and early 2000s with basic speech recognition software like Dragon NaturallySpeaking. These primitive AI note taking applications could transcribe spoken words into text but required extensive training to recognize individual voices and offered limited accuracy. Unlike today's sophisticated AI notes systems, these tools functioned primarily as digital dictation devices with minimal "intelligence" in processing the content.
Microsoft's OneNote, launched in 2003, represented another early step, allowing users to organize notes digitally with some basic search capabilities. However, it still relied heavily on the user to structure and make sense of information.
The Middle Phase: Smart Organization and Basic Understanding
Around 2010-2015, we witnessed the emergence of more sophisticated note apps like Evernote that introduced smarter organizational features. These platforms began incorporating rudimentary AI capabilities to automatically categorize notes, recognize images, and make content searchable. The AI note taker tools of this era could perform basic pattern recognition but lacked true contextual understanding.
Google Keep, introduced in 2013, brought cloud-based note-taking capabilities with improved search functionality powered by Google's search algorithms. This period marked the transition from simple digital notebooks to more intelligent information management systems.
The AI Revolution: Contextual Understanding and Assistance
The real transformation in AI notes assistant technology began around 2018-2019 with the emergence of advanced natural language processing models. Applications like Notion and Roam Research introduced more sophisticated knowledge management frameworks that laid the groundwork for truly intelligent notes systems.
The watershed moment came with the introduction of GPT-3 and similar large language models that could understand context and generate human-like text. Suddenly, AI note taking tools weren't just recording information; they could understand, summarize, and even respond to it.
Current State: Multi-modal Understanding and Proactive Assistance
Today's cutting-edge AI notes applications like Mem.ai, Otter.ai, Notion AI, and Tana represent the fourth generation of this technology. These modern AI notes assistant tools incorporate several advanced capabilities:
1. Multi-modal understanding: Today's note assist technology can process text, voice, images, and even video, extracting meaningful information from various types of content.
2. Contextual awareness: Modern AI notes systems understand not just individual notes but their relationships to other information, your calendar, your behavior patterns, and more.
3. Proactive suggestions: Rather than merely recording information, advanced AI note taking applications can suggest connections, next steps, or related concepts.
4. Real-time collaboration: AI notes tools now facilitate simultaneous multi-user collaboration with intelligent merge capabilities and conflict resolution.
5. Integration with knowledge workflows: Today's systems connect with other productivity tools to create comprehensive knowledge ecosystems.
The technology underpinning modern AI notes assistant systems typically involves transformer-based language models, vector embeddings for semantic search, named entity recognition for identifying key concepts, and increasingly, multi-modal processing capabilities for handling different types of media.
What Are the Strengths and Limitations of AI Notes Assistant Technology?
Understanding both the powerful capabilities and inherent limitations of AI notes assistant systems is essential for using them effectively. Let's explore where these tools excel and where human intervention remains necessary.
Advantages of AI Notes Technology
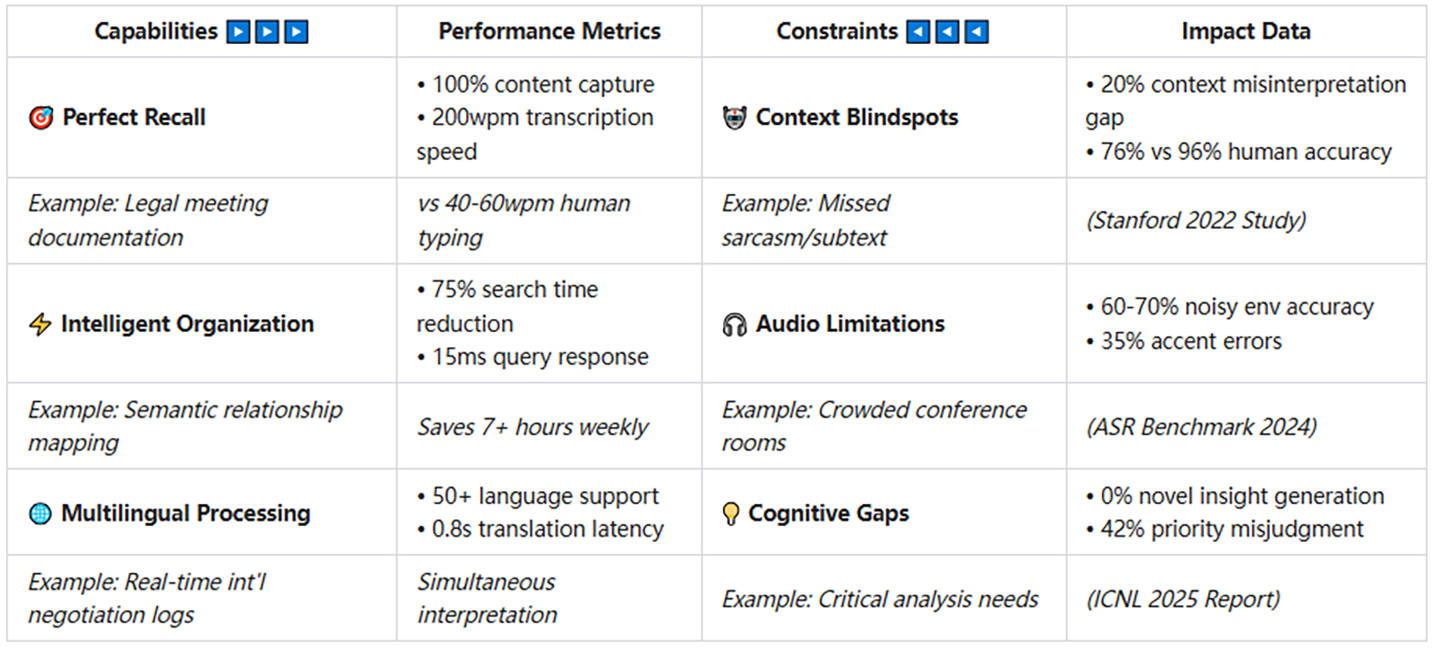
Perfect Memory and Comprehensive Capture
Unlike human note-takers, AI notes assistant applications never suffer from fatigue, distraction, or selective attention. During meetings or lectures, a typical person captures only about 30-40% of the information presented, while AI note taker systems can record 100% of what's said. This comprehensive capture creates a more reliable record, especially crucial for detailed technical discussions or legal contexts.
Speed and Efficiency
Modern AI notes systems can transcribe speech at rates exceeding 200 words per minute with accuracy rates approaching 95% for clear speech in optimal conditions. This far exceeds the average person's handwriting or typing speed (typically 40-60 words per minute), allowing users to focus on participation rather than documentation.
Intelligent Organization and Retrieval
Perhaps the most significant advantage of AI notes assistant technology is not just in capturing information but in making it findable later. Research indicates that professionals spend approximately 9.5 hours per week searching for information. AI-powered notes systems reduce this time by up to 75% through semantic search, automatic categorization, and relationship mapping between concepts.
Multi-lingual Capabilities
Advanced AI note taking tools can now transcribe and translate between dozens of languages in real-time, breaking down language barriers in international business and education contexts. This capability is particularly valuable in our increasingly globalized world.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their impressive capabilities, AI notes assistant technology faces several important limitations:
Contextual Understanding Gaps
While AI has made tremendous strides in natural language understanding, today's systems still struggle with subtle contexts, implicit information, and cultural nuances. An AI notes assistant might accurately transcribe every word of a meeting but miss the unspoken tension in the room or fail to recognize when participants are using sarcasm or humor.
According to a 2022 study by Stanford University researchers, even advanced language models correctly interpret contextual cues only about 76% of the time, compared to humans' 96% accuracy rate. This gap becomes particularly problematic in sensitive negotiations or therapy sessions where subtext carries significant meaning.
Accuracy in Challenging Environments
The performance of AI note taking systems degrades significantly in noisy environments, with multiple speakers, or with strong accents. While professional human transcriptionists maintain approximately 95% accuracy in challenging audio conditions, even leading AI transcription tools see their accuracy drop to 60-70% in similar situations.
Creativity and Critical Thinking Limitations
AI notes applications excel at capturing and organizing information but struggle with the higher-order thinking that characterizes truly valuable notes. They cannot yet reliably:
- Distinguish between important and unimportant information without explicit training
- Generate novel insights or creative connections between distantly related concepts
- Apply critical thinking to evaluate the quality or validity of information
These limitations highlight why AI notes assistant technology works best as a complement to human thinking rather than a replacement.
How Is AI Notes Assistant Technology Impacting Different Industries?
The integration of AI notes assistant capabilities is transforming workflows across numerous sectors, creating both opportunities and challenges. Let's examine these impacts across several key industries.
Education: Transforming Learning and Teaching
AI notes technology is reshaping education in several significant ways:
Positive Impacts
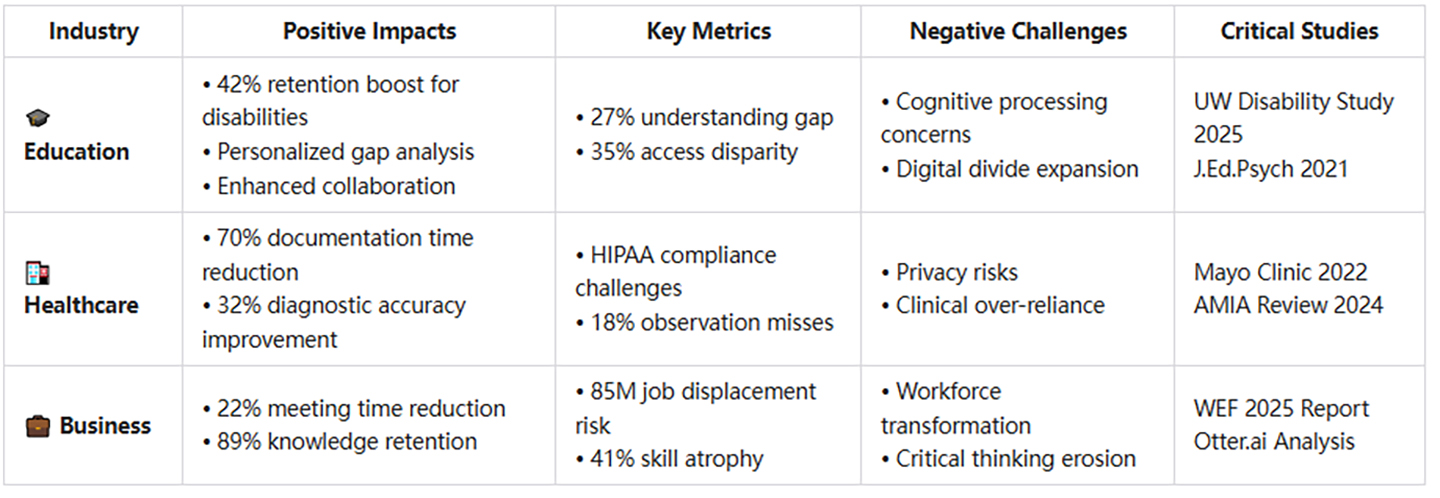
- Accessibility improvements: AI note taking tools have proven particularly valuable for students with disabilities. Research from the University of Washington found that students with ADHD, dyslexia, or physical disabilities who used AI notes assistant applications showed a 42% improvement in information retention compared to traditional note-taking methods.
- Personalized learning support: Systems like Notion AI and Mem.ai can analyze students' notes over time, identifying knowledge gaps and suggesting supplementary resources tailored to individual learning patterns.
- Enhanced collaborative learning: Shared AI-powered notes create richer collaborative learning environments where students can contribute to and benefit from collective knowledge.
Negative Impacts
However, these technologies raise legitimate concerns:
- Potential cognitive downsides: Some educators worry that over-reliance on AI notes assistant tools may inhibit the cognitive processing that occurs during manual note-taking. A 2021 study in the Journal of Educational Psychology found that students who took handwritten notes demonstrated 27% better conceptual understanding than those who relied solely on transcription.
- Equity and access issues: The digital divide means that advanced AI note taking solutions remain inaccessible to many students from disadvantaged backgrounds, potentially widening educational disparities.
Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care and Reducing Administrative Burden
The healthcare industry has embraced AI notes technology to address several critical challenges:
Positive Impacts
- Reducing documentation burden: Physicians spend an estimated 16 minutes on electronic health record (EHR) documentation for every patient visit. AI notes assistant tools can reduce this time by up to 70%, allowing more focus on patient care.
- Improving clinical documentation accuracy: A 2022 Mayo Clinic study found that AI-assisted clinical documentation improved diagnostic coding accuracy by 32% compared to traditional methods, potentially reducing billing errors and improving care coordination.
Negative Impacts
However, implementation challenges persist:
- Privacy and security concerns: Healthcare AI notes systems must navigate strict HIPAA regulations, and any breach could have serious consequences for patient confidentiality.
- Over-reliance risks: There's concern that medical professionals might become over-dependent on AI notes technology, potentially missing critical observations that automated systems fail to capture.
Business and Professional Services: Revolutionizing Meetings and Knowledge Work
In corporate environments, AI notes assistant technology is transforming how meetings are conducted and knowledge is managed:
Positive Impacts
- Meeting efficiency: With AI note taker tools automatically documenting discussions, meetings can focus more on decision-making than record-keeping. One study by Otter.ai found that organizations implementing AI transcription reduced meeting times by an average of 22%.
- Knowledge retention: Companies report significantly improved institutional knowledge retention when using AI notes systems, with information remaining accessible despite employee turnover.
Negative Impacts
These benefits come with significant challenges:
- Job displacement concerns: Administrative roles focused on documentation are increasingly at risk as AI notes assistant technology improves. The World Economic Forum estimates that up to 85 million jobs globally could be displaced by automation technologies including AI by 2025.
- Skill atrophy: There's growing concern that professionals might lose critical summarization and information processing skills when over-relying on AI tools.
What Ethical Concerns Surround AI Notes Assistant Technology?
The rapid adoption of AI notes assistant systems raises several profound ethical questions that users and organizations must navigate carefully.
Privacy and Surveillance Considerations
AI note taking tools necessarily process vast amounts of potentially sensitive information. This raises several concerns:
- Ambient recording: Many AI notes applications run continuously in the background, potentially capturing conversations that participants don't intend to record.
- Data retention policies: Questions about how long transcripts are stored, who can access them, and how they might be used remain concerning. According to a 2023 survey by the Electronic Frontier Foundation, only 37% of AI note taking services provide clear information about data retention periods.
- Third-party access: Many AI notes assistant providers use collected data to improve their models, raising questions about whether human reviewers might access sensitive content.
Intellectual Property and Copyright Issues
AI note taking tools create complex intellectual property questions:
- Ownership ambiguity: When an AI notes assistant generates summaries or extracts insights from recorded content, the ownership of these derived works becomes legally ambiguous.
- Unauthorized recording: In two-party consent states, recording conversations without explicit permission from all participants is illegal, yet many users of AI notes applications overlook this requirement.
- Academic integrity concerns: Is a note assist system that rewrites lecture content creating a potential academic integrity issue for students?
Bias and Representation Problems
Like all AI systems, notes assistants can perpetuate and amplify biases:
- Speech recognition disparities: Research consistently shows that speech recognition accuracy varies significantly across accents, dialects, and demographic groups. A 2020 Stanford study found error rates nearly twice as high for African American speakers compared to white speakers across major AI transcription platforms.
- Terminology bias: AI notes systems may misrepresent or incorrectly transcribe terminology from marginalized communities or specialized fields they haven't been adequately trained on.
- Attention bias: The way AI notes assistant technology summarizes content reflects underlying biases about what information matters most, potentially marginalizing minority perspectives.
How Can We Use AI Notes Assistant Technology Responsibly?
Given both the tremendous potential and significant concerns surrounding AI notes assistant systems, how can individuals and organizations approach these tools responsibly?
Best Practices for Individuals
As individual users of AI note taking technology, we can adopt several practices to maximize benefits while minimizing risks:
Maintain Critical Thinking
- Use AI notes as a supplement: Rather than completely outsourcing note-taking, use AI notes assistant tools to complement your own thinking and organization. Research shows that the cognitive processing involved in manual note-taking improves understanding and retention.
- Review and refine AI-generated content: Always review transcriptions and summaries for accuracy, especially for important information. Studies indicate that people who critically review AI-generated notes retain 38% more information than those who simply store them.
- Develop personal knowledge systems: Use AI notes assistant technology within your own knowledge management framework rather than becoming dependent on a single platform's organization method.
Respect Ethical Boundaries
- Always obtain consent: Before activating AI note taker tools in conversations or meetings, explicitly inform all participants and obtain their permission.
- Be transparent about AI usage: When sharing notes or insights derived from AI notes assistant systems, disclose the technology's role in their creation.
- Protect sensitive information: Consider carefully what types of conversations should not be processed through AI notes systems, especially regarding confidential or personal matters.
Organizational Guidelines and Policies
For organizations implementing AI notes assistant technology at scale, additional considerations apply:
Develop Clear Governance
- Create explicit policies: Establish clear guidelines about when and how AI note taking tools can be used within your organization, including requirements for disclosure and consent.
- Provide training: Ensure that all employees understand both the capabilities and limitations of AI notes systems to prevent over-reliance or misuse.
- Establish review procedures: For critical documentation, implement human review processes to verify the accuracy of AI-generated content.
Address Potential Disruption
For industries facing disruption from AI notes assistant technology, proactive adaptation is essential:
- Upskill affected workers: Administrative professionals can transition from transcription to higher-value roles involving analysis and insight generation from the content AI systems capture.
- Redefine job roles: Rather than eliminating positions, organizations can redefine roles to focus on the uniquely human capabilities that complement AI notes systems.
- Create new value propositions: Service providers can shift from offering basic transcription to providing expert curation, analysis, and insight generation from AI-captured content.

FAQs About AI Notes Assistant Technology
Q: Is AI notes assistant safe to use for confidential business meetings?
A: The safety of using AI notes assistant technology for confidential meetings depends on several factors. Enterprise-grade solutions like Otter for Business or Microsoft's Copilot offer enhanced security features including end-to-end encryption and robust access controls. However, no system is completely immune to security risks.
Before using any AI note taker for sensitive content, carefully review the provider's privacy policy, data storage practices, and security certifications. Many organizations implement a tiered approach, using AI notes tools for general meetings but relying on more secure methods for highly confidential discussions.
Q: How accurate are modern AI notes applications?
A: The accuracy of AI note taking tools varies significantly depending on conditions. Under optimal circumstances—clear speech, minimal background noise, standard accents—leading AI notes assistant systems achieve 90-95% transcription accuracy. However, performance degrades in challenging environments.
Factors affecting accuracy include:
- Number of speakers and overlapping speech
- Background noise levels
- Speaker accents and speech patterns
- Technical terminology or jargon
- Audio quality
For critical applications, human review remains essential to catch and correct errors that AI notes systems may make.
Q: Will AI notes assistant technology replace professional transcriptionists?
A: While AI notes technology has disrupted traditional transcription services, complete replacement of professional transcriptionists appears unlikely in the near term. Instead, we're seeing a transformation of the profession.
Professional transcriptionists increasingly work alongside AI tools, focusing on quality assurance, editing complex passages, and handling specialized content where AI accuracy lags. The most successful professionals are adapting by developing expertise in specific domains (legal, medical, technical) where specialized knowledge adds significant value beyond what AI note taking alone can provide.
Q: How can students use AI notes assistant ethically in academic settings?
A: Students can use AI notes technology ethically by:
1. Consulting institutional policies: Many universities have developed specific guidelines regarding AI tools—check these before implementation.
2. Using AI notes as a supplement: Relying exclusively on AI transcription may reduce active engagement and learning. Use these tools to enhance, not replace, your own note-taking.
3. Practicing proper citation: If sharing or submitting AI-generated notes, clearly attribute content that was automatically transcribed or summarized.
4. Avoiding recordings without permission: Never record lectures or discussions without explicit permission from instructors and participants.
Some institutions are proactively integrating AI notes assistant technology into their accessibility services, making official transcripts available to all students and eliminating potential equity issues.
Conclusion: The Future of AI Notes Assistant Technology
As we look toward the future of AI notes assistant technology, several trends appear likely to shape its continued evolution and impact.
First, we can expect increasing multimodal capabilities, with AI notes systems processing not just text and audio but also visual information, body language, and emotional cues. This will create richer, more contextually aware documentation that captures both explicit and implicit information.
Second, AI note taking tools will likely become more specialized, with domain-specific solutions optimized for particular fields like healthcare, legal, educational, and scientific applications. These specialized systems will incorporate field-specific terminology and frameworks that general-purpose tools may miss.
Third, we'll likely see deeper integration between AI notes assistant technology and other productivity and knowledge management systems, creating seamless information ecosystems where insights flow naturally between different applications and contexts.
However, as these technologies advance, the ethical questions they raise will only become more pressing. Organizations and societies must proactively develop governance frameworks that maximize the benefits of AI notes systems while protecting privacy, promoting equity, and preserving human agency.
The most successful approach will likely view AI notes assistant not as a replacement for human information processing but as a powerful complement to it—handling the mechanical aspects of information capture and organization while freeing human minds to focus on what they do best: critical thinking, creative connection-making, and contextual understanding.
By approaching these powerful tools with both enthusiasm and appropriate caution, we can harness the tremendous potential of AI notes assistant technology while navigating its limitations and challenges responsibly.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!








No comments yet. Be the first to comment!