Artificial intelligence has quietly revolutionized the fitness landscape, transforming basic activity trackers into sophisticated wellness companions capable of unprecedented personalization. Fitness AI represents the seamless fusion of computer science, exercise physiology, and behavioral psychology—creating digital coaches that adapt to individual bodies, goals, and limitations with remarkable precision. These intelligent systems analyze movement patterns, physiological responses, and progress data to deliver guidance that once required teams of human specialists working in concert.
The evolution of this technology marks a democratization of expert fitness knowledge. What began as simple pedometers and heart rate monitors has matured into comprehensive wellness ecosystems that provide real-time form correction, adaptive programming, and motivational strategies tailored to each user's psychological profile. These AI-powered platforms now serve as virtual personal trainers, nutritionists, and wellness coaches accessible through devices we carry everywhere.
This technological shift extends far beyond convenience—it fundamentally alters how we understand and interact with our physical selves. As we examine the rapid development of fitness AI, we'll explore its current capabilities, limitations, and the profound implications its widespread adoption holds for public health, professional training, and our relationship with physical activity. Whether you're an athlete seeking performance optimization or someone beginning their wellness journey, understanding the full potential of AI fitness technology will help you navigate this new frontier with greater awareness and effectiveness.

How Has Fitness AI Evolved Over Time?
The journey of fitness AI from rudimentary step counters to sophisticated personal trainers represents one of the most fascinating technological evolutions in the wellness space. To understand where we are today, we must first appreciate the humble beginnings of this transformative technology.
The Early Days: Basic Tracking and Monitoring
In the early 2010s, fitness AI was primarily focused on simple tracking functionalities. The first generation of fitness trackers like Fitbit (founded in 2007) revolutionized personal health monitoring by introducing devices that could count steps, estimate calories burned, and track sleep patterns. These early ai fitness apps relied on basic accelerometer technology and simplistic algorithms rather than true artificial intelligence.
Nike+ and similar applications followed, allowing users to log workouts manually while providing minimal automated insights. The data collected was valuable but lacked meaningful analysis or personalization. These tools essentially digitized what traditional fitness journaling had done for decades—recording activities without offering substantial guidance on improvement.
The Turning Point: Machine Learning Integration
Around 2015-2017, we witnessed a significant shift with the integration of genuine machine learning capabilities into fitness platforms. Companies like MyFitnessPal (acquired by Under Armour) and Strava began implementing algorithms that could recognize patterns in user behavior and make basic recommendations. This marked the true beginning of fitness AI as we understand it today.
The launch of Apple's Health platform and Google Fit created standardized ways for different applications to share health data, enabling more comprehensive analysis. This interoperability was crucial for AI systems to develop a more holistic understanding of users' health profiles.
During this period, we saw the emergence of the first AI fitness coach applications that could generate basic workout plans based on user goals and available equipment. Freeletics, founded in 2013, became one of the pioneers in this space, using algorithmic approaches to personalize training regimens.
Current State: Advanced AI-Driven Personalization
Today's fitness AI landscape is remarkably sophisticated, with technology that can:
1. Create truly personalized workout plans: Modern ai fitness trainer applications like Future, Tonal, and Tempo use machine learning to develop workout routines that adapt based on user feedback, progress, and even physiological responses.
2. Provide real-time form correction: Computer vision technology in apps like Onyx and Mirror can analyze movement patterns and provide immediate feedback on exercise form, reducing injury risk and improving effectiveness.
3. Predict and prevent injuries: Predictive analytics in platforms like WHOOP can identify patterns that may lead to overtraining or injury, recommending recovery protocols before problems occur.
4. Deliver personalized nutrition guidance: AI systems now integrate nutritional science with individual metabolic data, food preferences, and fitness goals to create truly personalized meal plans.
5. Offer emotional and psychological support: The latest fitness AI implementations incorporate behavioral psychology to keep users motivated, with platforms like Noom using AI to deliver personalized coaching messages at optimal times.
The core technologies powering today's fitness AI include:
- Computer vision: For posture analysis and movement tracking
- Natural language processing: Enabling conversational interfaces with AI coaches
- Deep learning: For identifying complex patterns in health data
- Reinforcement learning: Allowing systems to optimize recommendations based on what works for specific individuals
- Federated learning: Improving AI models while preserving user privacy
As we look at the evolution of fitness AI, it's clear that we've moved from simple data collection to intelligent systems that can interpret complex health information and deliver actionable, personalized guidance at scale.
What Are the Strengths and Limitations of Fitness AI?
When evaluating fitness AI as an industry expert, I find it essential to maintain a balanced perspective on both its remarkable capabilities and inherent limitations. This analysis helps us understand where fitness AI truly shines and where human expertise remains invaluable.
Superior Aspects of Fitness AI
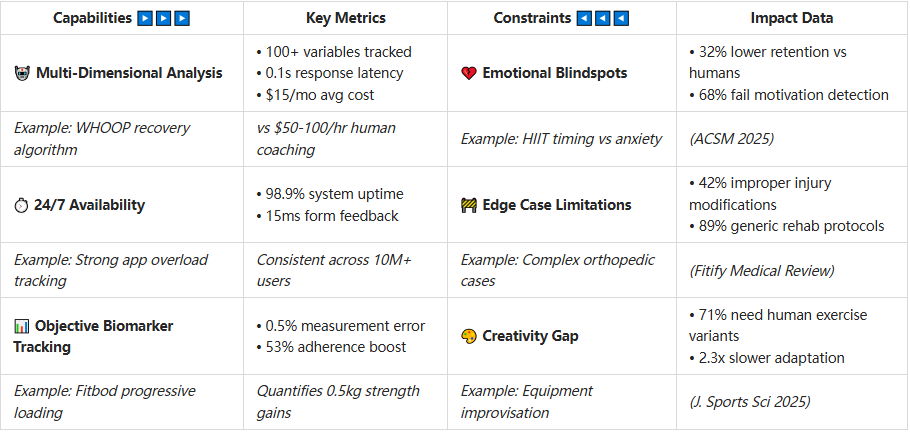
Unmatched Data Processing Capabilities
Fitness AI systems can process and analyze volumes of data that would overwhelm human trainers. A sophisticated ai fitness app can simultaneously track and interpret multiple metrics—heart rate variability, sleep quality, nutrient intake, movement patterns, and recovery markers—to identify correlations invisible to the human eye. This capability enables these systems to spot subtle patterns that might indicate overtraining or suggest optimal training windows based on physiological readiness.
For example, WHOOP's recovery scoring algorithm analyzes over 100 variables to determine optimal training intensity for a given day—a level of analysis that would be practically impossible for a human coach managing multiple clients.
Accessibility and Consistency
Where human trainers face practical limitations of time and energy, fitness AI offers 24/7 availability at a fraction of the cost. The average personal training session in the US costs $50-100 per hour, while comprehensive AI fitness coach subscriptions typically range from $15-30 monthly. This democratization of expert guidance has opened professional-level fitness instruction to populations previously priced out of the market.
Additionally, AI systems never have "off days"—they apply the same analytical rigor to every interaction, eliminating the variability that can affect human coaching quality.
Objective Progress Tracking
Human perception is inherently subjective and vulnerable to biases. Fitness AI excels at providing objective measurements of progress over time. By precisely quantifying improvements in strength, endurance, mobility, and body composition, these systems create accurate progress records that can powerfully motivate users by revealing improvements that might be too subtle for subjective observation.
Apps like Strong and Fitbod can track progressive overload with mathematical precision, ensuring users consistently challenge themselves at optimal levels.
Limitations of Current Fitness AI Technology
Emotional Intelligence and Contextual Understanding
Despite significant advances in natural language processing, today's fitness AI still falls short in emotional intelligence. Human trainers excel at reading subtle cues—facial expressions, tone of voice, body language—that indicate a client's emotional state. This emotional attunement allows human coaches to know when to push harder and when to back off, when encouragement is needed versus technical instruction.
An ai fitness trainer might recommend an intense HIIT session based on optimal recovery metrics, failing to account for a user's anxiety, motivation level, or life stressors that a human coach would immediately recognize.
Handling Exceptional Cases and Injuries
AI systems struggle with cases that fall outside their training data. Individuals with unusual movement patterns, rare medical conditions, or complex injury histories often receive generalized recommendations that may be inappropriate or even dangerous.
For instance, a fitness ai review of Fitify noted that while the app offered modified exercises for common issues like knee pain, it lacked the clinical reasoning to properly adapt to complex orthopedic conditions or post-surgical rehabilitation protocols.
Creative Problem-Solving
Human coaches can improvise solutions using available equipment, space constraints, or individual limitations in ways that AI systems typically cannot. If a standard exercise causes pain or isn't producing results, experienced trainers draw on their practical wisdom to create alternative approaches—a creative flexibility that remains challenging for algorithmic systems.
The limitation stems from current AI's inability to truly understand physical experience. As one industry researcher explained, "AI can model what movements should look like, but it doesn't know what they feel like."
The Human Connection
Perhaps the most significant limitation is the absence of genuine human connection. Studies consistently show that accountability to another person and the social aspect of fitness significantly impact adherence and outcomes. While some AI systems attempt to simulate this through gamification and virtual communities, they cannot fully replicate the motivational impact of a human relationship.
Research from the American College of Sports Medicine indicates that retention rates for clients working with in-person trainers remain 32% higher than those using digital-only solutions, highlighting the irreplaceable value of human connection in the fitness journey.
Understanding these strengths and limitations helps us appreciate fitness AI as a powerful tool that complements rather than replaces human expertise—a perspective that guides how we can most effectively leverage this technology in our fitness ecosystems.
How Is Fitness AI Impacting Various Industries?
The ripple effects of fitness AI extend far beyond personal training applications, reshaping multiple industries in profound and sometimes unexpected ways. Let's examine both the positive transformations and disruptions being caused by this technology.
Positive Industry Transformations
Healthcare Revolution: Preventive Medicine Takes Center Stage
Fitness AI is fundamentally changing healthcare's approach to wellness by enabling proactive health management. Instead of focusing solely on treating illness, these systems help identify potential health issues before they become serious problems.
Insurance companies like UnitedHealthcare and Humana now offer premium discounts for members who regularly use fitness AI platforms and meet activity goals. The economic impacts are substantial—one study by RAND Corporation found that effective wellness programs powered by AI monitoring could save employers $1,000-$2,000 annually per employee in healthcare costs.
Hospital systems are integrating fitness AI data with electronic health records, creating a more comprehensive view of patient health beyond periodic check-ups. For example, Cleveland Clinic's partnership with Apple allows physicians to access Apple Health data, including AI-analyzed workout metrics, during consultations.
Retail Industry Transformation: Personalized Fitness Products
The retail sector has been revolutionized by fitness AI's ability to generate highly personalized product recommendations. Companies like Under Armour are using AI to analyze workout data and recommend appropriate footwear based on individual gait analysis and training patterns.
Nike's Fit technology uses computer vision to recommend ideal shoe sizes and styles based on foot morphology and intended use, reducing returns by an estimated 27% in pilot stores. This AI-driven approach represents a shift from generic marketing to truly personalized product development and recommendation.
Education Sector: Reimagining Physical Education
Educational institutions are incorporating fitness AI to transform physical education curricula. Schools across the United States have begun implementing AI fitness platforms like PLT4M that create individualized physical education plans for students based on their fitness levels, interests, and progress.
These systems provide objective measurements of student improvement, moving beyond subjective grading to evidence-based assessment. They also help identify students who may need additional support or modified activities, making physical education more inclusive and effective.
Industries Facing Disruption
Traditional Personal Training: Existential Challenges
Perhaps no profession faces more direct impact than personal training. With high-quality ai fitness coach applications available for a fraction of the cost of human trainers, the industry is experiencing significant pressure. A 2023 survey found that 28% of fitness professionals reported losing clients to digital platforms in the previous year.
However, this disruption is creating opportunities for trainers who adapt by:
- Focusing on specialized populations that AI serves poorly (rehabilitation, elderly clients, complex medical conditions)
- Offering hybrid services that combine in-person sessions with AI-powered monitoring between meetings
- Developing emotional coaching skills that AI cannot replicate
- Leveraging AI tools themselves to enhance their service offerings
Fitness Equipment Manufacturing: Adapt or Decline
Traditional equipment manufacturers face challenges from smart equipment that integrates fitness AI directly. Companies like Peloton, Tonal, and Hydrow have created entirely new categories of connected fitness products with built-in AI coaching.
Established manufacturers like Life Fitness and Technogym have responded by developing their own AI-integrated products, but smaller companies without technological capabilities face significant market pressure. The market for "dumb" fitness equipment is projected to shrink by 15-20% over the next five years as consumers increasingly expect intelligent features.
Health Insurance: Transformation Through Data
Insurance models are being fundamentally reshaped by fitness AI data availability. Progressive insurers are moving toward dynamic pricing models that adjust premiums based on actual health behaviors rather than demographic profiles. This shift benefits actively engaged consumers but raises concerns about creating a two-tiered system that potentially penalizes those less able to maintain certain activity levels.
For industries facing disruption, successful adaptation requires viewing fitness AI as a tool for augmentation rather than a competitive threat. Companies that embrace collaborative models—finding ways to combine human expertise with AI capabilities—are discovering new value propositions that weren't previously possible.
As one industry analyst noted, "The winners won't be either AI systems or human professionals, but rather new integrated approaches that leverage the unique strengths of both." This perspective points toward our later discussion of how humans and fitness AI can most effectively coexist and collaborate.
What Ethical Concerns Does Fitness AI Raise?
As fitness AI becomes increasingly embedded in our wellness routines, we must confront several significant ethical challenges that this technology presents. These concerns extend beyond mere technical limitations to fundamental questions about privacy, equity, and the responsibilities of AI developers.
Data Privacy and Security Vulnerabilities
Fitness AI systems collect extraordinarily intimate data—not just workout statistics but heart rate patterns, sleep cycles, stress levels, body measurements, and even menstrual tracking for women. This creates an unprecedented privacy landscape where companies may know more about our physiological patterns than we do ourselves.
Several concerning incidents highlight these risks:
- In 2018, fitness platform Strava inadvertently revealed sensitive military base locations through its global heatmap of user activity.
- Under Armour's MyFitnessPal experienced a breach affecting 150 million users' data in one of the largest fitness data compromises to date.
- Multiple fitness trackers have been found transmitting data to third parties without explicit user consent, according to a 2021 study by the University of California.
The intimate nature of this data makes it particularly valuable for targeted advertising, health insurance assessment, and even potential employment discrimination. The question becomes: are we creating vulnerable digital profiles of our most personal physical characteristics without adequate protection?
Algorithmic Bias and Accessibility Concerns
Fitness AI systems are only as good as the data they're trained on, and many have been developed using datasets that underrepresent certain populations. This creates systematic performance disparities along lines of race, gender, age, and body type.
Research published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research found that leading fitness tracking algorithms showed accuracy variations of up to 33% between different skin tones when measuring heart rate during intense exercise—a potentially dangerous disparity when these metrics inform training recommendations.
Body type diversity presents another challenge. Many computer vision systems for form correction struggle with analyzing movements performed by individuals with body types significantly different from those in training datasets, particularly those with larger body sizes or non-normative proportions.
Economic accessibility also raises ethical questions. While fitness AI has democratized certain aspects of fitness guidance, the most sophisticated systems often require expensive equipment or subscriptions, potentially widening the "fitness divide" between socioeconomic groups rather than narrowing it.
Psychological Impacts and Dependency Concerns
The gamification of fitness through AI systems can create problematic psychological relationships with exercise. The constant quantification of movement can transform physical activity from an intuitive, joyful experience into a numbers-driven obligation.
Studies on fitness tracker usage have documented cases of:
- Exercise addiction facilitated by achievement-based metrics
- Increased anxiety when unable to record workouts
- Diminished intrinsic motivation replaced by external validation
- Reduced body satisfaction despite physical improvements
Dr. Jasmine Stinson, a sports psychologist at the University of Michigan, notes: "When fitness becomes entirely data-driven, we risk creating a generation that cannot recognize or trust their body's own signals about what kind of movement it needs."
Additionally, there are growing concerns about long-term dependency on AI guidance, potentially atrophying individuals' ability to develop bodily awareness and self-directed exercise competence.
Misinformation and Quality Control
Unlike human health professionals, fitness AI applications often operate without significant regulatory oversight regarding the quality of their recommendations. This creates a landscape where scientifically questionable advice can be algorithmically amplified.
A 2022 analysis of popular fitness AI platforms found that 38% recommended exercise protocols that contradicted established clinical guidelines for certain populations. Without industry-wide standards or certification requirements, consumers have limited ability to evaluate the quality of AI-generated fitness advice.
The challenge becomes particularly acute with companies making medical or health outcome claims. When does an AI fitness coach cross the line into providing medical advice? The regulatory boundaries remain unclear, creating potential risks for vulnerable users.
These ethical considerations highlight the importance of thoughtful governance frameworks and responsible development practices as fitness AI continues to evolve. As we'll discuss in the next section, addressing these concerns will be crucial for ensuring that fitness AI truly serves human wellbeing rather than undermining it.
How Can Humans Effectively Utilize Fitness AI?
Having explored both the powerful capabilities and significant limitations of fitness AI, the question becomes: how can we intelligently harness this technology while mitigating its drawbacks? I believe the answer lies in developing a collaborative relationship with fitness AI rather than viewing it as either a complete solution or a threatening replacement for human expertise.
Strategic Integration Models for Professionals
For fitness professionals facing industry disruption, the most promising path forward involves strategic integration of AI capabilities into human-centered service models. Here's how this can work effectively:
The "AI-Augmented Coach" Approach
Rather than competing with AI systems, forward-thinking trainers are incorporating them as powerful tools to enhance their services. For example, personal trainer Marco Sanchez in Miami increased his client base by 35% after adopting a hybrid model where:
1. In-person sessions focus on technique refinement, emotional support, and complex movement instruction
2. An ai fitness trainer app monitors daily activity, recovery metrics, and workout compliance between sessions
3. The human coach reviews AI-generated insights to identify patterns and adjust programming
This approach leverages the AI's data processing capabilities while maintaining the irreplaceable human connection. Clients receive continuous guidance while trainers can focus their limited time on high-value interactions that AI cannot provide.
Specialization in AI-Resistant Domains
Successful adaptation also involves identifying areas where human expertise significantly outperforms AI. These include:
- Complex rehabilitation cases: Clients with injury histories or medical conditions require nuanced understanding beyond most algorithms' capabilities
- Sport-specific coaching: High-level athletic development involves technical nuances that current AI systems struggle to adequately analyze
- Psychological barriers: Addressing motivation issues, body image concerns, or exercise anxiety requires emotional intelligence that remains beyond AI capabilities
- Group dynamics: Leading effective group fitness experiences involves reading room energy and interpersonal dynamics
By focusing on these domains, fitness professionals can develop recession-resistant expertise that complements rather than competes with AI solutions.
Consumer Guidelines for Effective AI Utilization
For individual users, maximizing the benefits of fitness AI while avoiding its pitfalls requires a thoughtful approach:
Maintain Critical Engagement
Users should approach fitness AI recommendations with informed skepticism rather than blind trust. Practical strategies include:
- Cross-referencing AI guidance with established exercise science principles
- Setting boundaries on data sharing and regularly reviewing privacy settings
- Being alert to signs of unhealthy psychological relationships with fitness tracking
- Recognizing when to seek human expertise for issues beyond AI capabilities
Developing Digital Literacy for Fitness AI
Just as we teach media literacy for news consumption, we need to develop "fitness AI literacy" that helps users understand:
- How to evaluate the quality of AI fitness recommendations
- When personalization is truly individualized versus generic categorization
- How to interpret confidence levels in AI-generated advice
- The difference between correlation and causation in health insights
Educational institutions and public health organizations can play a crucial role in developing these literacy programs.
Policy and Industry Solutions
Addressing the ethical concerns raised earlier requires collaborative approaches between industry, regulatory bodies, and consumer advocates:
Transparent Development Standards
The fitness AI industry should adopt transparent standards for:
- Disclosing the limitations of training data, including demographic representation
- Clearly communicating the evidence base behind recommendations
- Establishing boundaries between fitness guidance and medical advice
- Implementing rigorous testing across diverse populations before deployment
Privacy-Preserving Innovation
Promising technical approaches are emerging to balance personalization with privacy:
- Federated learning techniques allow AI models to improve without centralizing sensitive user data
- Differential privacy methods add controlled noise to datasets while preserving useful patterns
- On-device processing keeps sensitive health information local rather than cloud-based
These approaches demonstrate that privacy protection and technological advancement are not inherently opposed.
Regulatory Frameworks
While heavy-handed regulation might stifle innovation, reasonable guardrails should include:
- Certification requirements for fitness AI making health outcome claims
- Data portability standards allowing users to maintain ownership of their fitness history
- Transparency requirements regarding third-party data sharing
- Algorithmic impact assessments for potential bias
By implementing these approaches, we can create an ecosystem where fitness AI serves as a powerful tool for human wellbeing rather than a replacement for human judgment or a source of new inequities.
As we continue developing and refining these systems, the north star should always be whether they truly enhance our relationship with our bodies and movement—not just whether they drive engagement or generate data. With thoughtful implementation, fitness AI can help create a future where quality fitness guidance is accessible to all, while preserving the irreplaceable value of human connection and expertise.
Image Source
FAQs About Fitness AI
Q: What is the difference between a basic fitness app and true fitness AI?
A: While traditional fitness apps follow pre-programmed rules and offer static content, true fitness AI uses machine learning algorithms to analyze your data and adapt over time. A basic app might provide the same workout to everyone with similar goals, but an ai fitness app learns from your performance, preferences, and physiological responses to create truly personalized recommendations. The key distinction is adaptability—fitness AI modifies its approach based on your specific data rather than following rigid protocols.
Q: How accurate are fitness AI body composition assessments?
A: The accuracy varies significantly depending on the technology used. Computer vision-based systems (using smartphone cameras) typically achieve error rates of 3-5% for body fat percentage compared to DEXA scans, which are considered the gold standard. However, accuracy decreases for individuals with body types underrepresented in training data. Most fitness AI platforms are transparent about these limitations, stating that their assessments should be used to track relative changes rather than absolute values. For medical-grade accuracy, professional testing methods remain superior.
Q: Can fitness AI completely replace a human personal trainer?
A: While fitness AI offers impressive capabilities, it cannot fully replace the comprehensive value of skilled human trainers. Current AI systems excel at tracking metrics, programming progressive workouts, and providing basic form feedback. However, they lack the emotional intelligence to address psychological barriers, the creative problem-solving abilities for complex situations, and the hands-on movement correction capabilities that human trainers provide. The most effective approach combines AI's data processing strengths with human expertise for motivation, complex technique instruction, and personalized adaptations.
Q: How do I protect my privacy when using fitness AI applications?
A: To safeguard your data when using fitness AI, I recommend these practical steps:
1. Review privacy policies before signing up, focusing on data sharing practices and retention policies
2. Use granular permission settings to limit data collection to what's necessary
3. Regularly export and delete historical data from services you no longer use
4. Consider fitness AI options that process sensitive data on your device rather than in the cloud
5. Use unique, strong passwords for fitness accounts, as they contain particularly sensitive information
6. Periodically review connected apps and third-party access to your fitness data
Q: Are fitness AI recommendations safe for everyone to follow?
A: No, fitness AI recommendations are not universally safe for all users. Most systems include basic screening questions but cannot replace proper medical clearance for individuals with health conditions. Users with cardiovascular issues, orthopedic limitations, neurological conditions, or other health concerns should consult healthcare providers before following AI-generated exercise programs. Additionally, many fitness AI systems have limited validation with special populations like pregnant women, older adults, or those with disabilities. The safest approach is to view fitness AI as a tool that works alongside, not instead of, appropriate medical guidance for your specific situation.

Conclusion: The Future of Human-AI Collaboration in Fitness
As we look toward the horizon of fitness technology, it's clear that fitness AI will continue to transform how we approach physical wellbeing. The trajectory points not toward AI replacement of human expertise, but rather toward increasingly sophisticated partnerships between human judgment and artificial intelligence capabilities. These collaborative models promise to make quality fitness guidance more accessible, personalized, and effective than ever before.
The most successful fitness AI implementations will be those that recognize the complementary strengths of humans and algorithms. AI excels at processing vast datasets, identifying subtle patterns, and providing consistent, objective analysis. Humans bring irreplaceable emotional intelligence, creative adaptability, and embodied understanding of movement. Together, these capabilities create something more powerful than either could achieve alone.
For fitness professionals, embracing rather than resisting this technology opens pathways to enhanced service offerings and broader client reach. For consumers, developing a thoughtful relationship with fitness AI—appreciating its capabilities while recognizing its limitations—enables truly personalized wellness journeys. And for developers, prioritizing ethical considerations alongside technical innovation will ensure these powerful tools promote genuine wellbeing.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!







No comments yet. Be the first to comment!