The field of digital mapping is undergoing a seismic shift, and AI mapper technology is becoming the driving force behind a new era of smart mapping solutions. As AI merges with GIS, traditional mapping methods are being revolutionized by machine learning algorithms that can process massive amounts of spatial data with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
AI mapper technology means much more than automation—it represents a fundamental shift in the way we approach spatial data visualization, urban planning, autonomous vehicle navigation, and countless other applications that rely on precise geographic information. This technological shift not only changes the tools we use, it also redefines the nature of mapping work and opens up new possibilities for industries that rely on location-based intelligence.

How Did AI Map Generator Technology Evolve from Traditional Cartography?
The journey of AI Map Generator development represents one of the most remarkable technological progressions in modern digital infrastructure. To understand the magnitude of this transformation, we must first examine where traditional cartography began and trace the pivotal innovations that led to today's sophisticated AI-powered mapping solutions.
The Foundation: Traditional Cartography and Early Digital Mapping
Traditional cartography relied heavily on manual processes that required extensive human expertise and time-intensive methodologies. Cartographers would spend months manually digitizing physical maps, relying on ground surveys, aerial photography, and painstaking hand-drawn representations to create geographic visualizations. The process was not only labor-intensive but also prone to human error and limited in scope and scalability.
The first major breakthrough came with the introduction of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in the 1960s and 1970s, which allowed for digital storage and basic manipulation of geographic data. These early systems represented a significant advancement from purely manual methods, but they still required substantial human input and were limited by computational constraints.
This transformation exemplifies how AI Map Generator technology has moved from static, manually-updated maps to dynamic, real-time systems. HERE's UniMap technology represents a watershed moment in automated mapping, using AI to create what they call "live maps"—constantly evolving representations of the world that reflect real-time changes.
Google revolutionized the field with Google Maps and its Earth Engine, which employs machine learning models to automatically classify vegetation, urban development, and water bodies with 95% accuracy. The integration of Street View imagery with Neural Radiance Fields demonstrates how AI can transform photographic data into comprehensive 3D representations of places.
Ecopia AI has taken a different approach, focusing on converting high-resolution geospatial imagery into comprehensive vector maps using AI-based mapping systems. Their technology extracts high-definition vector data with the accuracy of trained GIS professionals while providing unprecedented speed and scalability.
Technological Breakthroughs That Defined the Modern Era
The introduction of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in the 2010s marked a critical turning point for AI Map Generator technology. These deep learning models enabled automated feature recognition capabilities that could identify geographic elements with remarkable precision. Research shows that CNN-based systems can now classify terrain types with precision rates exceeding 96%, compared to traditional automated methods achieving only 78% accuracy.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) further expanded the possibilities, enabling AI systems to generate realistic landscapes and fill in missing geographical details. These networks have proven particularly valuable in creating synthetic training data and enhancing map completeness in areas where traditional data collection is challenging.
The integration of Natural Language Processing (NLP) has transformed how users interact with mapping systems. Modern AI Map Generator tools can now interpret complex natural language queries, such as "places with a vintage vibe in SF," and automatically analyze rich information about nearby businesses to provide contextually relevant suggestions.
Current State-of-the-Art Technologies
Today's AI Map Generator systems employ sophisticated technological stacks that combine multiple AI approaches. Semantic mapping technologies enable consistent reference architectures across different mapping systems, ensuring interoperability and standardization.
Real-time processing capabilities represent perhaps the most impressive advancement. HERE Technologies, for example, can process "tens of millions of kilometers of vehicle sensor data per hour" to maintain current map representations. This capability enables what industry leaders call "live maps"—dynamic representations that update automatically as the physical world changes.
Machine learning-based automation has reached the point where tools like MapScale can achieve 100,000 times faster map production compared to traditional manual methods. This dramatic improvement in efficiency has made it possible to maintain up-to-date mapping data across global scales that would be impossible to achieve through human effort alone.
The current generation of AI Map Generator technology also incorporates predictive capabilities, using historical data and pattern recognition to anticipate geographical changes before they occur. This predictive functionality is particularly valuable for urban planning, infrastructure development, and autonomous vehicle navigation systems.
What Are the Key Advantages and Limitations of AI Map Generator Technology?
Understanding the capabilities and constraints of AI Map Generator technology is crucial for making informed decisions about implementation and application. The technology offers transformative advantages while simultaneously presenting significant challenges that require careful consideration and strategic mitigation.
Unprecedented Speed and Efficiency Advantages
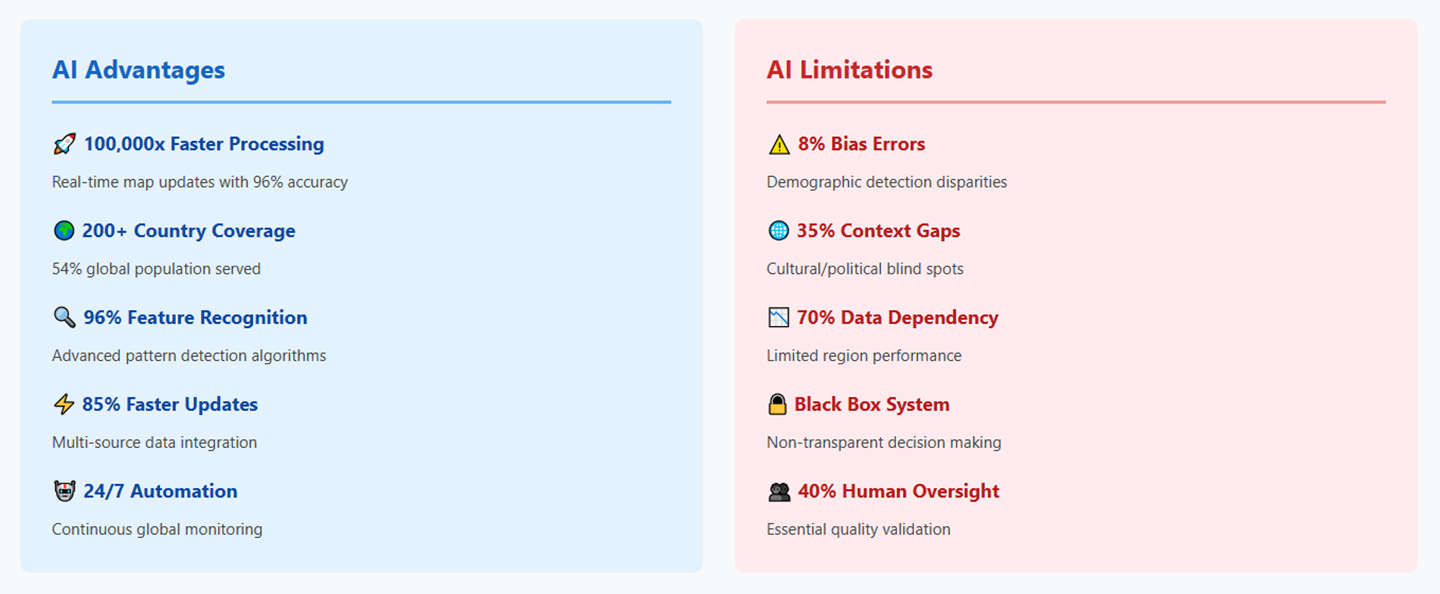
The most striking advantage of AI Map Generator technology lies in its processing speed capabilities. Traditional mapping processes that once required weeks or months of manual labor can now be completed in minutes. Research demonstrates that AI systems can process "tens of millions of kilometers of vehicle sensor data per hour," enabling real-time map updates that were previously impossible.
For organizations managing large-scale mapping operations, this represents not just an improvement but a complete paradigm shift in operational capabilities.
The efficiency gains extend beyond raw processing speed to include automated error detection and correction capabilities. AI systems can identify inconsistencies, detect missing information, and flag potential inaccuracies faster and more consistently than human reviewers. This automated quality assurance significantly reduces the time required for map validation and maintenance.
Superior Accuracy Through Advanced Algorithms
Modern AI Map Generator systems achieve remarkable accuracy levels that often exceed human performance. Convolutional neural networks can classify terrain types with precision rates exceeding 96%, compared to traditional automated methods that typically achieve only 78% accuracy. This improvement in accuracy is particularly significant for applications requiring precise geographical information, such as autonomous vehicle navigation and emergency response planning.
The accuracy advantages stem from AI's ability to process and learn from vast training datasets. Unlike human cartographers who may be limited by individual experience and regional knowledge, AI systems can incorporate learnings from millions of data points across diverse geographical contexts. This comprehensive learning approach enables more consistent and reliable map generation across different environments and conditions.
Furthermore, AI systems excel at pattern recognition tasks that may challenge human perception. They can identify subtle geographical features, detect changes in satellite imagery, and recognize complex spatial relationships that might be overlooked in manual analysis. This capability is particularly valuable for monitoring environmental changes, urban development, and infrastructure modifications.
Scalability and Global Coverage Capabilities
AI Map Generator technology offers unparalleled scalability advantages that enable global mapping initiatives previously considered impractical. Companies like HERE Technologies now provide mapping services across over 200 countries and territories, covering approximately 54% of the world's population. This global reach is made possible by AI's ability to process diverse data sources and adapt to different geographical contexts automatically.
The scalability extends to data integration capabilities. Modern AI systems can simultaneously process satellite imagery, vehicle sensor data, IoT device information, and crowdsourced updates to maintain comprehensive and current map databases. This multi-source integration approach ensures that maps remain accurate and relevant across rapidly changing environments.
Critical Accuracy and Context Limitations
Despite impressive technical capabilities, AI Map Generator systems face significant limitations in accuracy and contextual understanding. Research reveals that AI-generated maps often contain inaccuracies, misleading information, and unexpected features that can compromise their reliability. These limitations are particularly pronounced when dealing with complex geopolitical situations, cultural contexts, or regions with limited training data.
The challenge of contextual understanding represents a fundamental limitation of current AI systems. While AI excels at pattern recognition and data processing, it struggles with nuanced decision-making that requires cultural, historical, or political awareness. For example, AI systems may incorrectly identify or misrepresent culturally sensitive locations, historical boundaries, or politically disputed territories.
Bias and representation issues constitute another critical limitation. AI systems trained on biased datasets may perpetuate or amplify existing inequalities in map representation. Research shows that biases in mapping data can lead to inaccurate identification of underserved communities, potentially impacting emergency response efforts and resource allocation.
Technical and Operational Constraints
The "black box" nature of many AI systems presents significant challenges for AI Map Generator applications where transparency and explainability are crucial. Users may struggle to understand how AI systems reach specific mapping decisions, making it difficult to validate results or identify potential errors. This opacity can be particularly problematic in critical applications such as emergency response or infrastructure planning.
Data dependency represents another fundamental limitation. AI Map Generator systems require vast amounts of high-quality training data to function effectively, and their performance is directly tied to the quality and representativeness of this data. In regions with limited data availability or poor data quality, AI systems may produce unreliable results.
The inability to consistently reproduce results poses challenges for applications requiring high reliability. Unlike traditional mapping methods that follow standardized procedures, AI-generated maps may vary between different training runs or when using slightly different input parameters.
The Need for Human Oversight and Intervention
Current AI Map Generator technology still requires significant human oversight for optimal performance. Human intervention is particularly critical for quality validation, error correction, and contextual interpretation that AI systems cannot perform reliably. This requirement for human oversight somewhat limits the promised efficiency gains and raises questions about the optimal balance between automation and human expertise.
The limitations highlight the importance of implementing AI mapping technology as a tool to augment rather than replace human cartographic expertise. Successful implementations typically involve hybrid approaches that leverage AI efficiency while maintaining human oversight for critical decision-making and quality assurance.
How Is AI Map Generator Technology Impacting Different Industries?
The transformative power of AI Map Generator technology extends across multiple industries, creating both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges that organizations must navigate carefully. Understanding these impacts is essential for stakeholders seeking to harness the technology's potential while mitigating associated risks.
Revolutionary Transformation in the Automotive Industry
The automotive sector represents perhaps the most dramatically impacted industry, with AI Map Generator technology serving as the backbone for next-generation vehicle systems. Currently, 70% of the global automotive market relies on AI-powered mapping services, with over 222 million vehicles shipped with advanced location services. This widespread adoption underscores the critical role that intelligent mapping plays in modern automotive innovation.
Autonomous driving systems depend entirely on AI-generated high-definition maps that provide real-time environmental awareness beyond the vehicle's sensor range. These systems require precise lane-level mapping data, traffic sign recognition, and dynamic hazard detection capabilities that traditional static maps simply cannot provide. The integration of AI mapping enables vehicles to navigate complex scenarios, from construction zones to weather-related disruptions, with human-like adaptability.
Electric vehicle (EV) optimization represents another significant application area where AI mapping delivers tangible value. AI systems can predict optimal charging routes, estimate battery consumption based on terrain and traffic conditions, and provide accurate range calculations that prevent "charge anxiety" among EV drivers. This capability is particularly crucial as the automotive industry transitions toward electrification.
The development of software-defined vehicles (SDVs) has created new opportunities for AI mapping integration. Modern vehicles can receive real-time map updates via cloud-based software, enabling continuous improvement and adaptation to changing road conditions. This dynamic update capability transforms vehicles from static platforms into continuously evolving systems that become more capable over time.
Logistics and Supply Chain Optimization
The logistics industry has experienced remarkable efficiency gains through AI Map Generator implementation, with some organizations reporting annual savings of nearly $1 million per warehouse facility through automated freight processing. These improvements stem from AI's ability to optimize complex logistical operations in real-time while adapting to dynamic conditions.
Route optimization represents a core application where AI mapping delivers immediate value. By analyzing historical data, current traffic conditions, and predictive models, AI systems can generate transportation plans that minimize costs and delivery times while maximizing efficiency. This optimization capability becomes particularly valuable for organizations managing large-scale distribution networks with multiple variables and constraints.
Demand forecasting accuracy has improved significantly, with AI systems achieving up to 95% accuracy in predicting future demand patterns. This enhanced forecasting capability enables logistics companies to optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. The integration of AI mapping with demand forecasting allows for location-specific predictions that account for regional variations and local factors.
Warehouse and inventory management has been transformed through AI's ability to predict demand patterns, optimize reorder points, and identify efficient safety stock levels. These improvements lead to reduced picking times, better space utilization, and overall warehouse efficiency improvements that can significantly impact operational costs.
Urban Planning and Smart City Development
Urban planning has witnessed perhaps the most intellectually significant transformation, with AI systems now capable of outperforming human urban planners in creating projects under the "15-minute city" concept. This capability represents a fundamental shift in how cities are designed and developed.
Rapid urban prototyping enables planning teams to generate and compare multiple urban scenarios in real-time, facilitating more informed decision-making processes. Digital Blue Foam's Urban Insights tool exemplifies this capability, allowing project teams to generate urban scenarios and compare location quality using data from various open sources.
Environmental monitoring and sustainability planning benefit significantly from AI mapping capabilities. AI systems can track changes in natural environments, monitor wildlife habitats, and assess climate change impacts with unprecedented precision and scale. This monitoring capability enables proactive environmental management and sustainable development planning.
Automated compliance checking with zoning regulations and building codes streamlines the approval process while ensuring regulatory adherence. AI systems can automatically verify that proposed developments meet local requirements, reducing approval times and minimizing compliance errors.
Gaming and Entertainment Industry Innovation
The gaming and entertainment industries have embraced AI Map Generator technology to create more immersive and dynamic content experiences. Procedural content generation has revolutionized game development by automating the creation of maps, levels, and entire game worlds.
Companies like Cybever demonstrate the practical impact of this technology, enabling developers to create complex 3D worlds in minutes rather than weeks. Their AI tools can automatically place assets into maps while considering historical, cultural, and logical contexts, ensuring realistic and engaging game environments.
Fantasy and tabletop gaming applications have also benefited significantly from AI mapping technology. Tools like Inkarnate and other AI-powered generators enable game masters and players to create detailed fantasy maps with professional-quality results, democratizing content creation for gaming communities.
The entertainment industry's adoption extends beyond gaming to film and television production, where AI-generated backgrounds and environments reduce production costs while expanding creative possibilities. This application demonstrates the cross-industry versatility of AI mapping technology.
Addressing Industry Displacement and Adaptation Challenges
While AI Map Generator technology creates significant opportunities, it also poses challenges for traditional industry roles. Traditional cartographers and GIS professionals face potential displacement as automated systems handle tasks previously requiring specialized human expertise. However, this displacement is creating new opportunities for professionals who can adapt to work collaboratively with AI systems.
The transformation requires reskilling and adaptation strategies that help industry professionals transition from manual mapping tasks to AI system management, quality assurance, and strategic planning roles. Organizations implementing AI mapping technology must invest in training programs that enable their workforce to evolve alongside technological capabilities.
Dependency risks emerge when organizations become overly reliant on automated systems without maintaining human expertise for oversight and contingency planning. Successful implementations require balanced approaches that leverage AI efficiency while preserving human capabilities for critical decision-making and system validation.
The industry impacts of AI Map Generator technology demonstrate both the transformative potential and the implementation challenges that organizations must navigate. Success requires strategic planning, workforce development, and careful consideration of the balance between automation and human expertise.
What Ethical Challenges Does AI Map Generator Technology Present?
The rapid advancement of AI Map Generator technology brings forth complex ethical challenges that demand immediate attention and thoughtful resolution. These challenges span multiple domains, from fundamental questions about intellectual property rights to concerns about privacy, bias, and the potential for misinformation. Understanding these ethical implications is crucial for responsible development and deployment of AI mapping systems.
Copyright Ownership and Intellectual Property Dilemmas
The question of who owns AI generated maps presents one of the most pressing ethical and legal challenges in the field. Under current U.S. copyright law, works created entirely by generative AI fall into the public domain, as legal frameworks typically require human authorship for copyright protection. This creates a complex landscape where the value and ownership of AI-generated content remain unclear.
The U.S. Copyright Office has clarified that "AI-generated content that is more than de minimis" should be explicitly identified and excluded from copyright registration. However, human additions to AI-generated works, such as prompt instructions or subsequent modifications, may be eligible for copyright protection. This creates a nuanced ownership model where the human contribution determines the extent of intellectual property rights.
Training data copyright concerns add another layer of complexity to the ownership question. AI systems are typically trained on vast datasets that may include copyrighted materials scraped from the internet without explicit permission. While the fair use doctrine may protect some AI applications, the legal landscape remains unsettled. The challenge is particularly acute when AI systems reproduce elements that closely resemble copyrighted source materials.
For organizations implementing AI Map Generator technology, these ownership ambiguities create significant business and legal risks. Companies must navigate uncertain intellectual property landscapes while making substantial investments in AI-powered mapping capabilities. The lack of clear legal precedents makes it difficult to assess potential liability or establish robust business models around AI-generated mapping content.
Privacy and Surveillance Implications
AI Map Generator systems often require vast amounts of location-based data to function effectively, raising serious privacy concerns about data collection, storage, and usage. Modern mapping systems collect data from multiple sources, including vehicle sensors, mobile devices, satellite imagery, and IoT devices, creating comprehensive profiles of individual and collective movement patterns.
Government surveillance capabilities enabled by AI mapping technology pose additional concerns about civil liberties and democratic governance. The same technologies that enable efficient traffic management and emergency response can also facilitate mass surveillance and location tracking. The potential for misuse of these capabilities requires careful consideration of governance frameworks and oversight mechanisms.
Data sharing with third parties compounds privacy risks, as mapping companies often partner with multiple organizations to enhance their services. The complex web of data sharing agreements and partnerships makes it difficult for individuals to understand how their location data is being used and by whom. This opacity undermines informed consent and individual autonomy over personal information.
Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination Risks
AI Map Generator systems can perpetuate and amplify existing biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes that affect vulnerable communities. Research demonstrates that biases in mapping data can lead to inaccurate identification of underserved areas, potentially impacting emergency response efforts and resource allocation.
Emergency response allocation represents a critical area where mapping bias can have life-or-death consequences. If AI systems systematically underrepresent certain communities or misclassify residential areas, emergency services may be misdirected or delayed when responding to crises.
Resource distribution inequalities can be exacerbated when AI mapping systems reflect historical biases in data collection and representation. Areas with limited historical data coverage or systematic underinvestment may continue to receive inadequate attention in AI-generated maps, perpetuating existing inequalities.
Misinformation and Trust Erosion
The potential for AI generated maps to contain inaccuracies or misleading information poses significant risks to public trust and decision-making processes. Unlike traditional maps that undergo rigorous human review processes, AI-generated maps may contain subtle errors that are difficult to detect but can have serious consequences.
Deepfake geography represents an emerging threat where AI-generated maps could be intentionally created to mislead or manipulate public opinion. The same technologies that enable rapid map creation could be used to generate false geographical information for political, economic, or military purposes. The difficulty in detecting such manipulations makes this a particularly concerning development.
Decision-making based on incorrect data can have far-reaching consequences when AI-generated maps are used for critical applications such as urban planning, disaster response, or infrastructure development. The authority and apparent precision of AI-generated maps may lead users to trust inaccurate information, potentially resulting in poor decisions with significant real-world impacts.
Verification and trustworthiness challenges arise from the "black box" nature of many AI systems, making it difficult for users to understand how mapping decisions are made or to validate the accuracy of generated content. This opacity undermines the ability to establish trust and accountability in AI mapping systems.
Transparency and Explainability Deficits
The complexity of modern AI Map Generator systems often makes it difficult to understand how specific mapping decisions are reached, creating challenges for accountability and error correction. This lack of transparency is particularly problematic in applications where understanding the decision-making process is essential for validation and trust.
Algorithmic opacity prevents users from understanding why certain geographical features are included or excluded from maps, how boundaries are determined, or how conflicting data sources are resolved. This opacity makes it difficult to identify potential errors or biases in the mapping process.
Accountability challenges emerge when AI systems make mapping decisions that have negative consequences but the decision-making process cannot be understood or explained. Without clear accountability mechanisms, it becomes difficult to address errors, compensate for damages, or prevent similar problems in the future.
The ethical challenges presented by AI Map Generator technology require proactive attention from developers, regulators, and users. Addressing these challenges is essential for ensuring that the benefits of AI mapping technology can be realized while minimizing potential harms to individuals and society.
How Can We Effectively Collaborate with AI Map Generator Technology?
Successfully integrating AI Map Generator technology into professional workflows requires thoughtful collaboration strategies that leverage artificial intelligence capabilities while maintaining human expertise and oversight. The most effective approaches recognize AI as a powerful tool that augments human capabilities rather than replacing human judgment and creativity.
Addressing Industry Transformation Through Strategic Collaboration
The automotive industry has pioneered effective collaboration models that demonstrate how human expertise can work synergistically with AI mapping systems. Rather than viewing AI as a replacement for traditional navigation systems, leading automotive companies have implemented tiered review systems where AI handles routine processing while human experts oversee complex scenarios and exception handling.
Fleet operations and logistics companies benefit from implementing hybrid collaboration models where AI systems handle route optimization and predictive analytics while human dispatchers maintain oversight of unusual situations and customer relations. This approach enables organizations to achieve the efficiency gains of AI while preserving the flexibility and judgment that human operators provide.
For urban planning and architecture professionals, effective collaboration involves using AI mapping tools for rapid prototyping and scenario analysis while maintaining human control over final design decisions and community engagement processes. The most successful implementations treat AI as a powerful analytical tool that can explore design possibilities faster than traditional methods, while human planners provide the creative vision and contextual understanding that AI cannot replicate.
Implementing Human-in-the-Loop Quality Assurance Systems
Validation and verification protocols represent essential components of effective AI mapping collaboration. Organizations should implement systematic review processes where human experts validate AI-generated maps against ground truth data, identify potential errors or biases, and provide feedback to improve system performance. These protocols should be tailored to specific use cases and risk levels, with more critical applications receiving more intensive human oversight.
Continuous monitoring systems enable organizations to maintain quality while scaling AI mapping operations. By implementing automated anomaly detection systems combined with human review of flagged content, organizations can achieve both efficiency and reliability. This approach allows human experts to focus their attention on the most challenging or high-risk mapping decisions while allowing AI to handle routine tasks.
Error correction and feedback loops create opportunities for continuous improvement in AI mapping systems. When human reviewers identify errors or areas for improvement, this feedback should be systematically incorporated into training processes to enhance future performance. This collaborative approach treats errors as learning opportunities rather than failures.
Mitigating Ethical Risks Through Responsible Implementation
Bias detection and mitigation strategies require ongoing collaboration between technical teams and domain experts who understand the potential impacts of mapping biases. Organizations should implement regular audits of AI-generated maps to identify potential disparities in representation or accuracy across different communities or geographic regions. These audits should involve diverse stakeholders who can provide insights into potential blind spots or unintended consequences.
Privacy protection measures must be built into collaborative workflows from the beginning rather than added as an afterthought. This includes implementing data minimization principles, obtaining appropriate consent for data collection, and establishing clear governance frameworks for data sharing and retention. Human oversight is essential for ensuring that privacy protection measures are effectively implemented and maintained.
Transparency and explainability initiatives help build trust and accountability in AI mapping systems. Organizations should invest in developing interpretable AI models and clear documentation of decision-making processes. When full explainability is not possible, organizations should clearly communicate the limitations and uncertainties associated with AI-generated maps.
Building Workforce Capabilities for AI Collaboration
Training and reskilling programs are essential for helping traditional cartography and GIS professionals adapt to work effectively with AI mapping systems. These programs should focus on developing skills in AI system management, quality assurance, and strategic analysis rather than attempting to preserve outdated manual processes. Successful programs help professionals transition from routine mapping tasks to higher-value activities that leverage their expertise and judgment.
Cross-disciplinary collaboration skills become increasingly important as AI mapping projects often involve teams with diverse technical and domain expertise. Professionals need to develop communication skills that enable effective collaboration between AI specialists, domain experts, and end users. This includes the ability to translate business requirements into technical specifications and communicate AI capabilities and limitations to non-technical stakeholders.
Ethical awareness and decision-making training helps teams navigate the complex ethical challenges associated with AI mapping technology. This training should cover topics such as bias detection, privacy protection, and responsible AI deployment practices. Teams should develop frameworks for ethical decision-making that can be applied consistently across different projects and use cases.
Developing Governance Frameworks for Responsible AI Mapping
Regulatory compliance strategies must account for the evolving legal landscape around AI and mapping technology. Organizations should stay informed about relevant regulations and work proactively to ensure compliance with data protection, intellectual property, and consumer protection laws. This includes developing clear policies for AI training data usage and establishing procedures for handling potential copyright or privacy violations.
Industry standards and best practices provide frameworks for responsible AI mapping implementation. Organizations should actively participate in industry working groups and standards development processes to help establish common approaches to quality, ethics, and interoperability. Following established standards helps ensure compatibility with other systems and demonstrates commitment to responsible technology deployment.
Stakeholder engagement processes ensure that AI mapping deployments consider the needs and concerns of affected communities. This is particularly important for applications that impact public services, urban planning, or community development. Meaningful stakeholder engagement helps identify potential negative impacts and develops mitigation strategies that protect vulnerable populations.
Technology Integration and Future-Proofing Strategies
Scalable architecture design enables organizations to adapt their AI mapping capabilities as technology evolves. This includes implementing modular systems that can incorporate new AI techniques and data sources as they become available. Organizations should avoid vendor lock-in and design systems that can integrate with multiple AI platforms and data providers.
Continuous learning and improvement processes help organizations stay current with rapidly evolving AI mapping technology. This includes establishing partnerships with research institutions, participating in technology conferences, and maintaining connections with AI development communities. Organizations should allocate resources for experimentation with new techniques and technologies.
Performance monitoring and optimization ensures that AI mapping systems continue to meet organizational needs over time. This includes establishing key performance indicators, implementing automated monitoring systems, and conducting regular assessments of system effectiveness. Organizations should be prepared to adjust their collaboration strategies as technology capabilities and business requirements evolve.
Effective collaboration with AI Map Generator technology requires a strategic approach that balances automation with human expertise, addresses ethical challenges proactively, and builds organizational capabilities for long-term success. The most successful implementations treat AI as a powerful collaborative partner that enhances rather than replaces human intelligence and creativity.
FAQs About AI Map Generator Technology
Q: What exactly is an AI Map Generator and how does it work?
A: An AI Map Generator is a sophisticated system that uses artificial intelligence algorithms to automatically create maps from various data sources including satellite imagery, sensor data, and geographic databases. These systems employ machine learning techniques such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to analyze spatial patterns and generate accurate geographic representations. The technology can process tens of millions of kilometers of sensor data per hour, creating real-time maps that adapt to changing conditions.
Q: Can AI Map Generators create maps for gaming and entertainment purposes?
A: Absolutely! AI generated maps are revolutionizing the gaming and entertainment industries through procedural content generation. Tools like Cybever enable game developers to create complex 3D worlds in minutes rather than weeks, automatically placing assets while considering historical and cultural contexts. Fantasy map generators and tabletop gaming applications allow users to create professional-quality maps for role-playing games and interactive entertainment experiences.
Q: What are the main ethical concerns with AI-generated maps?
A: The primary ethical challenges include copyright ownership ambiguity (AI-generated maps fall into the public domain under U.S. law), privacy concerns from extensive location data collection, algorithmic bias that may misrepresent certain communities, and the potential for misinformation through inaccurate or manipulated geographical data. These concerns require careful consideration of governance frameworks and oversight mechanisms.
Q: How is AI Map Generator technology impacting traditional cartography jobs?
A: While AI Map Generator technology automates many routine mapping tasks, it's creating new opportunities for professionals who can adapt to work collaboratively with AI systems. Traditional cartographers are transitioning from manual mapping tasks to roles involving AI system management, quality assurance, strategic analysis, and human oversight of automated processes. Success requires reskilling programs that help professionals develop new competencies in AI collaboration.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Intelligent Cartography
The evolution of AI Map Generator technology represents more than just a technological advancement—it embodies a fundamental transformation in how we understand, visualize, and interact with our spatial world. From its humble beginnings in manual cartography to today's sophisticated systems capable of processing millions of kilometers of data in real-time, this technology has reshaped industries and redefined possibilities across multiple sectors.
The advantages are undeniable: unprecedented speed achieving 100,000x faster map production, superior accuracy with 96% precision in terrain classification, and global scalability covering over 200 countries. The technology has democratized map creation, allowing everyone from game developers to urban planners to generate professional-quality geographical visualizations.
Yet, as our research reveals, the challenges are equally significant. Issues of copyright ownership, algorithmic bias affecting underrepresented communities, privacy concerns from extensive data collection, and the potential for misinformation require urgent attention. The "black box" nature of many AI systems creates accountability gaps, while dependency risks threaten traditional cartographic expertise and skills.
The path forward lies not in viewing AI as a replacement for human intelligence, but as a powerful collaborative partner. The most successful implementations employ human-in-the-loop systems, tiered review processes, and hybrid approaches that leverage AI efficiency while preserving human creativity and judgment. Organizations must invest in workforce development, establish ethical governance frameworks, and maintain the delicate balance between automation and human oversight.
The future of cartography will be defined by how well we navigate these challenges while harnessing the transformative potential of artificial intelligence. By embracing collaboration over replacement, transparency over opacity, and human values over pure efficiency, we can ensure that AI Map Generator technology becomes a force for positive transformation that enhances rather than diminishes our human capabilities and democratic values.
The maps we create today will guide the decisions of tomorrow. Let us ensure they reflect not just the precision of our algorithms, but the wisdom of our collective human judgment.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!






No comments yet. Be the first to comment!