Forget everything you thought you knew about AI. The chatbot landscape hasn’t just evolved—it’s exploded, redrawing the boundaries between humans and machines. What began as clunky, rule-based scripts has rapidly transformed into intelligent, ever-learning conversational agents that now serve as the backbone of modern business infrastructure.
But are we truly ready for what we've unleashed? These chatbots are no longer confined to handling basic customer service—they're redefining how we communicate, work, learn, and make decisions. This is more than progress; it's a full-scale paradigm shift that blurs the lines between assistance and autonomy, between tool and collaborator.
And yet, as industries rush to embrace this AI revolution, the ethical, social, and economic consequences are racing ahead—largely unexamined, unregulated, and underestimated. The question isn't whether chatbots will change our world—they already are. The real question is: at what cost?

How Have AI Chatbots Evolved from Simple Scripts to Sophisticated Conversational Partners?
The journey of AI chatbot development reads like a tale of technological ambition meeting human ingenuity. Understanding this evolution helps us appreciate both the remarkable achievements and the significant challenges that lie ahead.
The Humble Beginnings: Rule-Based Systems
The earliest AI chatbots were remarkably simple by today's standards. In 1966, Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, a program that could simulate conversation by recognizing keywords and responding with pre-programmed phrases. ELIZA operated on basic pattern matching—essentially an elaborate version of "if-then" statements. When users typed "I am sad," ELIZA might respond with "Why are you sad?" This primitive approach could handle only the most basic interactions, yet it was revolutionary for its time.
The 1970s and 1980s saw the emergence of more sophisticated rule-based systems. These early chatbot AI implementations relied on extensive databases of pre-written responses and decision trees. Companies like IBM began exploring commercial applications, creating systems that could handle simple customer inquiries about business hours, product information, and basic troubleshooting. However, these systems were brittle—any deviation from expected inputs would result in confusion or generic responses.
The Internet Era: Chatbots Go Mainstream
The 1990s brought the internet revolution, and with it, new opportunities for AI chatbots. AOL's SmarterChild, launched in 2001, became one of the first widely-used conversational agents, entertaining millions of users on instant messaging platforms. While still rule-based, SmarterChild demonstrated the potential for chatbots to engage users in more natural, entertaining conversations.
This period also saw the emergence of customer service chatbots on websites. Companies realized that AI chatbots could handle routine inquiries 24/7, reducing labor costs and improving response times. However, these systems remained limited in scope, often frustrating users with their inability to understand context or handle complex queries.
The Machine Learning Revolution: A New Dawn
The real transformation began in the 2010s with advances in machine learning and natural language processing. Instead of relying solely on pre-programmed responses, AI chatbots began learning from vast datasets of human conversations. Google's development of the Transformer architecture in 2017 marked a crucial turning point, enabling models to understand context and generate more coherent responses.
Apple's Siri, launched in 2011, represented a breakthrough in voice-activated AI chatbots, while IBM's Watson demonstrated the potential for AI systems to process and analyze vast amounts of information. These systems could handle more complex queries, understand context to some degree, and even exhibit personality traits.
The Large Language Model Era: Chatbot AI Reaches New Heights
The introduction of GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) models by OpenAI marked the beginning of the current era. GPT-3, released in 2020, demonstrated unprecedented capabilities in generating human-like text, understanding context, and even exhibiting creativity. ChatGPT's public release in November 2022 triggered a global awakening to the potential of AI chatbots, garnering over 100 million users within just two months.
Today's AI chatbots leverage transformer architectures, attention mechanisms, and training on massive datasets containing billions of parameters. They can engage in sophisticated conversations, write code, compose poetry, analyze complex documents, and even exhibit reasoning capabilities that seemed impossible just a few years ago.
Core Technologies Powering Modern AI Chatbots
Modern AI chatbots rely on several key technologies working in concert:
Natural Language Processing (NLP): This enables chatbots to understand and interpret human language, including context, sentiment, and intent. Advanced NLP models can parse complex sentences, understand idioms, and even detect sarcasm.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning: These technologies allow AI chatbots to learn from interactions and improve over time. Neural networks with millions or billions of parameters can recognize patterns in human communication that would be impossible to program manually.
Transformer Architecture: This breakthrough technology enables AI chatbots to understand long-range dependencies in text, maintaining context across entire conversations rather than just individual exchanges.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): This technique combines the conversational abilities of large language models with access to specific knowledge bases, enabling chatbots to provide accurate, up-to-date information.
The sophistication of these technologies means that modern AI chatbots can handle complex, multi-turn conversations, understand nuanced requests, and even exhibit creativity and humor. They're no longer just answering machines—they're becoming digital companions and productivity tools.
What Are the Key Advantages and Limitations of AI Chatbots?
As AI chatbots become increasingly sophisticated, it's crucial to understand both their remarkable capabilities and their inherent limitations. This balanced perspective helps us deploy these technologies effectively while avoiding unrealistic expectations.
Where AI Chatbots Excel: The Superhuman Advantages
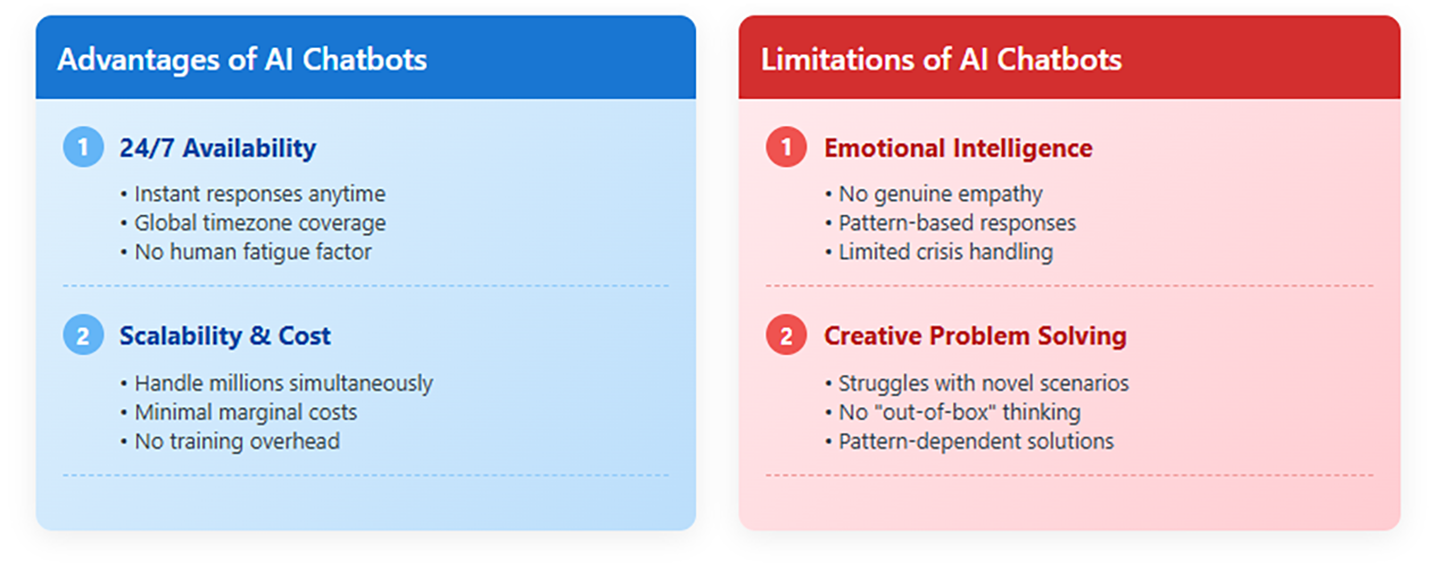
24/7 Availability and Instant Response
Unlike human agents, AI chatbots never sleep, take breaks, or call in sick. They can handle thousands of simultaneous conversations without fatigue, providing instant responses at any hour. This capability is particularly valuable for global businesses serving customers across different time zones. A customer in Tokyo can get immediate support at 3 AM local time, while the company's human staff sleeps peacefully.
Scalability and Cost Efficiency
Perhaps the most compelling advantage of AI chatbots is their ability to scale infinitely without proportional increases in cost. While hiring and training human agents requires significant investment in recruitment, training, benefits, and infrastructure, deploying additional chatbot instances is relatively inexpensive. A single AI chatbot can theoretically handle millions of conversations simultaneously, making it incredibly cost-effective for businesses of all sizes.
Consistency and Accuracy
Human agents, regardless of their training and expertise, can have bad days, make mistakes, or provide inconsistent information. AI chatbots, when properly trained and maintained, deliver consistent responses based on their training data. They don't have mood swings, personal biases (at least not intentional ones), or memory lapses that might affect their performance.
Multilingual Capabilities
Modern AI chatbots can communicate in dozens of languages, instantly breaking down language barriers that would require expensive multilingual human staff. They can switch between languages within a single conversation, accommodate regional dialects, and even help with translation tasks.
Data Processing and Analysis
AI chatbots can instantly access and analyze vast amounts of data to provide informed responses. They can cross-reference customer history, product databases, and knowledge bases in milliseconds, providing comprehensive answers that might take human agents minutes or hours to compile.
The Crucial Limitations: Where Human Intervention Remains Essential
Emotional Intelligence and Empathy
Despite their impressive capabilities, AI chatbots struggle with genuine emotional understanding. While they can recognize emotional language patterns and respond appropriately, they lack the deep empathy that human agents bring to sensitive situations. When a customer is dealing with a traumatic experience, financial hardship, or emotional distress, the nuanced understanding and genuine compassion of a human agent becomes irreplaceable.
Complex Problem-Solving and Creativity
AI chatbots excel at pattern recognition and generating responses based on training data, but they struggle with truly novel problems that require creative thinking or complex reasoning. When faced with unique situations that don't match their training patterns, they may provide generic responses or fail to understand the problem's nuances.
Contextual Understanding Beyond Training
While modern AI chatbots can maintain context within conversations, they often struggle with broader contextual understanding that extends beyond their training data. They may miss subtle implications, cultural references, or situational nuances that human agents would intuitively understand.
Hallucination and Misinformation
One of the most significant limitations of current AI chatbots is their tendency to "hallucinate"—generating plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information. This occurs because these systems are trained to generate coherent text rather than to verify factual accuracy. They may confidently provide wrong information, create fake citations, or make up statistics that sound credible but are entirely fabricated.
The Technical Reasons Behind These Limitations
Understanding why these limitations exist helps us work within them effectively. AI chatbots are statistical models trained on patterns in text data. They don't truly "understand" information in the way humans do—instead, they predict the most likely next words based on their training. This approach works remarkably well for many tasks but breaks down when dealing with:
- Situations requiring genuine understanding rather than pattern matching
- Ethical dilemmas that require moral reasoning
- Real-time information beyond their training cutoff
- Complex multi-step reasoning that requires maintaining logical consistency
These limitations aren't necessarily permanent—they represent the current state of technology rather than fundamental impossibilities. However, acknowledging them is crucial for deploying AI chatbots responsibly and effectively.
How Are AI Chatbots Transforming Industries and Displacing Traditional Jobs?
The integration of AI chatbots across industries represents one of the most significant workforce disruptions since the industrial revolution. While these technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for efficiency and innovation, they also raise profound questions about employment, economic inequality, and the future of work.
Industries Experiencing Positive Transformation
Customer Service and Support
The customer service industry has embraced AI chatbots more enthusiastically than perhaps any other sector. Companies like Zendesk report that businesses using AI chatbots see a 67% reduction in response time and a 33% increase in customer satisfaction scores. AI chatbots handle routine inquiries—password resets, order tracking, basic troubleshooting—freeing human agents to focus on complex issues requiring empathy and creative problem-solving.
Consider the banking industry, where AI chatbots now handle approximately 80% of routine customer inquiries. Bank of America's virtual assistant, Erica, has conducted over 1 billion customer interactions since its launch, helping customers check balances, transfer funds, and receive financial advice. This transformation has allowed banks to provide 24/7 support while reducing operational costs by up to 30%.
Healthcare and Telemedicine
In healthcare, AI chatbots are revolutionizing patient engagement and preliminary diagnosis. Babylon Health's AI chatbot has conducted millions of medical consultations, providing initial symptom assessment and triaging patients to appropriate care levels. During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI chatbots helped overwhelmed healthcare systems by conducting initial screenings, providing public health information, and reducing the burden on human medical staff.
E-commerce and Retail
Retail AI chatbots have transformed online shopping experiences, providing personalized recommendations, handling returns, and guiding customers through complex purchases. Sephora's chatbot helps customers find products based on their skin type, preferences, and past purchases, resulting in higher conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
Education and Training
Educational institutions are leveraging AI chatbots to provide personalized learning experiences. Duolingo's AI-powered conversation practice helps language learners engage in realistic dialogues, while university chatbots handle student inquiries about admissions, course schedules, and campus resources.
Industries Facing Disruption and Job Displacement
Traditional Call Centers
The most immediate impact of AI chatbots has been on call center employment. Industry analysts estimate that AI chatbots could eliminate up to 85% of first-level customer service positions by 2030. While this creates efficiency gains for businesses, it threatens millions of jobs worldwide, particularly in developing countries where call center operations have been major employers.
Administrative and Clerical Work
AI chatbots are increasingly handling administrative tasks that once required human workers. Insurance companies use chatbots to process claims, schedule appointments, and update customer information. Legal firms deploy AI chatbots to handle routine inquiries, schedule consultations, and provide basic legal information.
Data Entry and Processing
Traditional data entry roles are becoming obsolete as AI chatbots can extract information from documents, process forms, and update databases with higher accuracy and speed than human workers. This transformation particularly affects entry-level positions that many workers rely on for economic mobility.
The Ripple Effects: Economic and Social Implications
The displacement of traditional jobs by AI chatbots creates several concerning trends:
Increased Economic Inequality
As AI chatbots eliminate middle-skilled jobs while creating demand for high-skilled AI specialists, we risk widening the gap between skilled and unskilled workers. The benefits of increased productivity may accrue primarily to business owners and technology companies, while displaced workers struggle to find alternative employment.
Geographic Displacement
Countries that built their economies around call centers and business process outsourcing face particular challenges. The Philippines, India, and other nations that employed millions in these sectors must now reimagine their economic strategies as AI chatbots reduce demand for offshore human labor.
Skills Gap Challenges
While AI chatbots eliminate some jobs, they create new opportunities in AI development, training, and maintenance. However, the workers displaced by these technologies often lack the technical skills required for emerging roles, creating a significant retraining challenge.
Real-World Case Studies: Success and Struggle
Success Story: H&M's AI Transformation
Fashion retailer H&M successfully integrated AI chatbots into their customer service operations, handling over 70% of customer inquiries without human intervention. However, they also invested heavily in retraining displaced customer service representatives for roles in AI chatbot training, quality assurance, and complex problem resolution. This approach maintained employment levels while improving service quality.
Struggle Story: Traditional Travel Agencies
The travel industry has seen significant disruption as AI chatbots handle booking inquiries, itinerary planning, and travel recommendations. Many traditional travel agencies have closed as customers increasingly rely on AI-powered travel platforms. While some agencies have adapted by focusing on complex, personalized travel planning, many travel agents have been displaced without adequate retraining opportunities.
What Ethical Dilemmas Do AI Chatbots Create in Our Digital Age?
The rapid deployment of AI chatbots across industries has outpaced our ability to address the ethical implications of these technologies. As these systems become more sophisticated and ubiquitous, they raise fundamental questions about privacy, authenticity, responsibility, and human dignity.
The Copyright and Intellectual Property Minefield
One of the most contentious ethical issues surrounding AI chatbots involves the use of copyrighted content in training data. These systems are trained on vast datasets scraped from the internet, including books, articles, code, and other creative works, often without explicit permission from creators or copyright holders.
The Training Data Dilemma
AI chatbots like GPT-4 were trained on datasets containing millions of copyrighted works. When these systems generate responses, they're essentially recombining and regurgitating information from these sources. This raises fundamental questions: Is this fair use or copyright infringement? Should creators be compensated when their work is used to train AI systems that may eventually compete with them?
The Attribution Problem
When an AI chatbot provides information or generates content, it rarely cites its sources. This creates a transparency problem—users can't verify information or give credit to original creators. For academic and professional applications, this lack of attribution poses serious concerns about intellectual honesty and accountability.
Privacy and Data Security Concerns
AI chatbots process enormous amounts of personal data, raising significant privacy concerns that extend far beyond traditional data collection practices.
Conversational Data Mining
Every interaction with an AI chatbot generates valuable data about users' thoughts, preferences, concerns, and behaviors. This conversational data is often more intimate and revealing than traditional web browsing data. Companies can analyze these interactions to build detailed psychological profiles, predict behavior, and influence decision-making.
Data Retention and Sharing
Many AI chatbot services retain conversation logs indefinitely, creating vast databases of personal information. Users often don't understand how their data is being used, stored, or potentially shared with third parties. The recent controversies surrounding ChatGPT's data retention policies highlight the need for greater transparency and user control.
The Misinformation and Manipulation Crisis
AI chatbots' tendency to generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information poses serious risks to public discourse and decision-making.
Hallucination and False Confidence
AI chatbots can confidently present fabricated information as fact. They might create fake historical events, invent scientific studies, or generate false statistics. This problem is particularly dangerous because these systems present information with apparent authority, and users often trust AI-generated content without verification.
Potential for Manipulation
The persuasive capabilities of AI chatbots raise concerns about their potential use for manipulation and propaganda. Bad actors could deploy sophisticated AI chatbots to spread misinformation, influence political opinions, or manipulate financial markets. The scale and sophistication of such operations could far exceed traditional propaganda efforts.
The Authenticity and Human Connection Crisis
As AI chatbots become more human-like, they challenge our understanding of authentic communication and relationships.
Deceptive Anthropomorphism
Many AI chatbots are designed to appear more human-like than they actually are, using phrases like "I think" or "I feel" when they don't actually experience thoughts or emotions. This anthropomorphism can deceive users into attributing human qualities to these systems, potentially leading to unhealthy emotional attachments or misplaced trust.
The Erosion of Human Skills
As we increasingly rely on AI chatbots for communication, problem-solving, and even emotional support, we risk atrophying our own human capabilities. Students might lose writing skills by depending on AI chatbots for essays, while professionals might lose critical thinking abilities by accepting AI-generated solutions without question.
Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination
AI chatbots inherit and amplify biases present in their training data, potentially perpetuating discrimination and inequality.
Representation Bias
Training datasets often underrepresent certain groups, leading to AI chatbots that work better for some users than others. Language models might perform poorly with non-standard dialects, cultural references, or perspectives that were underrepresented in training data.
Reinforcement of Stereotypes
AI chatbots might generate responses that reinforce harmful stereotypes about gender, race, religion, or other characteristics. Even when not explicitly biased, these systems might make assumptions or generalizations that reflect societal prejudices embedded in their training data.
The Accountability Gap
Perhaps the most fundamental ethical challenge is determining responsibility when AI chatbots make mistakes or cause harm.
Who's Responsible?
When an AI chatbot provides dangerous medical advice, generates harmful content, or makes discriminatory decisions, who bears responsibility? The AI company? The deploying organization? The individual user? Current legal frameworks struggle to address these questions, creating an accountability gap that could leave victims without recourse.
The Black Box Problem
Many AI chatbots operate as "black boxes"—even their creators don't fully understand how they generate specific responses. This lack of interpretability makes it difficult to identify and correct problematic behaviors, raising questions about the wisdom of deploying systems we don't fully understand.

How Should We Adapt to the AI Chatbot Revolution?
The AI chatbot revolution is not a distant future possibility—it's happening now, and our response will determine whether these technologies become tools of human flourishing or sources of economic disruption and social division. The key lies in proactive adaptation rather than reactive response.
Strategies for Industries and Workers Under Threat
Embrace Human-AI Collaboration Over Replacement
Rather than viewing AI chatbots as replacements for human workers, forward-thinking organizations are developing hybrid models that leverage the strengths of both humans and AI. In customer service, this means using AI chatbots to handle routine inquiries while human agents focus on complex, emotionally sensitive, or creative problem-solving tasks.
Call Centers of the Future: Progressive companies are transforming traditional call centers into "experience centers" where human agents work alongside AI chatbots. Agents receive AI-powered suggestions, real-time sentiment analysis, and instant access to relevant information, enabling them to provide superior service while AI handles the routine work.
Invest in Continuous Learning and Reskilling
The most successful adaptation strategy involves continuous learning and skill development. Workers in AI-threatened industries should focus on developing uniquely human capabilities that complement AI strengths:
- Emotional intelligence and empathy: These remain uniquely human strengths that AI chatbots cannot replicate
- Creative problem-solving: The ability to approach novel situations with innovative solutions
- Complex communication: Managing nuanced, multi-stakeholder conversations and negotiations
- AI collaboration skills: Learning to work effectively with AI tools rather than competing against them
Develop AI Literacy Across All Sectors
Organizations must invest in AI literacy training for all employees, not just technical staff. Understanding how AI chatbots work, their capabilities and limitations, and how to leverage them effectively is becoming as essential as computer literacy was in the 1990s.
Building Ethical AI Chatbot Frameworks
Implementing Transparency and Accountability Measures
Organizations deploying AI chatbots must establish clear transparency standards. This includes:
- Clear disclosure: Users should always know when they're interacting with an AI chatbot rather than a human
- Capability communication: Clearly communicate what the AI chatbot can and cannot do
- Escalation pathways: Provide easy ways for users to reach human support when needed
- Regular auditing: Continuously monitor AI chatbot interactions for bias, errors, and problematic behaviors
Addressing the Copyright and Attribution Challenge
To resolve copyright concerns, the industry must develop new frameworks for ethical AI training and deployment:
- Opt-in training data: Develop systems that only use content from creators who explicitly consent to AI training
- Revenue sharing models: Create mechanisms to compensate creators whose work contributes to AI training
- Attribution systems: Develop technical solutions that can trace AI-generated content back to its sources
- Fair use guidelines: Establish clear legal frameworks that balance innovation with creator rights
Privacy-by-Design Implementation
Organizations must build privacy protection into AI chatbot systems from the ground up:
- Data minimization: Collect only the data necessary for the chatbot's function
- User control: Provide users with clear options to control their data and delete conversation histories
- Anonymization: Develop techniques to learn from user interactions without storing personally identifiable information
- Consent clarity: Ensure users understand how their data will be used and shared
Regulatory and Policy Recommendations
Establish AI Chatbot Standards and Certifications
Just as we have safety standards for automobiles and medical devices, we need comprehensive standards for AI chatbots used in critical applications like healthcare, financial services, and education. These standards should cover:
- Accuracy requirements: Minimum standards for information accuracy in different domains
- Bias testing: Mandatory testing for discriminatory behavior across different user groups
- Safety protocols: Requirements for handling sensitive topics and potential harmful requests
- Performance monitoring: Ongoing assessment of AI chatbot behavior in real-world deployments
Create Economic Transition Support
Governments and organizations must develop comprehensive support systems for workers displaced by AI chatbots:
- Retraining programs: Publicly funded programs to help workers develop AI-complementary skills
- Transition assistance: Financial support during career transitions, similar to unemployment benefits but designed for technological displacement
- Education reform: Update educational curricula to prepare students for an AI-integrated workforce
- Universal basic income pilots: Experiment with economic support systems that could help society adapt to AI-driven productivity gains
Practical Implementation Guidelines
For Businesses Deploying AI Chatbots
1. Start with clear objectives: Define specific problems AI chatbots will solve rather than deploying them broadly
2. Maintain human oversight: Ensure human experts can review and correct AI chatbot responses
3. Monitor and iterate: Continuously track AI chatbot performance and user feedback
4. Train your team: Ensure human staff understand how to work with AI chatbots effectively
5. Plan for edge cases: Develop protocols for handling situations where AI chatbots fail or encounter novel problems
For Individuals Adapting to AI Chatbots
1. Develop AI literacy: Learn how AI chatbots work, their capabilities, and limitations
2. Verify information: Always fact-check important information provided by AI chatbots
3. Maintain human connections: Don't let AI chatbots replace human relationships and interactions
4. Focus on uniquely human skills: Develop capabilities that complement rather than compete with AI
5. Stay informed: Keep up with developments in AI ethics and regulation
For Educational Institutions
1. Update curricula: Integrate AI literacy into all educational programs
2. Teach critical thinking: Emphasize the importance of evaluating AI-generated information
3. Prepare for new careers: Develop programs for AI-complementary roles
4. Address cheating concerns: Establish clear policies for AI chatbot use in academic work
5. Model ethical use: Demonstrate responsible AI chatbot deployment in educational settings
The AI chatbot revolution presents both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges. Our response must be proactive, ethical, and focused on ensuring these technologies serve human flourishing rather than replacing human dignity. By embracing collaboration over competition, transparency over opacity, and continuous learning over static responses, we can navigate this transformation successfully.
FAQs
Q: Will AI chatbots completely replace human customer service representatives?
A: While AI chatbots will handle an increasing percentage of customer interactions, complete replacement is unlikely. Human representatives will remain essential for complex issues, emotional situations, and cases requiring creative problem-solving. The future lies in human-AI collaboration rather than replacement.
Q: How can I tell if I'm talking to an AI chatbot or a human?
A: Ethical AI chatbot deployments should clearly identify themselves as AI systems. Look for disclaimers, consistent response patterns, and capabilities that seem superhuman (like instant access to vast databases). When in doubt, ask directly—AI chatbots should honestly identify themselves.
Q: Are conversations with AI chatbots private and secure?
A: Privacy depends on the specific service and its policies. Many AI chatbots store conversation logs for training and improvement purposes. Always read privacy policies, avoid sharing sensitive personal information, and use privacy-focused alternatives when available.
Q: Can AI chatbots be biased or discriminatory?
A: Yes, AI chatbots can exhibit biases present in their training data or design. They might perform differently for different user groups or reflect societal prejudices. Responsible AI development includes bias testing and mitigation, but users should remain aware of these limitations.
Q: How accurate is information provided by AI chatbots?
A: AI chatbots can provide accurate information on many topics, but they're also prone to "hallucination"—generating plausible-sounding but incorrect information. Always verify important facts from authoritative sources, especially for medical, legal, or financial advice.
Q: What should I do if an AI chatbot provides harmful or inappropriate content?
A: Report the incident to the service provider immediately. Most platforms have reporting mechanisms for inappropriate AI behavior. Document the interaction if possible, and seek human support for sensitive issues.
Conclusion
The AI chatbot revolution represents a pivotal moment in human history, comparable to the introduction of the internet or the industrial revolution. These technologies offer unprecedented opportunities to enhance human capability, improve efficiency, and solve complex problems. However, they also present significant challenges that require thoughtful, proactive responses from individuals, organizations, and society as a whole.
The evolution of AI chatbots from simple rule-based systems to sophisticated conversational agents demonstrates the remarkable pace of technological advancement. Today's AI chatbots can engage in nuanced conversations, provide personalized assistance, and handle complex tasks that seemed impossible just a few years ago. Yet they remain fundamentally limited by their training data, prone to hallucination, and lacking the emotional intelligence and creative problem-solving abilities that make human intelligence unique.
The impact on industries and employment is already profound and will only intensify. While AI chatbots create new opportunities and efficiencies, they also threaten traditional jobs and risk exacerbating economic inequality. The challenge is not to resist this transformation but to guide it in directions that benefit humanity broadly rather than concentrating advantages among a few.
The ethical challenges surrounding AI chatbots—from copyright infringement to privacy violations to the spread of misinformation—require immediate attention and coordinated responses. We cannot afford to address these issues reactively after harm has already occurred. Instead, we must build ethical considerations into the development and deployment of these technologies from the beginning.
Perhaps most importantly, we must remember that AI chatbots are tools created by humans to serve human purposes. They should enhance rather than replace human capabilities, support rather than undermine human dignity, and contribute to rather than detract from human flourishing. The choices we make today about how to develop, deploy, and regulate these technologies will shape the future of human-AI interaction for generations to come.
The AI chatbot revolution is not a force of nature beyond human control—it's a technological transformation that we can and must actively shape. By embracing transparency, investing in human development, addressing ethical concerns proactively, and maintaining focus on human values, we can ensure that AI chatbots become powerful tools for human empowerment rather than sources of displacement and division.
The future belongs to those who can effectively collaborate with AI while maintaining their uniquely human capabilities. As we stand at this crossroads, our choices today will determine whether the AI chatbot revolution becomes a story of human triumph or a cautionary tale of technological disruption. The power to shape this future lies in our hands—we must use it wisely.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!






No comments yet. Be the first to comment!