AI plagiarism checker tools have emerged as essential guardians of intellectual integrity, because content creation and information sharing have reached unprecedented levels, the problem of plagiarism has evolved from simple copy-paste violations to sophisticated forms of content theft. AI plagiarism checker has developed increasingly advanced algorithms to detect everything from verbatim copying to AI-generated content. These digital sentinels scan billions of webpages, academic papers, and digital repositories to identify potential instances of plagiarism, protecting the original work of creators across disciplines.
With the explosion of AI writing tools like ChatGPT and Claude, the ability to detect artificially generated content has become just as crucial as identifying traditional plagiarism, transforming AI plagiarism checkers from simple utility tools into sophisticated systems central to maintaining academic honesty, creative integrity, and intellectual property rights in our increasingly AI-augmented world.
The Early Forms of AI Plagiarism Checker
The journey of AI plagiarism checker technology began with relatively simple text-matching algorithms. These early tools primarily focused on comparing submitted text against existing databases to detect direct copying—a fundamental yet limited approach to combating academic dishonesty and content theft.
Representative Tools and Basic Functions
The pioneering AI plagiarism checker solutions like Turnitin, PlagScan, and Copyleaks operated by cross-referencing submitted content against massive text repositories. When educators needed to check plagiarism turnitin was often their first choice, as it offered a straightforward way to identify verbatim copying in student papers. These tools effectively addressed straightforward plagiarism by identifying verbatim copying or slightly modified text. However, their capabilities were constrained to detecting only the most obvious forms of content theft.
Early Limitations
Despite their utility, first-generation AI plagiarism checker technology suffered from significant shortcomings. The systems predominantly relied on keyword matching and basic text similarity calculations, making them effective only against "word-for-word plagiarism" while struggling with synonym substitutions, sentence restructuring, or cross-lingual plagiarism. For students and educators wondering how to check on plagiarism effectively, these early tools provided only partial solutions.
Besides, these primitive tools couldn't accurately determine whether content was AI-generated and often produced false positives by flagging legitimate citations as plagiarism. Their limited contextual understanding led to imprecise detection results. Database coverage was restricted, making it difficult to detect content from unindexed sources or behind paywalls, and comparison against private databases was impossible.
Moreover, dependent on manual database entries, these systems failed to identify paraphrased content or synonym replacements. Most supported only English, resulting in lower accuracy when analyzing non-English texts or specialized terminology. The turnitin plagiarism checker, despite being an industry leader, still faced these fundamental constraints in its early iterations.

Breakthrough Points in AI Plagiarism Checker Development
The evolution of AI plagiarism checker technology witnessed several breakthrough moments that addressed many of the limitations of early systems, setting the foundation for today's sophisticated detection tools.
Technological Breakthroughs and Representative Companies
The introduction of AI, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and deep learning technologies dramatically enhanced detection capabilities. AI systems began understanding semantics, recognizing paraphrasing, and identifying complex plagiarism techniques. Originality.ai emerged as an industry leader when founder Jon Gillham developed machine learning-based detection tools capable of identifying various forms of plagiarism, including paraphrasing and semantic plagiarism, while also detecting AI-generated content with improved accuracy.
QuillBot and similar companies launched AI-powered detection tools that could identify AI-generated content, cross-language plagiarism, hidden characters, and image-to-text conversion cheating methods. The quillbot plagiarism checker represented a significant advancement, offering both paraphrasing tools and plagiarism detection in one platform. In 2023, Copyleaks introduced a specialized AI detection tool for the news publishing industry, complete with enterprise-level LMS and API integration capabilities, allowing educational institutions and businesses to seamlessly incorporate AI content detection into their native platforms. This system could differentiate between AI-generated and human-written content across more than a dozen languages, achieving an impressive 99.1% accuracy rate with only a 0.2% false positive rate.
Overcoming Previous Limitations
The new generation of AI plagiarism checker tools not only improved detection of paraphrasing and semantic plagiarism but also gained the ability to identify AI-generated text from platforms like ChatGPT, solving the traditional tools' inability to distinguish between human and AI writing. For programmers needing to check plagiarism code, specialized tools emerged that could analyze not just text but programming syntax and logic patterns. Additionally, enhanced multilingual support and contextual understanding expanded detection scope and improved accuracy. Meanwhile, databases underwent significant expansion, encompassing tens of trillions of web pages and tens of thousands of open journals.
Current State and Mainstream AI Plagiarism Checker Tools
Today's AI plagiarism checker landscape features sophisticated solutions that employ advanced technologies to tackle increasingly complex plagiarism challenges.
Mainstream Tools and Core Technologies
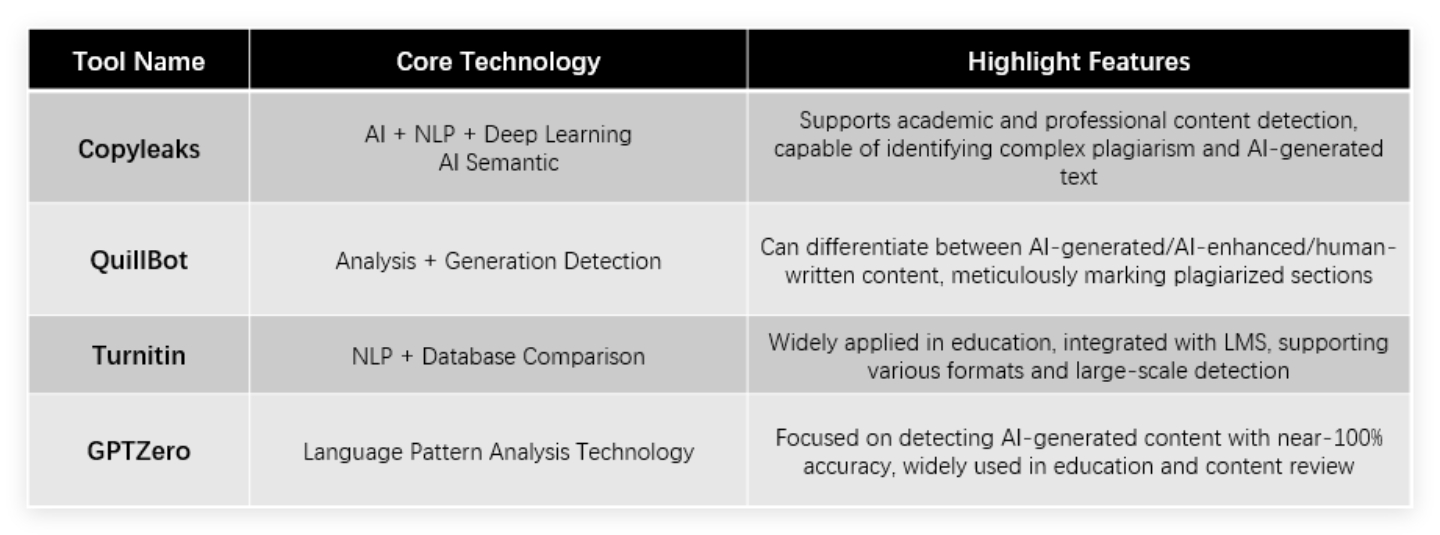
The current market is dominated by several powerful platforms. The copyleaks plagiarism checker leverages a combination of AI, NLP, and deep learning to support both academic and professional content detection, capably identifying complex plagiarism and AI-generated text. QuillBot's technology employs AI semantic analysis and generation detection features that can differentiate between AI-generated, AI-enhanced, and human-written content, meticulously marking plagiarized sections for easy review.
Turnitin continues its market dominance with NLP and extensive database comparison capabilities, being widely applied in education, integrated with learning management systems, and supporting various formats for large-scale detection. For students and educators who need to check for plagiarism turnitin remains a go-to solution. Meanwhile, GPTZero focuses on language pattern analysis technology specifically designed to detect AI-generated content with near-100% accuracy, making it widely used in education and content review processes.
The grammarly plagiarism checker has also become increasingly popular, combining grammar checking with plagiarism detection to offer a comprehensive writing improvement solution. For programming environments, specialized AI code plagiarism checker tools have emerged that can analyze not just text similarities but algorithmic patterns and logical structures.
Complex Problems Handled by AI Plagiarism Checkers
Challenges in Detecting AI-Generated Content
Traditional plagiarism detection tools, which primarily rely on text similarity matching, often struggle to identify content generated by advanced language models like GPT-4. To address this, tools such as Originality.ai have developed specialized detection capabilities. In an empirical study evaluating six AI text detection tools, Originality.ai achieved a 97% accuracy rate in distinguishing AI-generated content, outperforming other tools in precision and recall metrics.
Semantic-Level Plagiarism Recognition
When plagiarists employ techniques like synonym substitution and sentence restructuring, conventional tools may fail to detect the underlying plagiarism. Advanced detection methods now utilize semantic analysis to identify such cases. For instance, by leveraging word embeddings, systems can assess the semantic similarity between texts, effectively identifying paraphrased content that maintains the original meaning. Studies have demonstrated that these methods can achieve high F1 scores, indicating a strong balance between precision and recall in detecting semantic plagiarism.
Multimodal Content Detection
Modern plagiarism extends beyond traditional text to include code, images, and other formats. For code plagiarism, tools like MOSS (Measure of Software Similarity) analyze the structure of programs across various programming languages, effectively detecting similarities even when superficial changes are made. These tools focus on the syntax and control structures of code, which are less likely to be altered by plagiarists.
Cross-Language Detection Challenges
Detecting plagiarism across different languages poses significant challenges. Recent approaches employ word embedding techniques to map words from different languages into a shared semantic space, facilitating the detection of cross-language plagiarism. For example, research has shown that using word embeddings can achieve an F1 score of 89.15% in English-French similarity detection tasks, highlighting the effectiveness of this method in cross-lingual contexts.
How AI Plagiarism Checker Surpasses Human Capabilities
The advantages of AI plagiarism checker technology over manual checking are substantial and growing more pronounced as the technology advances.
Outstanding Advantages Compared to Manual Methods
AI plagiarism checkers offer remarkable speed and scale advantages, detecting tens of thousands of words in seconds, far exceeding human comparison efficiency. This makes turnitin plagiarism checker and similar tools invaluable for processing large volumes of academic submissions or content reviews. The best free plagiarism checker options now provide capabilities that would require teams of human experts to match, offering accessibility to users with limited resources.
The high precision of modern systems allows them to identify complex rewrites, AI-generated content, and cross-language plagiarism that would be virtually impossible for humans to detect manually. For instructors who need to check for plagiarism turnitin and similar tools offer an efficiency that transforms what was once a painstaking process into a streamlined workflow.
Multilingual and large database support has expanded dramatically, with tools like Unicheck supporting semantic comparison across 50+ languages, providing broad coverage and strong detection capabilities. This multilingual ability makes them particularly valuable in international educational institutions and publishing houses. The plagiarism checker quillbot offers represents another step forward, combining rewriting assistance with detection capabilities.
Modern systems can be embedded into workflows, enabling real-time, batch detection that seamlessly fits into existing processes. The copyleaks plagiarism checker, for instance, offers API integration that allows organizations to incorporate plagiarism detection directly into their content management systems, creating a seamless experience for users.
Most Evident Use Cases
The superiority of AI plagiarism checker solutions is particularly apparent in several key scenarios. Educational institutions, publishers, and content creators who need frequent checking benefit enormously from these tools. For example, the University of California, Berkeley has implemented Turnitin's AI detection module to maintain academic integrity at scale, demonstrating how institutions can effectively check plagiarism turnitin modules identify.
News media and academic journals requiring large-scale originality verification of submitted manuscripts benefit from automated systems that would be impossible to replicate manually. For anyone wondering how to check on plagiarism across hundreds or thousands of documents, AI-powered solutions provide the only feasible approach.
Multinational corporations checking for term repetition risks in multilingual contracts can use AI to identify potential legal issues across languages. For technical organizations that need to check plagiarism code across large codebases, specialized tools offer unprecedented efficiency in maintaining intellectual property compliance.
Academic publishers can quickly screen journal submissions for self-plagiarism, maintaining the integrity of their publications without excessive manual review. This capability is particularly valuable when dealing with researchers who may reuse portions of their previous work without proper attribution.
Professional Recommendations
To maximize the effectiveness of AI plagiarism checker tools, experts suggest several best practices. AI detection results should be manually reviewed to avoid false positives or negatives, especially in high-stakes situations like academic integrity cases or legal disputes. For organizations wondering how to check on plagiarism most effectively, this hybrid approach often yields the best results.
Detection tools should be regularly updated to keep pace with new AI writing and plagiarism trends, ensuring they remain effective against evolving threats. Combining AI detection with writing training improves original content creation capabilities, focusing on prevention rather than just detection. Parameter optimization through adjusting sensitivity thresholds helps balance false positive rates with detection accuracy, creating more reliable results.

Limitations of AI Plagiarism Checker Technology
Despite their impressive capabilities, AI plagiarism checker tools still face significant constraints that necessitate human oversight in certain contexts.
Scenarios Requiring Human Intervention
Several situations demand human judgment beyond what AI plagiarism checker can currently provide. Complex academic writing, creative writing, and other content requiring deep semantic understanding and professional background knowledge still benefit from expert human review. The plagiarism checker turnitin and similar tools might flag passages that require contextual interpretation.
When detection results fall into "gray areas," human judgment is needed to determine whether citations and rewrites comply with standards. This is where check plagiarism turnitin systems might flag legitimate academic practices that require contextual understanding. Even the best free plagiarism checker options cannot fully replace informed human judgment in these ambiguous cases.
Certain databases, paid content, and non-public materials cannot be compared automatically, limiting the scope of automated checks. This is a persistent challenge for even sophisticated detection systems. Legal effectiveness of contract terms requires professional legal review that goes beyond identifying textual similarities, and defining plagiarism in artistic design requires subjective aesthetic judgment that AI cannot yet replicate.
Reasons for These Limitations
Current limitations stem from several fundamental challenges. AI still struggles to comprehend context with 100% accuracy or to distinguish between reasonable citation and plagiarism. This contextual understanding remains a significant hurdle even for advanced systems like the grammarly plagiarism checker or sophisticated academic tools.
Database coverage remains limited despite significant expansion, making truly comprehensive checking impossible. There will always be content that exists outside the reach of even the most extensive plagiarism detection databases. Complex rewrites and creative expressions exceed algorithmic capabilities, presenting challenges that require human judgment to resolve effectively.
Directions for Technical Improvement
Several promising avenues for advancement are emerging in the field. Strengthening cross-language, cross-domain, and cross-modal detection capabilities would make code plagiarism checker tools more versatile across programming languages and paradigms. For developers who need to check for code plagiarism, these improvements would significantly enhance detection accuracy.
Enhancing contextual understanding and legitimate citation recognition would reduce false positives when using check for plagiarism turnitin and similar academic tools. This improvement would help distinguish between proper academic citation and actual plagiarism more effectively.
Expanding database coverage to improve detection depth and breadth across more sources and languages would enhance the comprehensiveness of plagiarism detection. Introducing domain knowledge bases (such as legal clause libraries) would assist judgment in specialized fields where context matters tremendously.
Recording webpage version histories to prevent tampering, using solutions like IBM Hyperledger, would enhance the evidentiary value of plagiarism detection results. Small sample learning techniques could reduce dependence on large datasets, making detection more efficient and accessible according to latest research findings.
FAQs About AI Plagiarism Checker
Q: What is an AI plagiarism checker and how does it work?
A: AI plagiarism checker tools utilize artificial intelligence technologies (such as natural language processing and machine learning) to analyze text content and identify potential plagiarism. These tools compare submitted text against vast online resources, academic databases, and previously submitted documents to detect direct copying, minor modifications, or rewritten content. For example, PlagiarismCheck.org uses deep internet searching and custom databases to provide accurate real-time results while ensuring data security.
Q: What advantages does using an AI plagiarism checker offer?
A: The benefits include efficiency (quickly scanning large volumes of text), multi-level detection (identifying not just direct copying but also modified or rewritten text), data security (services like PlagiarismCheck.org allow users to delete their text at any time), and integration capabilities (many tools support integration with learning management systems like Moodle and Canvas). The turnitin plagiarism check functionality, for instance, processes thousands of student papers daily across educational institutions worldwide.
Q: What are common application scenarios for AI plagiarism checker tools?
A: These AI plagiarism checkers are widely used in education (helping teachers assess the originality of student assignments), publishing (ensuring manuscript originality), corporate content review (checking marketing materials and reports for uniqueness), and research institutions (verifying paper originality before publication). For programming assignments, instructors often check plagiarism code to ensure students are developing their own solutions rather than copying existing ones.
Q: What issues should be considered when using an AI plagiarism checker?
A: Important considerations include the possibility of false positives (AI detection tools may incorrectly flag human writing as AI-generated, especially for non-native writers), detection range limitations (some tools may not access all databases or paid resources), and dependency issues (over-reliance on tools may neglect the importance of cultivating students' original writing abilities). Understanding how to check on plagiarism effectively requires recognizing these limitations.
Q: What mainstream AI plagiarism checker tools are available?
A: Popular options include Turnitin (widely used in educational institutions, offering plagiarism detection and AI writing detection), PlagiarismCheck.org (providing deep internet searching, custom databases, and AI content detection), Copyleaks (supporting multilingual detection with three-level text similarity detection and AI-generated content identification), and Grammarly (offering plagiarism detection alongside grammar checking, suitable for individual users). For developers, specialized tools to check plagiarism code across various programming languages are also available.
Q: How can the accuracy of AI plagiarism checker tools be improved?
A: Strategies include using multiple detection tools in combination to enhance comprehensiveness and accuracy, incorporating manual review in critical situations to avoid misidentification, continuously updating databases to cover the latest resources and content, and providing user training to correctly interpret and use detection results. For the best free plagiarism checker options, regular updates and accuracy improvements are particularly important to maintain effectiveness.
Conclusion: The Evolving Landscape of AI Plagiarism Detection
The evolution of AI plagiarism checker technology represents a fascinating journey from simple text matching to sophisticated semantic analysis systems that can identify not only traditional plagiarism but also AI-generated content. This progression mirrors the broader development of artificial intelligence itself, growing more nuanced and capable with each technological advancement.
However, current AI detection tools face significant challenges. Studies have shown that these tools often struggle to reliably distinguish between human-written and AI-generated text, especially when the AI-generated content has been paraphrased or minimally edited. For instance, research indicates that paraphrasing AI-generated text can significantly reduce the accuracy of detection tools, making it difficult to identify such content reliably.
Moreover, there are concerns about the fairness of these tools. Evidence suggests that AI detectors may exhibit bias against non-native English writers, misclassifying their work as AI-generated due to linguistic differences. This raises ethical questions about the deployment of such tools in educational settings, where they might inadvertently penalize certain groups of students.
Looking forward, experts emphasize the need for a balanced approach that combines technological solutions with human judgment. While AI can assist in identifying potential instances of plagiarism, it is crucial to involve educators in the evaluation process to account for context and intent. Additionally, ongoing research and development are essential to improve the accuracy and fairness of detection tools, ensuring they support academic integrity without introducing new forms of bias or error.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!






No comments yet. Be the first to comment!