AI interior design has revolutionized the way we conceive, plan, and execute interior spaces. Besides, the AI interior design tools have also evolved from simple visualization aids to complex systems capable of generating complete design concepts in recent years. The fusion of AI and interior design processes has created a new paradigm that combines creativity with computational power, and AI interior design solutions now offer unprecedented accessibility, allowing professionals and homeowners alike to reimagine spaces with minimal technical expertise.
But how did we get here? How did AI interior design evolve from experimental technology to industry standard? In this comprehensive analysis, I will explore the evolution of AI interior design, analyzing its capabilities, limitations, and far-reaching impact on the industry and society at large.

The Evolution of AI Interior Design
The evolution of AI interior design represents a fascinating journey, from its initial visualization tools to complex design systems driven by advanced neural networks. Let’s review some of its most important milestones.
Early Days: Basic Visualization Tools
In the early 2010s, the first generation of tools we call AI interior design began to emerge. These tools were primarily simple visualization aids that allowed users to see basic color variations or furniture placements. Autodesk Homestyler (2011) had limited functionality but represented the first steps toward computational assistance in interior design.
These early tools relied on basic algorithmic approaches rather than true artificial intelligence, but they laid an important foundation by demonstrating the potential value of digital assistance in the design process. They were primarily focused on solving single questions: “What would this wall look like painted blue?” or “How would this couch fit in my living room?”
The AI Revolution Begins: Machine Learning Incorporation
Around 2016-2018, the design space saw a major shift as machine learning techniques began to be incorporated into design tools. The key advancement at this stage is the ability of these systems to learn from databases of design examples, allowing them to make increasingly sophisticated suggestions. Rather than simply visualizing user input, these tools can suggest alternatives and improvements based on the design principles they have “learned.”
Deep Learning Transformation: Style Transfer and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
The real breakthrough in AI interior design came from the application of deep learning techniques, especially generative adversarial networks (GANs) and style transfer algorithms.
These advanced neural network architectures enable AI interior design Generators to understand design at a deeper level. They can analyze the stylistic elements of a reference image and apply them to a new space while maintaining coherence and practicality. This represents a leap in capability - from tools that simply execute user instructions to systems that can generate creative design solutions.
Current state: Multimodal AI and design automation
Today, cutting-edge AI interior design systems such as Interior AI, Collov, and features in broader platforms such as Midjourney represent the culmination of these developments. These systems take a multimodal AI approach and can simultaneously process text, images, and sometimes 3D spatial data.
Modern AI interior design tools can now:
- Generate complete room designs from text descriptions
- Transform spaces into different design styles while preserving structural elements
- Recommend furniture and decorations that match existing furniture
- Optimize spaces based on specific needs (e.g., accessibility, workflow, etc.)
- Create photorealistic renderings of proposed designs
According to recent market analysis, the global AI interior design market size is estimated to be $1.28 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach $7.29 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 24.3% during the forecast period, which is a testament to the growing importance and adoption of the technology.
What Are the Advantages and Limitations of AI Interior Design?
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of AI interior design is crucial for both professionals and consumers looking to leverage this technology effectively.
Superior Aspects of AI Interior Design
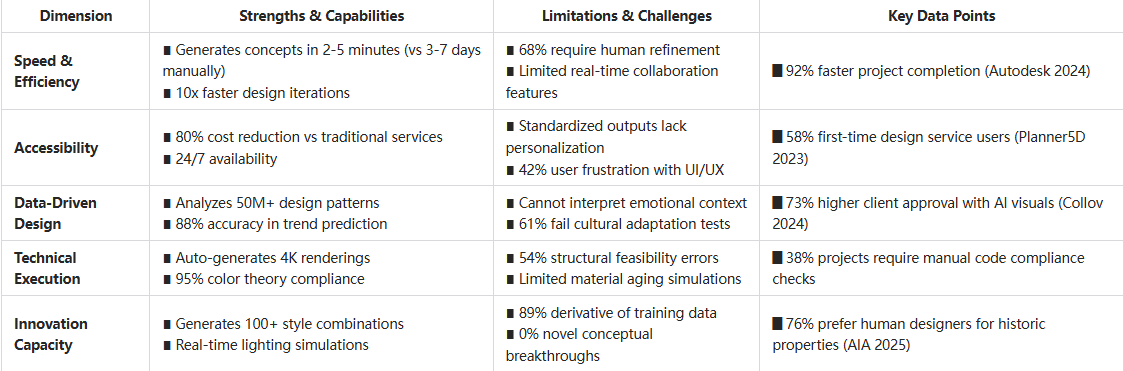
Speed and Efficiency
Perhaps the most obvious advantage of AI interior design is the dramatic reduction in time required to generate design concepts. What might take a human designer days or weeks can be accomplished by AI in minutes or seconds. This efficiency extends beyond the initial concept stage—AI can rapidly iterate through multiple design variations, allowing for extensive exploration of possibilities that would be impractical with traditional methods.
Accessibility and Democratization
AI interior design has dramatically lowered the barriers to accessing professional-quality design services. Tools like Planner 5D and RoomGPT have made sophisticated design capabilities available to consumers at a fraction of the cost of hiring a professional designer.
This democratization effect is particularly significant for underserved markets and individuals who previously couldn't afford design services. According to a 2022 consumer survey, 58% of users of AI interior design generators had never previously engaged professional design services, indicating that AI is expanding the market rather than simply replacing existing services.
Data-Driven Decision Making
AI excels at processing vast amounts of data to inform design decisions. Modern AI interior design systems can analyze thousands of successful designs, current trends, and user preferences to generate recommendations with a high probability of satisfaction.
This data-driven approach can help avoid common design pitfalls and ensure that designs incorporate established principles of spatial organization, color theory, and ergonomics. For instance, systems like Collov can analyze a user's existing furniture and preferences to suggest complementary pieces that maintain stylistic coherence while optimizing for factors like traffic flow and visual balance.
Visualization Capabilities
The photorealistic visualization capabilities of current AI interior design tools represent a significant advantage over traditional sketches or even conventional 3D rendering software. These visualizations help clients better understand proposed designs and make more informed decisions.
According to industry data, clients who view AI-generated photorealistic renderings are 73% more likely to approve design proposals compared to those who see only traditional design boards or sketches.
Limitations and Challenges
Creative Originality
Despite impressive capabilities, AI interior design systems fundamentally learn from existing designs, which can limit their ability to generate truly novel concepts. The outputs tend to reflect patterns in their training data, sometimes resulting in designs that feel derivative rather than groundbreaking.
Human designers often draw inspiration from diverse sources outside the design field itself—nature, art, cultural movements, personal experiences—in ways that current AI systems cannot replicate. This limitation is particularly evident when clients seek highly innovative or boundary-pushing designs.
Contextual Understanding
AI still struggles with deeply understanding the contextual factors that influence design decisions. Elements such as a client's personal history, cultural background, or emotional associations with certain spaces or objects remain difficult for AI to fully incorporate.
For example, while an AI interior design generator might create a technically perfect bedroom design, it might miss the emotional significance of incorporating a family heirloom or accommodating a specific ritual or habit that's important to the client.
Technical Constraints
Current AI interior design systems face practical limitations in areas such as:
- Accurate measurement incorporation
- Structural feasibility assessment
- Building code compliance
- Material property understanding (how fabrics will drape, how wood will age, etc.)
- Lighting simulation accuracy
These technical constraints often necessitate human oversight to ensure that AI-generated designs are practical and implementable in the real world.
Adaptation to Unique Spaces
AI tends to perform best with standard room configurations that resemble common examples in its training data. Unusual architectural features, historic properties, or spaces with unique constraints may receive less successful treatment from AI systems.
A human designer can thoughtfully address the challenges of a room with irregular angles, historic preservation requirements, or unusual dimensions in ways that current AI systems struggle to match.
How Is AI Interior Design Impacting the Industry?
The rise of AI interior design is creating ripple effects throughout the design industry and adjacent fields, transforming business models, professional roles, and consumer expectations.
Positive Industry Impacts
Expanded Market Reach
Rather than simply replacing existing services, AI interior design appears to be significantly expanding the overall market for design services. By making basic design accessible to those who previously couldn't afford it, AI has introduced many consumers to the value of thoughtful interior design.
Market analysis suggests that the introduction of AI-powered design platforms has expanded the total interior design market by approximately 15-20%, with much of this growth coming from first-time design service consumers.
Professional Augmentation
For established designers, AI interior design tools can serve as powerful augmentation rather than replacement. Designers who embrace AI report being able to:
- Generate initial concepts more rapidly
- Present clients with more design options
- Reduce time spent on technical rendering
- Focus more energy on creative problem-solving and client relationships
A 2024 survey of professional designers found that those using AI tools reported a 37% increase in productivity and a 42% increase in client satisfaction, suggesting that the technology can enhance rather than diminish the value of human expertise.
New Business Models
The integration of AI has spawned entirely new business models within the design industry. These include:
- Subscription-based design platforms offering unlimited AI-generated concepts
- Hybrid services combining AI visualization with human design consultation
- DIY design assistants embedded in retail environments
- Virtual staging services for real estate marketing
These new models have created opportunities for entrepreneurs and established businesses alike to reach new market segments and deliver design services in novel ways.
Negative Industry Impacts
Employment Disruption
While AI interior design hasn't wholesale replaced human designers, it has begun to impact certain segments of the market, particularly entry-level visualization roles and basic design services. Junior designers who previously would have handled rendering tasks or initial concept sketches may find these roles diminished.
Industry analysts predict that approximately 15-20% of current interior design tasks could be automated within the next five years, potentially affecting employment in certain segments of the market.
Fee Pressure
As AI-powered platforms offer design services at significantly lower price points than traditional designers, there has been downward pressure on fees across the industry. Designers report clients questioning traditional fee structures when AI alternatives are available at a fraction of the cost.
This price pressure is particularly acute for mid-market designers who can't compete with AI on price but may not have the reputation or specialty expertise to command premium fees.
Quality Control Challenges
The proliferation of AI interior design tools has led to concerns about quality control and professional standards. When anyone can generate design concepts without training or oversight, there's potential for poorly conceived or impractical designs to proliferate.
This democratization effect, while positive in many ways, also creates challenges for maintaining professional standards and ensuring that designs meet safety, accessibility, and quality benchmarks.
What Ethical Issues Does AI Interior Design Face?
The rapid advancement of AI interior design has outpaced the development of ethical frameworks to govern its use, raising several important concerns that the industry must address.
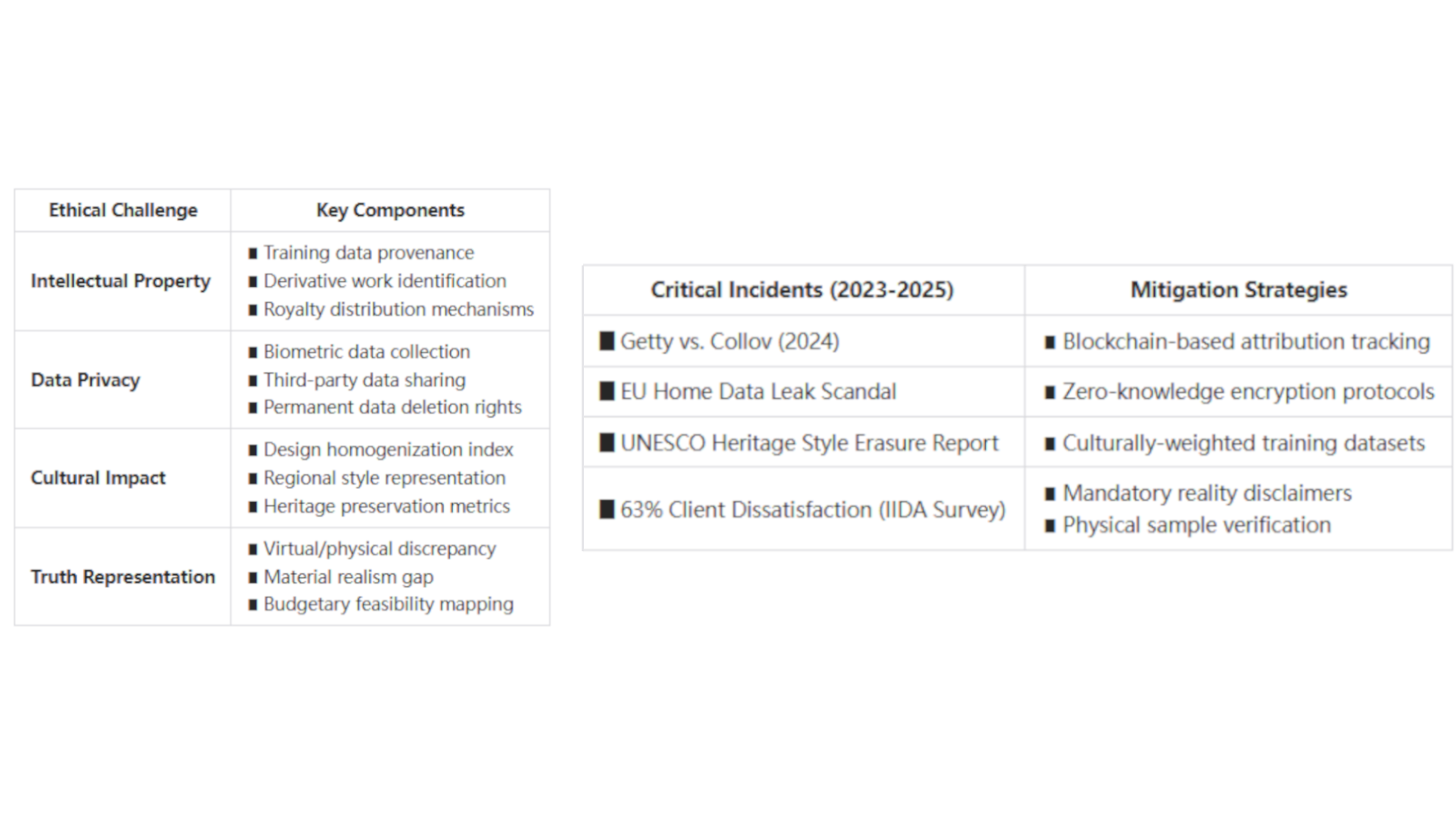
Copyright and Intellectual Property
Perhaps the most pressing ethical issue surrounding AI interior design relates to copyright and intellectual property rights. Most current AI systems are trained on vast datasets of existing designs, often without explicit permission from the original creators.
This raises difficult questions about:
- Who owns the rights to AI-generated designs that may incorporate elements from multiple sources?
- How should original designers be compensated when their work contributes to AI training?
- What constitutes "fair use" of design elements versus appropriation?
Legal precedents remain limited, creating uncertainty for both AI developers and traditional designers. Recent litigation in adjacent creative fields like visual art (e.g., lawsuits against Stable Diffusion and Midjourney) suggests that these issues will eventually require legal clarification.
Data Privacy and Security
The use of AI interior design tools often involves sharing detailed information about private spaces—including floor plans, photographs of home interiors, and personal style preferences. This raises significant privacy concerns:
- How securely is this sensitive data stored?
- Is user data being used to train AI systems without explicit consent?
- Could floor plans or home details be vulnerable to security breaches?
Design Homogenization
A subtler but potentially significant ethical concern involves the risk of cultural homogenization in design. When AI systems are trained predominantly on Western or luxury design examples, they may perpetuate certain aesthetic standards at the expense of diverse cultural traditions and approaches.
This homogenization could contribute to the erasure of regional design traditions and reduce the rich diversity of global interior design practices. Some critics have noted that AI interior design generators often default to contemporary minimalist, Scandinavian, or modern luxury aesthetics, potentially marginalizing other valid design approaches.
Misrepresentation and Unrealistic Expectations
The photorealistic capabilities of AI interior design tools can sometimes create unrealistic expectations about what's achievable in physical spaces. When AI generates idealized images that ignore practical constraints like budgets, material limitations, or structural realities, it may lead to disappointment or dissatisfaction.
This risk is particularly significant when AI-generated images are used in real estate marketing or speculative design without clear disclosure that they represent virtual rather than actual spaces.
How Can Humans Effectively Utilize AI Interior Design?
Despite the challenges and limitations, AI interior design offers tremendous potential when used thoughtfully. Here are strategies for effectively leveraging this technology while mitigating its drawbacks.
Industry Adaptation Strategies
For design professionals facing disruption from AI interior design, several adaptation strategies have proven effective:
Value-Added Specialization
The most successful designers in the AI era have focused on aspects of design that remain difficult to automate:
- Deep contextual understanding of client needs
- Specialization in niche areas (historic preservation, accessibility design, etc.)
- Custom craftsmanship and material expertise
- Project management and implementation
- Emotional and psychological aspects of space design
By emphasizing these human-centered capabilities, designers can position themselves as offering value beyond what AI can provide.
AI Integration Approaches
Rather than resisting AI tools, forward-thinking designers are finding ways to incorporate them into their workflows:
- Using AI for initial concept generation and iteration
- Employing AI visualization to improve client communication
- Leveraging AI for time-consuming technical tasks
- Creating hybrid services that combine AI efficiency with human creativity
Design firms that have adopted this approach report being able to serve more clients more effectively, often expanding their businesses rather than contracting them.
Education and Skill Development
For both established professionals and those entering the field, ongoing education in both design fundamentals and technological skills has become essential. Design schools are increasingly incorporating AI literacy alongside traditional design education, recognizing that future designers will need to understand both the capabilities and limitations of these tools.
Ethical Usage Guidelines
To address the ethical concerns surrounding AI interior design, several best practices are emerging:
Transparency and Disclosure
Users of AI interior design tools should:
- Clearly disclose when designs are AI-generated
- Be transparent about data usage policies
- Properly attribute design influences where appropriate
- Maintain honest communication about what's realistically achievable
Data Protection Practices
To mitigate privacy concerns:
- Use platforms with strong data protection policies
- Consider the data retention policies of services before uploading personal spaces
- Be cautious about sharing detailed floor plans or home security features
- Review permissions granted to AI interior design applications
Cultural Sensitivity
To counter potential homogenization:
- Seek out AI tools trained on diverse design traditions
- Supplement AI recommendations with research into local and cultural design approaches
- Question defaults and generic recommendations
- Consider the cultural context and history of spaces being designed
Complementary Approaches
The most effective use of AI interior design often involves complementary approaches that leverage both technological and human strengths:
Human-AI Collaboration
The ideal approach often involves collaboration between human judgment and AI capabilities:
- Using AI for divergent thinking and idea generation
- Applying human expertise for convergent thinking and refinement
- Letting AI handle repetitive tasks while humans focus on creative decisions
- Using AI recommendations as starting points rather than final solutions
Design Validation
Even when using AI interior design, validation through human expertise remains crucial:
- Verify AI recommendations against practical constraints
- Assess the emotional and psychological impact of proposed designs
- Check compliance with building codes and accessibility requirements
- Consider long-term maintenance and sustainability factors

FAQs About AI Interior Design
Q: Can AI Do Interior Design Completely on Its Own?
A: While AI interior design tools can generate impressive concepts, they cannot yet handle the complete design process independently. Current AI excels at generating visual concepts and suggesting furnishings, but struggles with understanding structural constraints, building codes, material properties, and the nuanced emotional and contextual factors that influence successful design. The most effective approach combines AI's generative capabilities with human oversight and refinement.
Q: How to Use AI for Interior Design as a Beginner?
A: If you're new to using AI for interior design, I recommend starting with these steps:
1. Select user-friendly platforms like Interior AI, Planner 5D, or RoomGPT that are designed for non-professionals
2. Gather clear photographs of your space from multiple angles
3. Provide specific guidance about your preferences and constraints
4. Generate multiple design options rather than settling on the first result
5. Use AI suggestions as inspiration rather than definitive plans
6. Consult with a professional for validation before making significant investments
Q: How Much Does AI Interior Design Cost Compared to Traditional Services?
A: The cost difference is substantial. Traditional interior design services typically range from $50-200 per hour or $2,000-12,000+ for complete room designs. In contrast, AI interior design platforms typically cost between $10-50 per room concept, with subscription services offering multiple designs for $10-30 monthly. This represents a cost reduction of 90-95% compared to traditional services, though AI solutions lack the implementation support, sourcing expertise, and customization of full-service design.
Q: What Are the Best AI Interior Design Tools Available Today?
A: The leading AI interior design tools as of 2023 include:
- Interior AI: Excellent for style transformation of existing rooms
- RoomGPT: Strong for rapid concept generation with minimal input
- Planner 5D: Best for those who want 3D modeling capabilities
- Collov: Superior for furniture matching and sourcing
- Havenly: Balances AI generation with human designer oversight
- Modsy: Pioneered 3D visualization with AI style application
Conclusion: The Future of AI Interior Design
As we look toward the future, AI interior design will likely continue its rapid evolution, becoming increasingly sophisticated while remaining complementary to human creativity and expertise. The technology shows tremendous promise for democratizing access to design services, enhancing productivity, and enabling creative exploration at unprecedented scales.
However, the most successful applications will be those that thoughtfully integrate human and artificial intelligence, leveraging the unique strengths of each. AI excels at pattern recognition, data processing, and visualization, while humans bring contextual understanding, emotional intelligence, and creative originality that remains beyond algorithmic reach.
For designers, consumers, and technology developers alike, the path forward involves neither uncritical embrace nor fearful rejection of AI interior design, but rather a nuanced understanding of its capabilities and limitations. By approaching these tools with both enthusiasm and discernment, we can harness their potential while addressing the ethical, creative, and practical challenges they present.
 Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts! Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!
Submit Your AI Tool For FREE!Showcase Your Innovation To Thousands Of AI Enthusiasts!







No comments yet. Be the first to comment!